本文主要在之前的区块链原形上添加了工作量证明,并且为后继的交易功能做好准备.
上一个章节我们已经创建了区块链的基本原形,但是区块的哈希计算和加入太过于简单,如果按照这种速度添加区块那么区块链估计一个小时就爆满了。
真实的比特币中是全网一个小时产生6个区块,我们的示例中也需要调整区块哈希计算的难度。
工作量证明
人为的提升哈希计算的阀值,加大哈希计算难度与工作量,这样的工作机制才能保证整个区块链数据的安全性和一致性。
工作量证明
区块链的一个关键点就是,一个人必须经过一系列困难的工作,才能将数据放入到区块链中。正是这种困难的工作,才使得区块链是安全和一致的。此外,完成这个工作的人也会获得奖励(这也就是通过挖矿获得币)。
这个机制与生活的一个现象非常类似:一个人必须通过努力工作,才能够获得回报或者奖励,用以支撑他们的生活。在区块链中,是通过网络中的参与者(矿工)不断的工作来支撑整个网络,也就是矿工不断地向区块链中加入新块,然后获得相应的奖励。作为他们努力工作的结果,新生成的区块就能够被安全地被加入到区块链中,这种机制维护了整个区块链数据库的稳定性。值得注意的是,完成了这个工作的人必须要证明这一点,他必须要证明确实是他完成了这些工作。
整个 “努力工作并进行证明” 的机制,就叫做工作量证明(proof-of-work)。要想完成工作非常地不容易,因为这需要大量的计算能力:即便是高性能计算机,也无法在短时间内快速完成。此外,这个工作的困难度会随着时间不断增长,以保持每个小时大概出 6 个新块的速度。在比特币中,这个工作的目的是为了找到一个块的哈希,同时这个哈希满足了一些必要条件。这个哈希,也就充当了证明的角色。因此,寻求证明(寻找有效哈希),就是实际要做的事情。
Hashcash
比特币使用 Hashcash ,一个最初用来防止垃圾邮件的工作量证明算法。它可以被分解为以下步骤:
- 取一些公开的数据(比如,如果是 email 的话,它可以是接收者的邮件地址;在比特币中,它是区块头)
- 给这个公开数据添加一个计数器。计数器默认从 0 开始
- 将 data(数据) 和 counter(计数器) 组合到一起,获得一个哈希
- 检查哈希是否符合一定的条件:
- 如果符合条件,结束
- 如果不符合,增加计数器,重复步骤 3-4
因此,这是一个暴力算法:改变计数器,计算一个新的哈希,检查,增加计数器,计算一个哈希,检查,如此反复。这也是为什么说它是在计算上是非常昂贵的,因为这一步需要如此反复不断地计算和检查。
现在,让我们来仔细看一下一个哈希要满足的必要条件。在原始的 Hashcash 实现中,它的要求是 “一个哈希的前 20 位必须是 0”。在比特币中,这个要求会随着时间而不断变化。因为按照设计,必须保证每 10 分钟生成一个块,而不论计算能力会随着时间增长,或者是会有越来越多的矿工进入网络,所以需要动态调整这个必要条件。
首先定义挖矿难度,也就是哈希值前多少位必须为0的检测标准。
#define DifficultyNum 6
我们删除原来在Block类中的Sethash()函数, 取而代之的是string Block::CalculateHash() 和 void Block::ProofOfWork(int difficultNum)
string Block::CalculateHash() 是根据区块Block的创建时间和区块描述和上一个区块的哈希以及_nNonce来计算一个哈希值 并放回。返回的值会发送给ProofOfWork()函数验证是否符合标准(前DifficultyNum位必须为零).
string Block::CalculateHash() { stringstream ss; ss << _tTime << _data << _prevHash << _nNonce; return sha256(ss.str()); } void Block::ProofOfWork(int difficultNum) { char cstr[DifficultyNum + 1]; for (uint32_t i = 0; i < DifficultyNum; ++i) { cstr[i] = '0'; } cstr[DifficultyNum] = '�'; string str(cstr); do { _nNonce++; _hash = CalculateHash(); } while (_hash.substr(0, difficultNum) != str); std::cout << "Block mined: " << _hash << std::endl; }
相应的 在创建区块后都要调用工作量证明函数
void Blockchain::AddBlock(string datain) { Block* prev = blocks.back(); Block* newblock = new Block(datain, prev->_hash); newblock->ProofOfWork(DifficultyNum); blocks.push_back(newblock); }
static Block* NewBlock(string datain, string prevBlockHash) { Block* p = new Block( datain, prevBlockHash); p->ProofOfWork(DifficultyNum); return p; }
main函数基本没有变化 我们运行查看效果
int main() { Blockchain* bc = TOOLS::NewBlockchain(); bc->AddBlock("Send 1 BTC to Ivan"); bc->AddBlock("Send 2 more BTC to Ivan"); for (int i = 0; i < bc->blocks.size(); i++) { std::cout << "Prev hash = " << bc->blocks[i]->_prevHash << std::endl; std::cout << "data = " << bc->blocks[i]->_data << std::endl; std::cout << "hash = " << bc->blocks[i]->_hash << std::endl << std::endl; } //退出之前 删除 delete bc; return 0; }
这个是难度为4的计算结果:

