目录
=======正文分割线======
一、前言
spring cloud大行其道的当下,如果不了解基本原理那么是很纠结的(看见的都是约定大于配置,但是原理呢?为什么要这么做?如何串联起来的?)。spring cloud是基于spring boot快速搭建的,今天咱们就看看spring boot容器启动流程(全文基于1.5.9版本)。(本文不讲解如何快速启动spring boot,那些直接官方看即可,官网文档飞机票)
二、容器启动
spring boot一般是指定容器启动main方法,然后以命令行方式启动Jar包,如下图:
1 @SpringBootApplication
2 public class Application {
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
5 }
6 }
这里核心关注2个东西:
下面我们就分别探究这两块内容。
2.1 @SpringBootApplication注解
源码如下:
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
3 @Documented
4 @Inherited
5 @SpringBootConfiguration
6 @EnableAutoConfiguration
7 @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
8 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
9 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
10 public @interface SpringBootApplication {
核心注解:
@SpringBootConfiguration(实际就是个@Configuration):表示这是一个JavaConfig配置类,可以在这个类中自定义bean,依赖关系等。-》这个是spring-boot特有的注解,常用到。
@EnableAutoConfiguration:借助@Import的帮助,将所有符合自动配置条件的bean定义加载到IoC容器(建议放在根包路径下,这样可以扫描子包和类)。-》这个需要详细深挖!
@ComponentScan:spring的自动扫描注解,可定义扫描范围,加载到IOC容器。-》这个不多说,spring的注解大家肯定眼熟
其中@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解的源码:
1 @SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
2 @Target(ElementType.TYPE)
3 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
4 @Documented
5 @Inherited
6 @AutoConfigurationPackage
7 @Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
8 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
核心是一个EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector类图如下:

核心方法在顶级接口ImportSelector的selectImports(),源码如下:
1 @Override
2 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
3 if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
4 return NO_IMPORTS;
5 }
6 try { //1.从META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties文件中载入483条配置属性(有一些有默认值),
7 AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
8 .loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
9 AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);//2.获取注解属性
10 List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata,//3.获取97个自动配置类
11 attributes);
12 configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);//4.移除重复的
13 configurations = sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);//5.排序
14 Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);//6.获取需要排除的
15 checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);//7.校验排除类
16 configurations.removeAll(exclusions);//8.删除所有需要排除的
17 configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);//9.过滤器OnClassCondition(注解中配置的当存在某类才生效)
18 fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);//10.触发自动配置导入监听事件
19 return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
20 }
21 catch (IOException ex) {
22 throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
23 }
24 }
这里注意3个核心方法:
1)loadMetadata 加载配置
其实就是用类加载器去加载:META-INF/spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties(spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.9.RELEASE-sources.jar)文件中定义的配置,返回PropertiesAutoConfigurationMetadata(实现了AutoConfigurationMetadata接口,封装了属性的get set方法)
2)getCandidateConfigurations获取默认支持的自动配置类名列表
自动配置灵魂方法,SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames 从META-INF/spring.factories(spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.9.RELEASE-sources.jar)文件中获取自动配置类key=EnableAutoConfiguration.class的配置。
