Spring创建bean的三种方式
1.第一种方式:使用默认构造函数创建
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 默认情况下使用的就是无参数的构造方法. --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean> </beans>
AccountServiceImpl.java
package com.itzn.service; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; public class AccountServiceImpl implements IAccountService { public AccountServiceImpl(){ System.out.println("默认构造"); } public void save() { System.out.println("保存方法"); } }
测试:AccountTest.java
package com.itzn.ui; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; import com.itzn.service.IAccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); IAccountService iAccountService = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService"); System.out.println(iAccountService); iAccountService.save(); } }
输出结果:
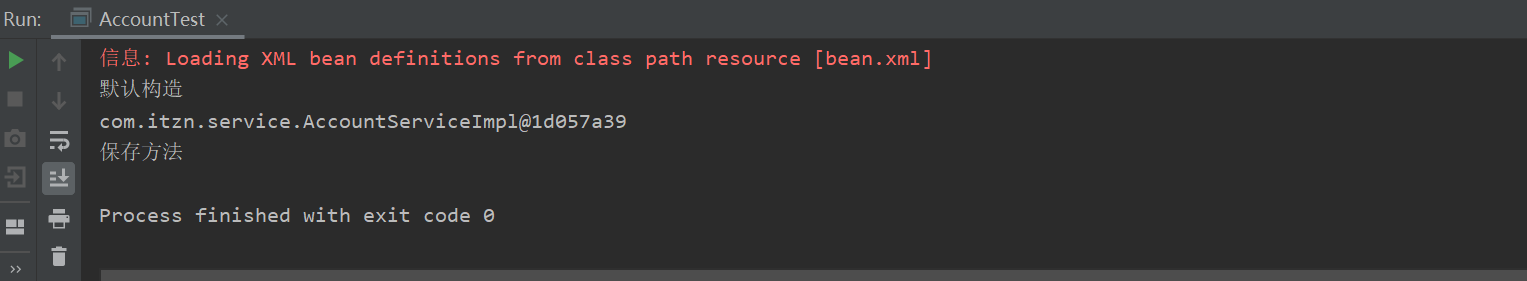
2.第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 第一种方式:默认情况下使用的就是无参数的构造方法. <bean id="accountService" class="com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean> --> <!-- 第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器) --> <bean id="beanFactory" class="com.itzn.factory.BeanFactory"></bean> <bean id="accountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getASIBean"></bean> </beans>
BeanFactory.java
package com.itzn.factory; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; public class BeanFactory { public AccountServiceImpl getASIBean(){ System.out.println("BeanFactory实例工厂的getASIBean方法..."); return new AccountServiceImpl(); } }
AccountTest .java
package com.itzn.ui; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; import com.itzn.service.IAccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); IAccountService iAccountService = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService"); System.out.println(iAccountService); iAccountService.save(); } }
测试结果:
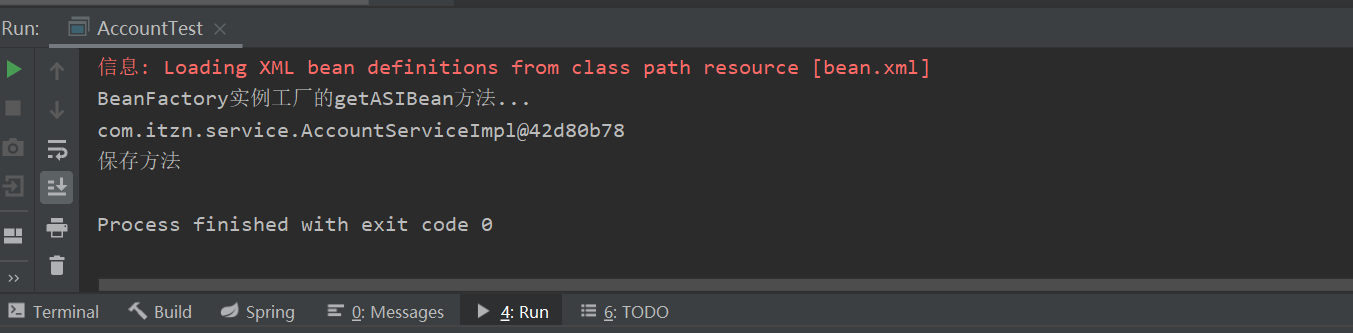
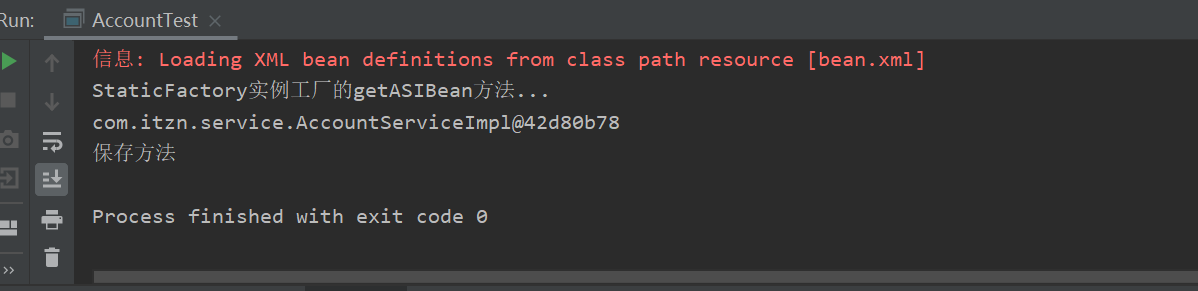
3.第三种方式:第三种方式:使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类中的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器)
bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 第一种方式:默认情况下使用的就是无参数的构造方法. <bean id="accountService" class="com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl"></bean> --> <!-- 第二种方式:使用普通工厂中的方法创建对象(使用某个类中的方法创建对象,并存入spring容器) <bean id="beanFactory" class="com.itzn.factory.BeanFactory"></bean> <bean id="accountService" factory-bean="beanFactory" factory-method="getASIBean"></bean> --> <!-- 第三种方式:使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象(使用某个类中的静态方法创建对象,并存入spring容器) --> <bean id="accountService" class="com.itzn.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="getASIBean"></bean> </beans>
StaticFactory.java
package com.itzn.factory; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; public class StaticFactory { public static AccountServiceImpl getASIBean(){ System.out.println("StaticFactory实例工厂的getASIBean方法..."); return new AccountServiceImpl(); } }
AccountTest.java
package com.itzn.ui; import com.itzn.dao.AccountDaoImpl; import com.itzn.dao.IAccountDao; import com.itzn.service.AccountServiceImpl; import com.itzn.service.IAccountService; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AccountTest { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); IAccountService iAccountService = (IAccountService) ac.getBean("accountService"); System.out.println(iAccountService); iAccountService.save(); } }
测试结果:
bean对象的作用范围
scope属性 :
* singleton:单例的.(默认的值.)
* prototype:多例的.
* request:web开发中.创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入request范围,request.setAttribute();
* session:web开发中.创建了一个对象,将这个对象存入session范围,session.setAttribute();
* globalSession:一般用于Porlet应用环境.指的是分布式开发.不是porlet环境,globalSession等同于session;
实际开发中主要使用singleton,prototype
Customer.java
package cn.itzn.srping.demo3; public class Customer { public Customer(){ System.out.println("Customer被实例化了"); } }
bean.xml
//单例配置 <bean id="customer" class="cn.itzn.srping.demo3.Customer"></bean> //多例配置 <bean id="customer" class="cn.itzn.srping.demo3.Customer" scope="prototype"></bean>
SpringTest.java
public class SpringTest { @Test public void Dome1() { ApplicationContext myContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); Customer customer1=(Customer) myContext.getBean("customer"); System.out.println(customer1); Customer customer2=(Customer) myContext.getBean("customer"); System.out.println(customer2); } }
bean对象的生命周期
单例对象:scope="singleton"
一个应用只有一个对象的实例。它的作用范围就是整个引用。
生命周期:
对象出生:当应用加载,创建容器时,对象就被创建了。
对象活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。
对象死亡:当应用卸载,销毁容器时,对象就被销毁了。
多例对象:scope="prototype"
每次访问对象时,都会重新创建对象实例。
生命周期:
对象出生:当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例。
对象活着:只要对象在使用中,就一直活着。
对象死亡:当对象长时间不用时,被 java 的垃圾回收器回收了。