使用DOT语言和Graphviz绘图(翻译)
简述
本文翻译自Drawing Graphs using Dot and Graphviz
1. 许可
Copyright (C) 2013, 2014 Tony Ballantyne. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts.
Code in this document is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This code is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
2. 介绍
2.1 什么是DOT?
DOT是纯文本图像描述语言,对于计算机和人来说,都很容易阅读。
2.2 什么是Graphviz?
Graphviz是一个开源的图像可视化的软件,所谓图像可视化就是使用一种简单的方法,来将结构化的信息表现成用抽象图片和网络构成的示意图。
2.3 谁适合看这篇文章?
这篇文章本来是我写来给自己当速成手册看的。不过现在看起来已经被我弄成给学计算机的学生看的教程了。现在这篇文章可以给任何想通过例子学习DOT的人看。
2.4 相关材料
我博客还有类似的其他文章TonyBallantyne.com/tech
如果你是想了解关于我作为一名SF and Fantasy writer的工作,但不幸点到这篇文章的话,下面的链接可能就对你比较有用:
- TonyBallantyne.com: 这里有我的小说和短故事
- Emacs Tutorial: 给作家的一个关于Emacs的简短介绍
- My Emacs Writing Setup: 关于我如何使用Emacs的Org Mode来写小说和短故事
译注:这儿所谓的相关材料其实是作者自己其他的一些文章,跟DOT关系不大
3. 安装
如果你要顺着这个教程继续下去,那你可能就需要要装Graphviz套件了。Graphviz可以在官网免费下载。
4. 基础例子
4.1 简单图例
graph graphname {
a -- b;
b -- c;
b -- d;
d -- a;
}
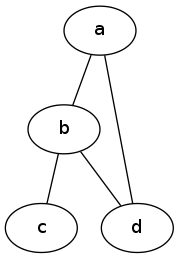
4.2 一样的图,不一样的布局
graph graphname {
rankdir=LR; //Rank Direction Left to Right
a -- b;
b -- c;
b -- d;
d -- a;
}
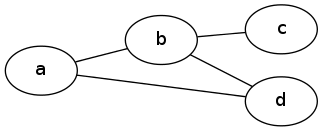
4.3 简单有向图
digraph graphname{
a -> b;
b -> c;
a -> c;
}
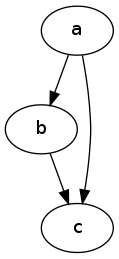
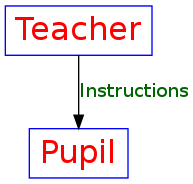
4.4 带标签的简单有向图
digraph graphname{
T [label="Teacher"] // node T
P [label="Pupil"] // node P
T->P [label="Instructions", fontcolor=darkgreen] // edge T->P
}
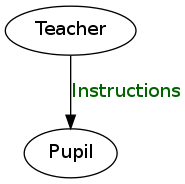
4.5 同样的图,不同的形状和颜色
digraph graphname {
T [label="Teacher" color=Blue, fontcolor=Red, fontsize=24, shape=box] // node T
P [label="Pupil" color=Blue, fontcolor=Red, fontsize=24, shape=box] // node P
T->P [label="Instructions", fontcolor=darkgreen] // edge T->P
}
这儿你可以选择的形状有: box, polygon, ellipse, oval, circle, point, egg, triangle, plaintext, diamond, trapezium, parallelogram, house, pentagon, hexagon, septagon, octagon, doublecircle, doubleoctagon, tripleoctagon 更多的形状看这里