这是难度为6的计算结果
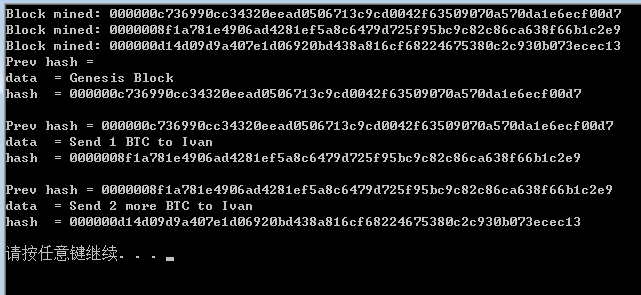
代码如下:

#include "stdafx.h" #include "Blockchain.h" #include "util.h" #include <vector> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { Blockchain* bc = TOOLS::NewBlockchain(); bc->AddBlock("Send 1 BTC to Ivan"); bc->AddBlock("Send 2 more BTC to Ivan"); for (int i = 0; i < bc->blocks.size(); i++) { std::cout << "Prev hash = " << bc->blocks[i]->_prevHash << std::endl; std::cout << "data = " << bc->blocks[i]->_data << std::endl; std::cout << "hash = " << bc->blocks[i]->_hash << std::endl << std::endl; } //退出之前 删除 delete bc; system("pause"); return 0; }

#include <cstring> #include <fstream> #include "sha256.h" const unsigned int SHA256::sha256_k[64] = //UL = uint32 {0x428a2f98, 0x71374491, 0xb5c0fbcf, 0xe9b5dba5, 0x3956c25b, 0x59f111f1, 0x923f82a4, 0xab1c5ed5, 0xd807aa98, 0x12835b01, 0x243185be, 0x550c7dc3, 0x72be5d74, 0x80deb1fe, 0x9bdc06a7, 0xc19bf174, 0xe49b69c1, 0xefbe4786, 0x0fc19dc6, 0x240ca1cc, 0x2de92c6f, 0x4a7484aa, 0x5cb0a9dc, 0x76f988da, 0x983e5152, 0xa831c66d, 0xb00327c8, 0xbf597fc7, 0xc6e00bf3, 0xd5a79147, 0x06ca6351, 0x14292967, 0x27b70a85, 0x2e1b2138, 0x4d2c6dfc, 0x53380d13, 0x650a7354, 0x766a0abb, 0x81c2c92e, 0x92722c85, 0xa2bfe8a1, 0xa81a664b, 0xc24b8b70, 0xc76c51a3, 0xd192e819, 0xd6990624, 0xf40e3585, 0x106aa070, 0x19a4c116, 0x1e376c08, 0x2748774c, 0x34b0bcb5, 0x391c0cb3, 0x4ed8aa4a, 0x5b9cca4f, 0x682e6ff3, 0x748f82ee, 0x78a5636f, 0x84c87814, 0x8cc70208, 0x90befffa, 0xa4506ceb, 0xbef9a3f7, 0xc67178f2}; void SHA256::transform(const unsigned char *message, unsigned int block_nb) { uint32 w[64]; uint32 wv[8]; uint32 t1, t2; const unsigned char *sub_block; int i; int j; for (i = 0; i < (int) block_nb; i++) { sub_block = message + (i << 6); for (j = 0; j < 16; j++) { SHA2_PACK32(&sub_block[j << 2], &w[j]); } for (j = 16; j < 64; j++) { w[j] = SHA256_F4(w[j - 2]) + w[j - 7] + SHA256_F3(w[j - 15]) + w[j - 16]; } for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) { wv[j] = m_h[j]; } for (j = 0; j < 64; j++) { t1 = wv[7] + SHA256_F2(wv[4]) + SHA2_CH(wv[4], wv[5], wv[6]) + sha256_k[j] + w[j]; t2 = SHA256_F1(wv[0]) + SHA2_MAJ(wv[0], wv[1], wv[2]); wv[7] = wv[6]; wv[6] = wv[5]; wv[5] = wv[4]; wv[4] = wv[3] + t1; wv[3] = wv[2]; wv[2] = wv[1]; wv[1] = wv[0]; wv[0] = t1 + t2; } for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) { m_h[j] += wv[j]; } } } void SHA256::init() { m_h[0] = 0x6a09e667; m_h[1] = 0xbb67ae85; m_h[2] = 0x3c6ef372; m_h[3] = 0xa54ff53a; m_h[4] = 0x510e527f; m_h[5] = 0x9b05688c; m_h[6] = 0x1f83d9ab; m_h[7] = 0x5be0cd19; m_len = 0; m_tot_len = 0; } void SHA256::update(const unsigned char *message, unsigned int len) { unsigned int block_nb; unsigned int new_len, rem_len, tmp_len; const unsigned char *shifted_message; tmp_len = SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE - m_len; rem_len = len < tmp_len ? len : tmp_len; memcpy(&m_block[m_len], message, rem_len); if (m_len + len < SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE) { m_len += len; return; } new_len = len - rem_len; block_nb = new_len / SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE; shifted_message = message + rem_len; transform(m_block, 1); transform(shifted_message, block_nb); rem_len = new_len % SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE; memcpy(m_block, &shifted_message[block_nb << 6], rem_len); m_len = rem_len; m_tot_len += (block_nb + 1) << 6; } void SHA256::final(unsigned char *digest) { unsigned int block_nb; unsigned int pm_len; unsigned int len_b; int i; block_nb = (1 + ((SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE - 9) < (m_len % SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE))); len_b = (m_tot_len + m_len) << 3; pm_len = block_nb << 6; memset(m_block + m_len, 0, pm_len - m_len); m_block[m_len] = 0x80; SHA2_UNPACK32(len_b, m_block + pm_len - 4); transform(m_block, block_nb); for (i = 0 ; i < 8; i++) { SHA2_UNPACK32(m_h[i], &digest[i << 2]); } } std::string sha256(std::string input) { unsigned char digest[SHA256::DIGEST_SIZE]; memset(digest,0,SHA256::DIGEST_SIZE); SHA256 ctx = SHA256(); ctx.init(); ctx.update( (unsigned char*)input.c_str(), input.length()); ctx.final(digest); char buf[2*SHA256::DIGEST_SIZE+1]; buf[2*SHA256::DIGEST_SIZE] = 0; for (int i = 0; i < SHA256::DIGEST_SIZE; i++) sprintf(buf+i*2, "%02x", digest[i]); return std::string(buf); }

#ifndef SHA256_H #define SHA256_H #include <string> class SHA256 { protected: typedef unsigned char uint8; typedef unsigned int uint32; typedef unsigned long long uint64; const static uint32 sha256_k[]; static const unsigned int SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE = (512/8); public: void init(); void update(const unsigned char *message, unsigned int len); void final(unsigned char *digest); static const unsigned int DIGEST_SIZE = ( 256 / 8); protected: void transform(const unsigned char *message, unsigned int block_nb); unsigned int m_tot_len; unsigned int m_len; unsigned char m_block[2*SHA224_256_BLOCK_SIZE]; uint32 m_h[8]; }; std::string sha256(std::string input); #define SHA2_SHFR(x, n) (x >> n) #define SHA2_ROTR(x, n) ((x >> n) | (x << ((sizeof(x) << 3) - n))) #define SHA2_ROTL(x, n) ((x << n) | (x >> ((sizeof(x) << 3) - n))) #define SHA2_CH(x, y, z) ((x & y) ^ (~x & z)) #define SHA2_MAJ(x, y, z) ((x & y) ^ (x & z) ^ (y & z)) #define SHA256_F1(x) (SHA2_ROTR(x, 2) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 13) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 22)) #define SHA256_F2(x) (SHA2_ROTR(x, 6) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 11) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 25)) #define SHA256_F3(x) (SHA2_ROTR(x, 7) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 18) ^ SHA2_SHFR(x, 3)) #define SHA256_F4(x) (SHA2_ROTR(x, 17) ^ SHA2_ROTR(x, 19) ^ SHA2_SHFR(x, 10)) #define SHA2_UNPACK32(x, str) { *((str) + 3) = (uint8) ((x) ); *((str) + 2) = (uint8) ((x) >> 8); *((str) + 1) = (uint8) ((x) >> 16); *((str) + 0) = (uint8) ((x) >> 24); } #define SHA2_PACK32(str, x) { *(x) = ((uint32) *((str) + 3) ) | ((uint32) *((str) + 2) << 8) | ((uint32) *((str) + 1) << 16) | ((uint32) *((str) + 0) << 24); } #endif