1 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata,
2 AnnotationAttributes attributes) {//话说这里2个入参没啥用啊...谁来给我解释一下...
3 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
4 getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
5 Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
6 "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
7 + "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
8 return configurations;
9 }
10 //返回的是EnableAutoConfiguration类
11 protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
12 return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
13 }
实际获取了什么?spring.factories文件如下,实际获取了# Auto Configure自动配置模块的所有类。
# Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer # Auto Configuration Import Listeners org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener # Auto Configuration Import Filters org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition # Auto Configure ===========这里就是全部的自动配置类=============================== org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.amqp.RabbitAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.BatchAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cassandra.CassandraAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cloud.CloudAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.couchbase.CouchbaseAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.dao.PersistenceExceptionTranslationAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.cassandra.CassandraRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.couchbase.CouchbaseRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.jpa.JpaRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.ldap.LdapRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.mongo.MongoRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jDataAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.neo4j.Neo4jRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.solr.SolrRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisRepositoriesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.rest.RepositoryRestMvcAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.web.SpringDataWebAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.elasticsearch.jest.JestAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.gson.GsonAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.h2.H2ConsoleAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hateoas.HypermediaAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.hazelcast.HazelcastJpaDependencyAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JdbcTemplateAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.JndiDataSourceAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.XADataSourceAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JmsAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.JndiConnectionFactoryAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.activemq.ActiveMQAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jms.artemis.ArtemisAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jersey.JerseyAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.JooqAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.kafka.KafkaAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.embedded.EmbeddedLdapAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ldap.LdapAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.liquibase.LiquibaseAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mail.MailSenderValidatorAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceResolverAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.DeviceDelegatingViewResolverAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mobile.SitePreferenceAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.embedded.EmbeddedMongoAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mongo.MongoAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.orm.jpa.HibernateJpaAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.reactor.ReactorAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.SecurityFilterAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.FallbackWebSecurityAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.security.oauth2.OAuth2AutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.sendgrid.SendGridAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.SessionAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.SocialWebAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.FacebookAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.LinkedInAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.social.TwitterAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.solr.SolrAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.jta.JtaAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.EmbeddedServletContainerAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.MultipartAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerPropertiesAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebClientAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration ============================================end================================================ # Failure analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer # Template availability providers org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider= org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider, org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
3)filter过滤器 根据OnClassCondition注解把不满足条件的过滤掉
1 private List<String> filter(List<String> configurations,
2 AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
3 long startTime = System.nanoTime();
4 String[] candidates = configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
5 boolean[] skip = new boolean[candidates.length];
6 boolean skipped = false;
//获取需要过滤的自动配置导入拦截器,spring.factories配置中就一个:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition
7 for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : getAutoConfigurationImportFilters()) {
8 invokeAwareMethods(filter);
9 boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, autoConfigurationMetadata);
10 for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
11 if (!match[i]) {
12 skip[i] = true;
13 skipped = true;
14 }
15 }
16 }
17 if (!skipped) {//多条件只要有一个不匹配->skipped = true,全部匹配-》skipped = false->直接返回
18 return configurations;
19 }
20 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(candidates.length);
21 for (int i = 0; i < candidates.length; i++) {
22 if (!skip[i]) {//匹配-》不跳过-》添加进result
23 result.add(candidates[i]);
24 }
25 }
26 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
27 int numberFiltered = configurations.size() - result.size();
28 logger.trace("Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
29 + TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startTime)
30 + " ms");
31 }
32 return new ArrayList<String>(result);
33 }
2.2 SpringApplication.run()静态方法
SpringApplication.run
1 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
2 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
3 stopWatch.start();
4 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
5 FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
6 configureHeadlessProperty();
7 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);//1.获取监听器
8 listeners.starting();-->启动!
9 try {
10 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
11 args);
12 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,//2.准备好环境,触发ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件
13 applicationArguments);
14 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);//打印启动提示字符,默认spring的字符图
15 context = createApplicationContext();//实例化一个可配置应用上下文
16 analyzers = new FailureAnalyzers(context);
17 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,//3.准备上下文
18 printedBanner);
19 refreshContext(context);//4.刷新上下文
20 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);//5.刷新上下文后
21 listeners.finished(context, null);--关闭!
22 stopWatch.stop();
23 if (this.logStartupInfo) {
24 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
25 .logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
26 }
27 return context;
28 }
29 catch (Throwable ex) {
30 handleRunFailure(context, listeners, analyzers, ex);
31 throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
32 }
33 }
如上图,容器启动流程可以分为5个主要步骤:
1.getRunListeners获取监听器(SpringApplicationRunListeners )
实际是SpringApplicationRunListener类
1 private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
2 Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
3 return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
4 SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
5 }
6
7 private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
8 return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
9 }
10
11 private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
12 Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
13 ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
14 // 使用Set确保的字符串的唯一性
15 Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(
16 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));// 1.载入工厂名称集合
17 List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes,// 2.创建工厂实例
18 classLoader, args, names);
19 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);// 排序
20 return instances;
21 }
1.1 载入工厂名称(loadFactoryNames)
当前类的类加载器从META-INF/spring.factories文件中获取SpringApplicationRunListener类的配置
1 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) {
2 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
3 try {
4 Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
5 ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
6 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
7 while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
8 URL url = urls.nextElement();
9 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url));
10 String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName);
11 result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames)));
12 }
13 return result;
14 }
15 catch (IOException ex) {
16 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() +
17 "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
18 }
19 }
上图,获取到工厂类名后,下面来看看META-INF/spring.factories中定义了啥:
# PropertySource Loaders org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader= org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader, org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader # Run Listeners 这里呢,看这里!!!! org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener= org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener # Application Context Initializers org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer= org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer, org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer, org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer, org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer # Application Listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener= org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener, org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener # Environment Post Processors org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor= org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor, org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor # Failure Analyzers org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer= org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer, org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer # FailureAnalysisReporters org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter= org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter
哇,都是些类全名称,且key都是接口,value都是实现类。我们根据key=“org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener”查询得到实现类value="org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener"事件发布启动监听器,一猜也知道肯定要用”反射”根据类名获取类实例,下面很快得到验证...