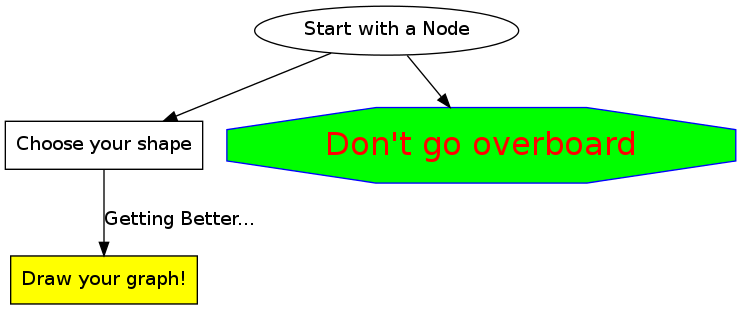
4.6 总结
digraph summary{
start [label="Start with a Node"]
next [label="Choose your shape", shape=box]
warning [label="Don't go overboard", color=Blue, fontcolor=Red,fontsize=24,style=filled, fillcolor=green,shape=octagon]
end [label="Draw your graph!", shape=box, style=filled, fillcolor=yellow]
start->next
start->warning
next->end [label="Getting Better...", fontcolor=darkblue]
}
5. 高级
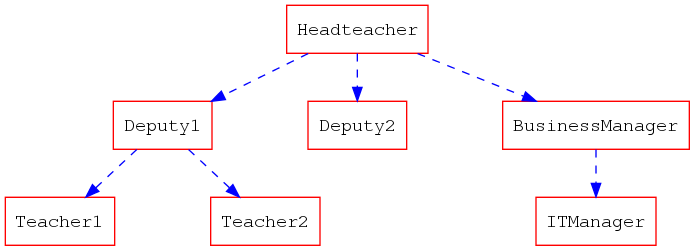
5.1 节省时间的技巧
单独地去定义每一个节点其实很浪费时间的,下面这个技巧能够让你快点儿。
digraph hierarchy {
nodesep=1.0 // increases the separation between nodes
node [color=Red,fontname=Courier,shape=box] //All nodes will this shape and colour
edge [color=Blue, style=dashed] //All the lines look like this
Headteacher->{Deputy1 Deputy2 BusinessManager}
Deputy1->{Teacher1 Teacher2}
BusinessManager->ITManager
{rank=same;ITManager Teacher1 Teacher2} // Put them on the same level
}
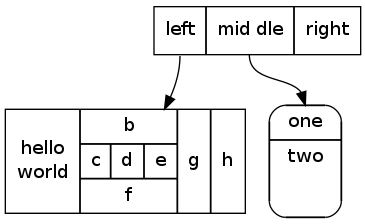
5.2 记录
你现在可以用HTML来定义这一类节点了,这里有更多相关信息。
digraph structs {
node[shape=record]
struct1 [label="<f0> left|<f1> mid dle|<f2> right"];
struct2 [label="{<f0> one|<f1> two
}" shape=Mrecord];
struct3 [label="hello
world |{ b |{c|<here> d|e}| f}| g | h"];
struct1:f1 -> struct2:f0;
struct1:f0 -> struct3:f1;
}
6. 例子
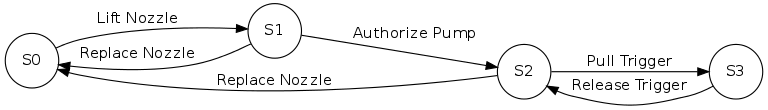
6.1 有限状态机
digraph finite_state_machine {
rankdir=LR;
size="8,5"
node [shape = circle];
S0 -> S1 [ label = "Lift Nozzle" ]
S1 -> S0 [ label = "Replace Nozzle" ]
S1 -> S2 [ label = "Authorize Pump" ]
S2 -> S0 [ label = "Replace Nozzle" ]
S2 -> S3 [ label = "Pull Trigger" ]
S3 -> S2 [ label = "Release Trigger" ]
}
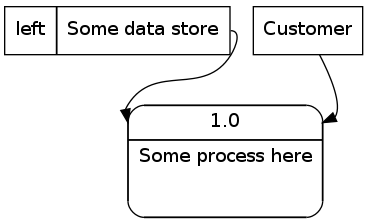
6.2 数据流示意图
digraph dfd{
node[shape=record]
store1 [label="<f0> left|<f1> Some data store"];
proc1 [label="{<f0> 1.0|<f1> Some process here
}" shape=Mrecord];
enti1 [label="Customer" shape=box];
store1:f1 -> proc1:f0;
enti1-> proc1:f0;
}
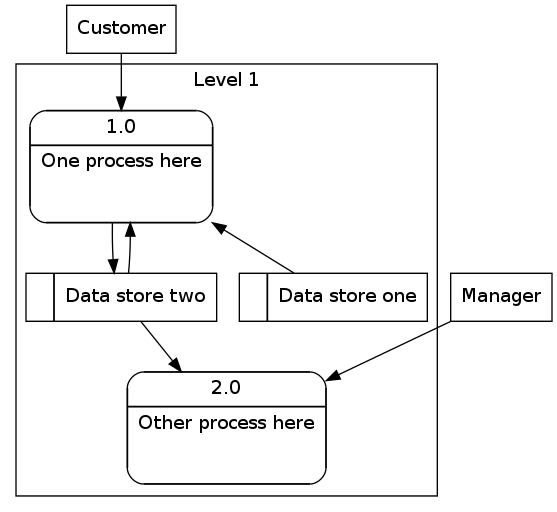
6.3 数据流示意图2
digraph dfd2{
node[shape=record]
subgraph level0{
enti1 [label="Customer" shape=box];
enti2 [label="Manager" shape=box];
}
subgraph cluster_level1{
label ="Level 1";
proc1 [label="{<f0> 1.0|<f1> One process here
}" shape=Mrecord];
proc2 [label="{<f0> 2.0|<f1> Other process here
}" shape=Mrecord];
store1 [label="<f0> |<f1> Data store one"];
store2 [label="<f0> |<f1> Data store two"];
{rank=same; store1, store2}
}
enti1 -> proc1
enti2 -> proc2
store1 -> proc1
store2 -> proc2
proc1 -> store2
store2 -> proc1
}
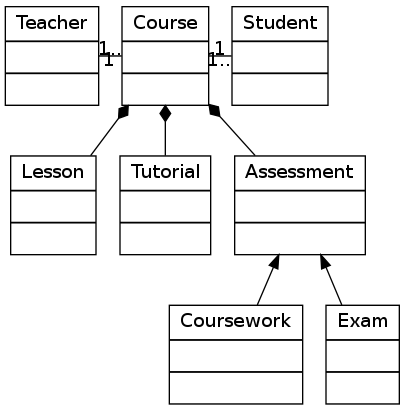
6.4 对象继承
digraph obj{
node[shape=record];
rankdir="BT";
teacher [label = "{<f0> Teacher|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
course [label = "{<f0> Course|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
student [label = "{<f0> Student|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
lesson [label = "{<f0> Lesson |<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
tutorial [label = "{<f0> Tutorial|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
assessment[label = "{<f0> Assessment|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
coursework [label = "{<f0> Coursework|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
exam [label = "{<f0> Exam|<f1>
|<f2>
}"];
{rank=same; teacher course student}
teacher->course [dir="forward",arrowhead="none",arrowtail="normal",headlabel="1",taillabel="1.."];
student->course [dir="forward",arrowhead="none",arrowtail="normal",headlabel="1",taillabel="1.."];
lesson->course [dir="forward",arrowhead="diamond",arrowtail="normal"];
tutorial->course [dir="forward",arrowhead="diamond",arrowtail="normal"];
assessment->course [dir="forward",arrowhead="diamond",arrowtail="normal"];
coursework->assessment;
exam->assessment;
}
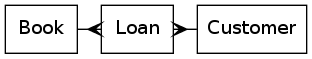
6.5 关系型实体
digraph ER{
node[shape=box];
Book;
Customer;
Loan;
{rank=same;Book,Customer,Loan}
Book->Loan[dir="forward",arrowhead="crow",arrowtail="normal"];