#include "Blockchain.h" class TOOLS{ public: static Block* NewGenesisBlock() { return NewBlock("Genesis Block", ""); } static Blockchain* NewBlockchain() { Block* pblock = NewGenesisBlock(); Blockchain* p = new Blockchain(pblock); return p; } static Block* NewBlock(string datain, string prevBlockHash) { Block* p = new Block( datain, prevBlockHash); p->ProofOfWork(DifficultyNum); return p; } private: };

#include <string> using namespace std; #define DifficultyNum 6 class Block { public: string _hash; //当前区块的哈希 string _data; //区块描述字符 string _prevHash; //记录上个块的哈希值 Block(const string& prevHash, const string& dataIn); //构造函数 string CalculateHash(); //计算本区块的可能哈希 返回值在MineBlock函数中验证 void ProofOfWork(int difficultNum); private: int64_t _nNonce; //区块随机数 用于哈希值的产生 time_t _tTime; //创建时间 };

#include "Block.h" #include "sha256.h" #include <time.h> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <iostream> using namespace std; string Block::CalculateHash() { stringstream ss; ss << _tTime << _data << _prevHash << _nNonce; return sha256(ss.str()); } Block::Block( const string& dataIn, const string& prevHash) { _tTime = time(nullptr); _nNonce = 0; _data = dataIn; _prevHash = prevHash; } void Block::ProofOfWork(int difficultNum) { char cstr[DifficultyNum + 1]; for (uint32_t i = 0; i < DifficultyNum; ++i) { cstr[i] = '0'; } cstr[DifficultyNum] = '�'; string str(cstr); do { _nNonce++; _hash = CalculateHash(); //std::cout << _hash ; } while (_hash.substr(0, difficultNum) != str); std::cout << "Block mined: " << _hash << std::endl; }

#include <vector> #include "Block.h" using namespace std; class Blockchain { public: Blockchain(Block* p); vector<Block*> blocks; void AddBlock(string datain); ~Blockchain() { for (int i = 0; i < blocks.size(); i++) { if (blocks[i] != NULL) { delete blocks[i]; blocks[i] = NULL; } } } private: };

#include "Blockchain.h" void Blockchain::AddBlock(string datain) { Block* prev = blocks.back(); Block* newblock = new Block(datain, prev->_hash); newblock->ProofOfWork(DifficultyNum); blocks.push_back(newblock); } Blockchain::Blockchain(Block* p) { blocks.clear(); blocks.push_back(p); }

/* * Updated to C++, zedwood.com 2012 * Based on Olivier Gay's version * See Modified BSD License below: * * FIPS 180-2 SHA-224/256/384/512 implementation * Issue date: 04/30/2005 * http://www.ouah.org/ogay/sha2/ * * Copyright (C) 2005, 2007 Olivier Gay <olivier.gay@a3.epfl.ch> * All rights reserved. * * Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without * modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions * are met: * 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer. * 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright * notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the * documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution. * 3. Neither the name of the project nor the names of its contributors * may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software * without specific prior written permission. * * THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE PROJECT AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND * ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE * IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE * ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE PROJECT OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE * FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL * DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS * OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) * HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT * LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY * OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF * SUCH DAMAGE. */
工程文件也可以在qq群中找到, 文件名为 MyBlockChainCppSample_part2
下一个章节介绍持久化
/*
作 者: itdef
欢迎转帖 请保持文本完整并注明出处
技术博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/itdef/
技术交流群 群号码:432336863
欢迎c c++ windows驱动爱好者 服务器程序员沟通交流
部分老代码存放地点
http://www.oschina.net/code/list_by_user?id=614253
*/
参考博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/simple_the_best/article/details/78104604
https://jeiwan.cc/posts/building-blockchain-in-go-part-2/


