除此之外,没有其他了。我们启动web服务器,在浏览器中输入地址,就可以看到浏览器上输出我们写好的页面。为了更好的理解上面这个过程,你需要学习关于Servlet生命周期的三个阶段,就是所谓的“init-service-destroy”。
以上的知识,我觉得对于你理解SpringMVC的设计思想,已经足够了。SpringMVC当然可以称得上是一个复杂的框架,但是同时它又遵循Servlet世界里最简单的法则,那就是“init-service-destroy”。我们要分析SpringMVC的初始化流程,其实就是分析DispatcherServlet类的init()方法,让我们带着这种单纯的观点,打开DispatcherServlet的源码一窥究竟吧。
1.DispacherServlet的初始化
1.<init-param>配置元素读取
用Eclipse IDE打开DispatcherServlet类的源码,ctrl+T看一下。
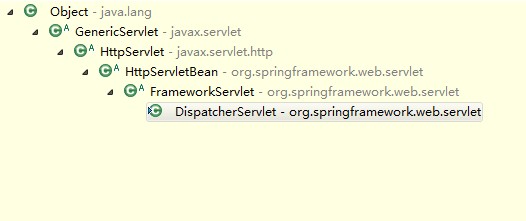
DispatcherServlet类的初始化入口方法init()定义在HttpServletBean这个父类中,HttpServletBean类作为一个直接继承于HttpServlet类的类,覆写了HttpServlet类的init()方法,实现了自己的初始化行为。
步骤:
1.封装以验证初始化参数
2.将当前的Servelt类转换成BeanWrapper
3.注册相对于Resource的属性编辑器
4.属性注入
5.servletBean的初始化
我在web.xml中注册的DispatcherServlet配置如下:
<!-- springMVC配置开始 -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/spring-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- springMVC配置结束 -->
可以看到,我注册了一个名为contextConfigLocation的<init-param>元素,其值为“classpath:spring/spring-servlet.xml”,这也是大家常常用来指定SpringMVC配置文件路径的方法。上面那段try,catch块包裹的代码发挥的作用,一个是将“classpath:spring/spring-servlet.xml”这段字符串转换成classpath路径下的一个资源文件,供框架初始化读取配置元素。在我的工程中是在spring文件夹下面的配置文件spring-servlet.xml。

另外一个作用,就是将contextConfigLocation的值读取出来,然后通过setContextConfigLocation()方法设置到DispatcherServlet中,这个setContextConfigLocation()方法是在FrameworkServlet类中定义的,也就是上面继承类图中DispatcherServlet的直接父类。
我们在setContextConfigLocation()方法上面打上一个断点,启动web工程,可以看到下面的调试结果。
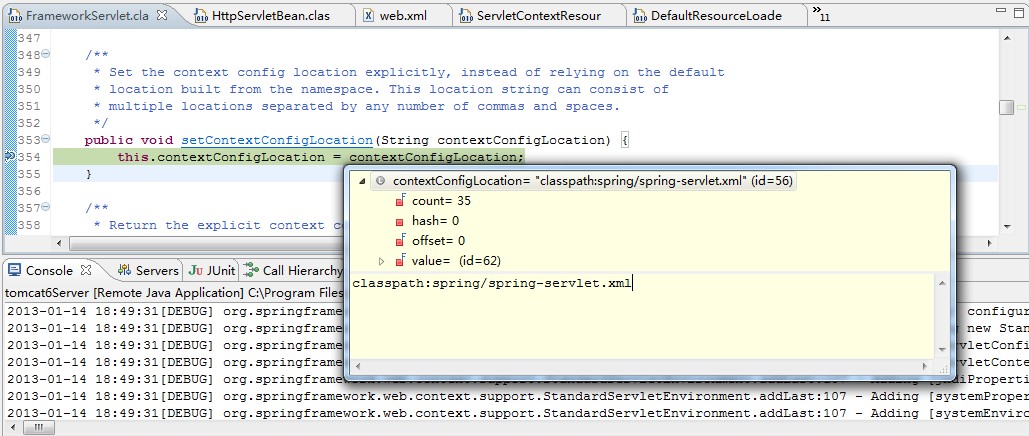
在HttpServletBean这个类的设计中,运用了依赖注入思想完成了<init-param>配置元素的读取。他抽离出HttpServletBean这个类的目的也在于此,就是“以依赖注入的方式来读取Servlet类的<init-param>配置信息”,而且这里很明显是一种setter注入。
明白了HttpServletBean类的设计思想,我们也就知道可以如何从中获益。具体来说,我们继承HttpServletBean类(就像DispatcherServlet做的那样),在类中定义一个属性,为这个属性加上setter方法后,我们就可以在<init-param>元素中为其定义值。在类被初始化后,值就会被注入进来,我们可以直接使用它,避免了样板式的getInitParameter()方法的使用,而且还免费享有Spring中资源编辑器的功能,可以在web.xml中,通过“classpath:”直接指定类路径下的资源文件。
注意,虽然SpringMVC本身为了后面初始化上下文的方便,使用了字符串来声明和设置contextConfigLocation参数,但是将其声明为Resource类型,同样能够成功获取。鼓励读者们自己继承HttpServletBean写一个测试用的Servlet类,并设置一个参数来调试一下,这样能够帮助你更好的理解获取配置参数的过程。
2.WebApplicaitonContext的建立
SpringMVC使用了Spring容器来容纳自己的配置元素,拥有自己的bean容器上下文。在SpringMVC初始化的过程中,非常关键的一步就是要建立起这个容器上下文,而这个建立上下文的过程,发生在FrameworkServlet类中,由上面init()方法中的initServletBean()方法触发。
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化WebApplicationContext容器
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//初始化FrameworkServlet
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
initWebApplicationContext()
对sevlet功能所使用的变量进行初始化
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
//1.context实例在构造函数中就已经被注入,因为servlet只能被实例化一次
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//刷新上下文环境
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
//2.根据contextAtrribute属性加载WebApplicaitonContext
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
//3.重新创建WebApplicationContext
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {