1. 什么是tkMybatis
tkMybatis:是基于 Mybatis 框架开发的一个工具,对底层 sql 进行了抽象封装,不需要考虑 sql 怎么写,只需要按照逻辑思维,遵循 tkmybatis 的语法即可实现数据库操作。
2. 入门使用
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>tk.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mapper-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.5</version>
</dependency>
- 创建 dao 层的 mapper 接口,每个接口都要继承 tk.mybatis.mapper.common.Mapper 接口。此接口的形式为 Mapper
,带了个泛型,此泛型一般指的是对应的 pojo 或者 domain。
public interface HouseMapper extends Mapper<House> {
}
3. 实现增删改查
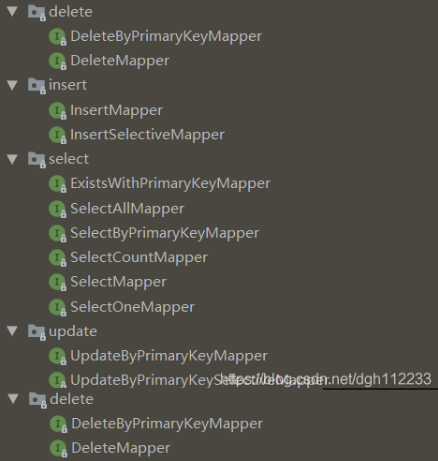
3.1 增加
InsertMapper 接口有一个方法 insert 方法,往数据库表插入一条记录,表有多少个字段,在 tkmybatis 生成的 insert sql 语句中就有多少个字段。
InsertSelectiveMapper 接口有一个方法 insertSelective,实体类参数中不为 null 的字段就会被考虑,在 tkmybatis 生成的 insert sql 语句中只会包含这些不为 null 的字段。
3.2 删除
DeleteByPrimaryKeyMapper接口有一个方法 deleteByPrimaryKey,顾名思义,以表的主键字段作为条件判断,进行删除。
DeleteMapper接口有一个方法 delete,参数就是数据库表对应的Java实体类,参数实体中哪些字段不为null,就会被作为删除sql语句的条件字段,且条件关系是 and,而不是 or。
注意:在定义实体类时,每个成员变量的类型都应该是Java类,不能是基本类型,比如整型,应该用 Integer,而不是 int。
如果用 int 的话,在没有给 int 成员变量赋值时,ava 会默认给它赋值为 0,由于 0 不是 null,所以会被 tkmybatis 当做是删除条件。
3.3 修改
UpdateByPrimaryKeyMapper 接口有一个方法 updateByPrimaryKey,根据主键字段准确地修改某一条记录。
UpdateByPrimaryKeySelectiveMapper 接口有一个方法 updateByPrimaryKeySelective,根据主键字段准确地修改某一条记录的部分字段(实体类参数的不为 null 的字段)。
3.4 查询
SelectMapper 接口有一个方法 select,参数实体类中哪些字段不为 null,就会被作为 select sql 语句中的条件字段,且字段之间的关系是 and。
List<T> select(T var1);
SelectOneMapper 接口有一个方法 selectOne,与 select 方法一样,只是返回结果只能为空或者一个,如果有多个,则抛出异常。
T selectOne(T var1);
SelectCountMapper 接口有一个方法 selectCount,查询满足条件的记录有多少条。
int selectCount(T var1);
SelectAllMapper 接口有一个方法 selectAll,查询全表所有记录。
List<T> selectAll();
SelectByPrimaryKeyMapper 接口有一个方法 selectByPrimaryKey,根据主键进行查询。
T selectByPrimaryKey(Object var1);
ExistsWithPrimaryKeyMapper 接口有一个方法 existsWithPrimaryKey,根据主键查询某条记录是否存在。
boolean existsWithPrimaryKey(Object var1);
4. 批量增删改查
4.1 批量增加
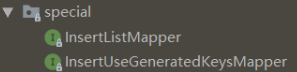
这两个功能有一个要求,那就是操作的数据库表必须有一个自增主键,因为它要求主键必须要有一个默认值,否则就抛出异常。
这两个接口是集成到 MySqlMapper 接口中了,所以 dao 层的 mapper 接口还要继承 MySqlMapper 接口才能使用批量插入功能。
public interface HouseMapper extends Mapper<House>, MySqlMapper<House> {
}
InsertListMapper 接口有一个方法 insertList,批量插入。
insert into table (所有字段,除了自增主键) values (?,..,?), ...,(?,...,?)
InsertUseGeneratedKeysMapper 接口有一个方法 insertUserGeneratedKeys,单个插入。
4.2 批量查询与批量删除

SelectByIdsMapper 接口有一个方法 selectByIds,按照多个主键 id 值进行查询,但是方法的参数是 String,那么主键id之间用逗号隔开就行。
List<T> selectByIds(String var1);
DeleteByIdsMapper 接口有一个方法 deleteByIds,按照多个主键 id 值进行删除。
int deleteByIds(String var1);
5. 自定义查询条件


上图接口都有一个共同点,就是需要 Example 对象作为方法的参数,Example 对象包含了我们各种自定义的查询条件,相当于 sql 语句中 where 部分的条件。
5.1 Example
Example 对象可以理解为 sql 语句层次的设置。
而 Example.criteria 对象可以理解为 sql 语句中的一个单一的条件表达式设置。
使用:
先创建 Example 对象,再创建 Example.criteria 对象,借助这两个对象,可以灵活地设置各种条件。
一个 example 包含了若干个 criteria ,每个 criteria 就是 sql 语句中条件部分的一个括号部分(没有嵌套)。
比如 (id = 5),criteria 包含了一个方法 void setAndOr(String andOr),它的意思相当于在括号前面加上 and 还是 or。
比如执行了方法 setAndOr("and"),那么 criteria 相当于 and (id = 5),而 example 就把这些 criteria 拼凑起了,比如 example 包含了 2 个 criteria,分别是 (id = 5) 和 and (name = "张三"),那么此 example 的效果就是 (id = 5) and (name = "张三")。
例:
@Test
public void testExample1() {
Example example = new Example(UserEntity.class);
example.createCriteria().andGreaterThan("useName", "张");
userMapper.selectByExample(example);
}
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_name,sex,age,address,phone FROM t_user WHERE ( ( user_name > ? ) )
==> Parameters: 张(String)
例:
where (age > 18 and sex = 1) or ( age < 30 and sex = 0)
@Test
public void testCriteria1() {
Example example = new Example(UserEntity.class);
// 新增条件1
Example.Criteria criteria1 = example.createCriteria();
criteria1.andGreaterThan("age", 18).andEqualTo("sex", 1);
// 新增条件2
Example.Criteria criteria2 = example.createCriteria();
criteria2.andLessThan("age", 30).andEqualTo("sex", 0);
// 设计不是很合理,example不应该代表criteria1与criteria2进行逻辑OR
example.or(criteria2);
userMapper.selectByExample(example);
}
==> Preparing: SELECT id,user_name,sex,age,address,phone FROM t_user WHERE ( ( age > ? and sex = ? ) or ( age < ? and sex = ? ) )
==> Parameters: 18(Integer), 1(Integer), 30(Integer), 0(Integer)
例:sql排序、去重、设置select字段
@Test
public void testExample() {
Example example = new Example(UserEntity.class);
// 设置排序字段
example.orderBy("age").asc().orderBy("useName").desc();
// 设置去重
example.setDistinct(true);
// 设置select 子句的字段
example.selectProperties("age", "useName");
userMapper.selectByExample(example);
}
==> Preparing: SELECT distinct age , user_name FROM t_user order by age ASC,user_name DESC
==> Parameters:
例:分页查询
通过RowBounds来实现分页查询,指定开始和分页大小。
public Result getPageByEvent(Paging paging, String eventId) {
// 这是分页
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(paging.getPageNum(), paging.getPageSize());
// new一个Example
Example example = new Example(Prize.class);
// 排序
example.orderBy("singleCont").asc();
// 添加条件
Example.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
// 前面 一个参数对应实体类的 属性,后一个对应 要传的值
criteria.andEqualTo("eventId", eventId);
List<Prize> prizes = prizeMapper.selectByExampleAndRowBounds(example, rowBounds);
return Result.success(new PageInfo<Prize>(prizes));
}
SELECT prize FROM t_prize order by ? LIMIT ?, ?
==> Parameters: singleCont(String), 1(Integer), 10(Integer)
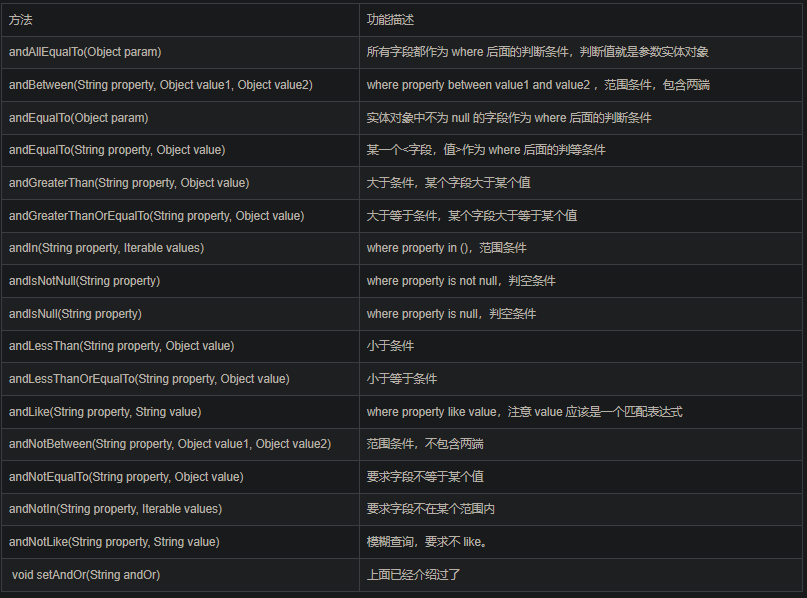
上表的方法都是“与”关系,即 and。 同样的,有相应的 “或” 关系,即 or。比如 orAllEqualTo、orGreaterThan 等等,都是将方法名中的 “and” 换成 “or”。
那 criteria 能否嵌套呢?能否有更方便的使用方式呢?回答:能,有。如下表:

Example 类包含的方法总结如下表:
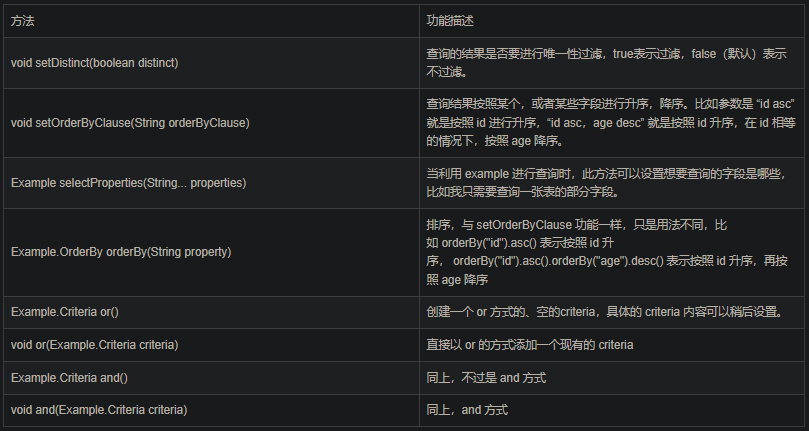
6. tkMybatis常用注解

6.1 @Id注解
通用Mapper在执行xxxByPrimaryKey(param)方法时,有两种情况。
情况一:没有使用@Id注解明确指定主键字段。
select emp_id,emp_name,emp_salary from t_employee where emp_id = ? and emp_name = ? and emp_salary = ?
// 之所以会生成上面这样的where子句是因为tk将实体类中的所有字段都拿来放在一起作为联合主键查询。
情况二:使用@Id注解明确标记和数据库表中主键字段对应的实体类属性。
select emp_id,emp_name,emp_salary from t_employee where emp_id = ?
6.2 @GeneratedValue注解
作用:让通用Mapper在执行insert操作之后将数据库自动生成的主键值回写到实体类对象中。
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Integer empId;
6.3 @Transient注解
作用:用于标记不与数据库表字段对应的实体类字段。
@Transient
private String otherThings; // 非数据库表中字段