Customer->Loan[dir="forward",arrowhead="crow",arrowtail="normal"];
}
7. 参考
以下可能是你在画图时候最有用的一些属性,完整的列表可以在这里看。
7.1 图像属性
label="My Graph"; # 给图像设置标签
rankdir=LR; # 将图片由原来的从上到下布局变成从左到右布局
{rank=same; a, b, c } # 将一组元素放到同一个level
splines="line"; # 让边框变为直线,没有曲线和锐角
K=0.6; # 用来在布局中影响spring属性,spring属性可以用于将节点往外推,这个在twopi和sfdp布局中很有用。
译注:暂时还没明白这个spring属性应该怎么翻,初步猜测是弹性。胡克定律里面的常量名也叫K。
7.2 交点属性
[label="Some Label"] # 给交点打标签
[color="red"] # 给交点上色
[fillcolor="blue"] # 设置交点的填充色
7.3 边的属性
[label="Some Label"] # 给边设置标签 (设置路径权重的时候很有用)
[color="red"] # 给交点上色 (标示路径的时候很有用)
[penwidth=2.0] # 给边适配厚度,标示路径的时候很有用。
7.4 尺寸, 背景颜色
fixedsize=true;
size="1,1";
resolution=72;
bgcolor="#C6CFD532";
# 不是我偷懒不翻译哦,原文就没有解释。
8. 附录
8.1 拓展阅读
An Introduction to GraphViz and dot
Graphviz Examples and Tutorial
8.2 使用Emacs的Org Mode
Emacs的Org Mode不管对于写作,还是执行和导出DOT图片都是个很理想的工作环境。
8.2.1 配置
下载并安装Graphviz,然后把相关路径加到exec-path这个变量里去。
你也要把你的.emacs文件更新成能够把DOT作为babel语言加载,下面这个配置可以很容易的设置DOT为babel语言,其他语言也可以类似操作
(org-babel-do-load-languages
(quote org-babel-load-languages)
(quote
(
(emacs-lisp . t)
(java . t)
(dot . t)
(ditaa . t)
(R . t)
(python . t)
(ruby . t)
(gnuplot . t)
(clojure . t)
(sh . t)
(ledger . t)
(org . t)
(plantuml . t)
(latex . t)
)
)
)
8.2.2 将Dot嵌入Emacs
Org Mode通过使用Library of Babel来解析各种语言。要想这么做的话,就用begin_src和end_src标签把你的dot代码想下面这样包含进去。你也需要在包裹的时候像下面那样添加一些命令行参数。
用<s[TAB]快捷键可以快速生成一个begin_src代码块。
#+begin_src dot :file ./img/example1.png :cmdline -Kdot -Tpng
graph graphname {
a -- b;
b -- c;
b -- d;
d -- a;
}
#+end_src
8.2.3 命令行相关
#+begin_ src dot :file ./img/example1.png :cmdline -Kdot -Tpng里的:cmdline -Kdot -Tpng就是命令行参数. 他们告诉dot如何渲染和展示。
-Kdot使用dot布局方式. 你也可以尝试其他的布局方式,比如Kneato,Kcirco,Ktwopi,Kfdp,Ksfdp-Tpng渲染成png格式
完整的命令行参数可以看这里
Date: <2013-10-21 Mon>
Author: Tony Ballantyne
Translator: Casa Taloyum
Created: 2014-04-12 Sat 10:13
Emacs 23.3.1 (Org mode 8.0.2)
评论系统我用的是Disqus,不定期被墙。所以如果你看到文章下面没有加载出评论列表,翻个墙就有了。
本文遵守CC-BY。 请保持转载后文章内容的完整,以及文章出处。本人保留所有版权相关权利。
我的博客拒绝挂任何广告,如果您觉得文章有价值,可以通过支付宝扫描下面的二维码捐助我。