1.2 创建spring工厂实例(createSpringFactoriesInstances)
根据第一步得到的Set<String> names(SpringApplicationRunListener的唯一实现类EventPublishingRunListener)生成"事件发布启动监听器"工厂实例
1 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
2 private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type,
3 Class<?>[] parameterTypes, ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args,
4 Set<String> names) {
5 List<T> instances = new ArrayList<T>(names.size());
6 for (String name : names) {
7 try {
8 Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);// 利用反射获取类
9 Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
10 Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass
11 .getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);// 得到构造器
12 T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);// 根据构造器和参数构造实例
13 instances.add(instance);
14 }
15 catch (Throwable ex) {
16 throw new IllegalArgumentException(
17 "Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
18 }
19 }
20 return instances;
21 }
2.准备好环境
构造一个ConfigurableEnvironment,这里不多说。
3.准备上下文
1 private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
2 ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
3 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
4 context.setEnvironment(environment);
5 postProcessApplicationContext(context);//单例一个BeanNameGenerator,把ResourceLoader设置进应用上下文
6 applyInitializers(context);//执行初始化器
7 listeners.contextPrepared(context);// 监听器执行上下文"已准备好"方法
8 if (this.logStartupInfo) {
9 logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
10 logStartupProfileInfo(context);
11 }
12
13 // 添加spring boot特殊单例bean
14 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments",
15 applicationArguments);
16 if (printedBanner != null) {
17 context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
18 }
19
20 // 载入资源
21 Set<Object> sources = getSources();
22 Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
23 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[sources.size()]));
24 listeners.contextLoaded(context);// 监听器执行"上下文已加载"方法
25 }
4.刷新上下文
1 private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
2 refresh(context);//核心类
3 if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
4 try {
5 context.registerShutdownHook();//注册关闭钩子,容器关闭时执行
6 }
7 catch (AccessControlException ex) {
8 // Not allowed in some environments.
9 }
10 }
11 }
12
13 protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
14 Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
15 ((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
16 }
最终执行的是AbstractApplicationContext抽象类的refresh方法。
1 public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
2 synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
3 //准备刷新的上下文环境,例如对系统属性或者环境变量进行准备及验证。
4 prepareRefresh();
5
6 //启动子类的refreshBeanFactory方法.解析xml
7 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
8
9 //为BeanFactory配置容器特性,例如类加载器、事件处理器等.
10 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
11
12 try {
13 //设置BeanFactory的后置处理. 空方法,留给子类拓展用。
14 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
15
16 //调用BeanFactory的后处理器, 这些后处理器是在Bean定义中向容器注册的.
17 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
18
19 //注册Bean的后处理器, 在Bean创建过程中调用.
20 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
21
22 //初始化上下文中的消息源,即不同语言的消息体进行国际化处理
23 initMessageSource();
24
25 //初始化ApplicationEventMulticaster bean,应用事件广播器
26 initApplicationEventMulticaster();
27
28 //初始化其它特殊的Bean, 空方法,留给子类拓展用。
29 onRefresh();
30
31 //检查并向容器注册监听器Bean
32 registerListeners();
33
34 //实例化所有剩余的(non-lazy-init) 单例Bean.
35 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
36
37 //发布容器事件, 结束refresh过程.
38 finishRefresh();
39 }
40
41 catch (BeansException ex) {
42 if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
43 logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
44 "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
45 }
46
47 //销毁已经创建的单例Bean, 以避免资源占用.
48 destroyBeans();
49
50 //取消refresh操作, 重置active标志.
51 cancelRefresh(ex);
52
53 // Propagate exception to caller.
54 throw ex;
55 }
56
57 finally {
58 //重置Spring的核心缓存
59 resetCommonCaches();
60 }
61 }
62 }
5.刷新完上下文后
spring boot提供的2个供用户自己拓展的接口:ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner。可以在容器启动完毕后(上下文刷新后)执行,做一些类似数据初始化的操作。
1 private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
2 List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<Object>();
3 runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());//从上下文中获取ApplicationRunner类型的bean
4 runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());//从上下文中获取CommandLineRunner类型的bean
5 AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);//排序
6 for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<Object>(runners)) {
7 if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
8 callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);//执行
9 }
10 if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
11 callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
12 }
13 }
14 }
两个区别在于入参不同,根据实际情况自己选择。
1 public interface CommandLineRunner {
8 void run(String... args) throws Exception;
10 }
11
12 public interface ApplicationRunner {
19 void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
20
21 }
CommandLineRunner中执行参数是原始的java启动类main方法的String[] args字符串数组参数;ApplicationRunner中的参数经过处理提供一些方法例如:
1 List<String> getOptionValues(String name);
根据名称获取值list,java 启动命令中 --foo=bar --foo=baz,则根据foo参数名返回list["bar", "baz"]
三、总结
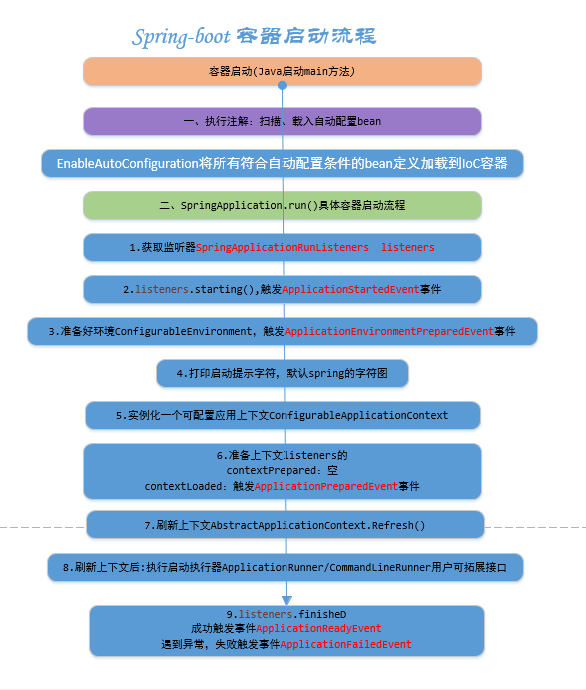
按照前面的分析,Spring-boot容器启动流程总体可划分为2部分:
1)执行注解:扫描指定范围下的bean、载入自动配置类对应的bean加载到IOC容器。
2)man方法中具体SpringAppliocation.run(),全流程贯穿SpringApplicationEvent,有6个子类:
ApplicationFailedEvent.class
ApplicationPreparedEvent.class
ApplicationReadyEvent.class
ApplicationStartedEvent.class
ApplicationStartingEvent.class
SpringApplicationEvent.class
这里用到了很经典的spring事件驱动模型,飞机票:Spring事件驱动模型和观察者模式
类图如下:

如上图,就是一个经典spring 事件驱动模型,包含3种角色:事件发布者、事件、监听者。对应到spring-boot中就是:
1.EventPublishingRunListener这个类封装了事件发布,
2.SpringApplicationEvent是spring-boot中定义的事件(上面说的6种事件),继承自ApplicationEvent(spring中定义的)
3.监听者 spring-boot并没有实现针对上述6种事件的监听者(我没找到...),这里用户可以自己实现监听者(上述6种事件)来注入spring boot容器启动流程,触发相应的事件。
例如:实现ApplicationListener<ApplicationReadyEvent>这个接口,在容器启动完毕时最后一步listener.finished时,如果启动没有异常,就会执行!可以做一些数据初始化之类的操作。
