leveldb
LevelDb是一个持久化存储的KV系统,并非完全将数据放置于内存中,部分数据也会存储到磁盘上。
想了解这个由谷歌大神编写的经典项目.
可以从数据结构以及数据结构的处理下手,也可以从示例的某一点深入跟进系统,查看处理流程.
windows下编译leveldb 地址 leveldb 源码编译 vs版本
目前手头资料中,源码中的文档以及网络的代码分析心得如下,本文也做了参考,感谢作者.
流程类
结构入手类
1 arena内存池略过。 nginx内存池 stl内存池均可参考实现原理(《stl源码分析》)
2 bloomfilter相当于多重哈希,比对哈希值判断是否有相同元素插入 略过。
3 数据结构skiplist 多数操作log(n)
参考 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000003051117
跳表的关键点在于定义和查找方法
定义如下:
SkipList的定义:
1. 一个跳表应该有几个层(level)组成;
2. 跳表的第一层包含所有的元素;
3. 每一层都是一个有序的链表;
4. 如果元素x出现在第i层,则所有比i小的层都包含x;
5. 第i层的元素通过一个down指针指向下一层拥有相同值的元素;
6. 在每一层中,-1和1两个元素都出现(分别表示INT_MIN和INT_MAX);
7. Top指针指向最高层的第一个元素。
图示:
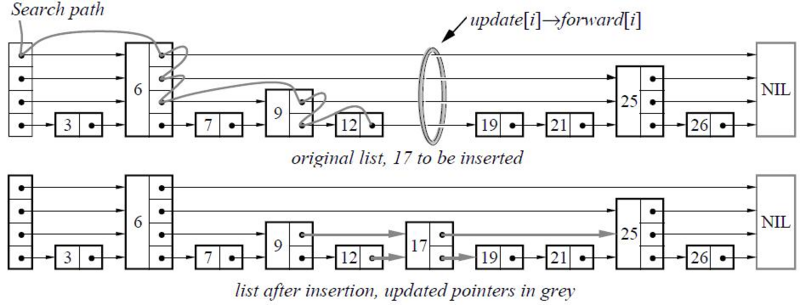
find
查找方法为
1 起点为最高层第一个元素 若元素小于查找值 则查找该元素的后继值
2 若元素大于查找值 则降低层级再次查找
3 若该元素的后继值 为NULL或者大于该值 ,则降低层数再次查找
4 直到查找成功或者达到表的最底层且无元素可查找
图示中查找 17
起点为最高层第一个元素 6 6<17 6的下一个元素为null 则在元素6中降低层级
再次查找6的下一个元素 是25 降低层级
再次查找6的下一个元素 是9
再次查找9的下一个元素 是25 降低层级
再次查找9的下一个元素 是12
再次查找12的下一个元素 是19 此处为最低层级 则未查找到(进行插入)
insert
查找也可用于insert 注意insert 元素时候层级是随机的
leveldb 中skiplist 结构如下(内存池与原子指针等结构暂时不予理会)

1 template<typename Key, class Comparator> 2 struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node { 3 explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { } 4 5 Key const key; 6 7 // Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can 8 // add the appropriate barriers as necessary. 9 Node* Next(int n) { 10 assert(n >= 0); 11 // Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized 12 // version of the returned Node. 13 return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load()); 14 } 15 void SetNext(int n, Node* x) { 16 assert(n >= 0); 17 // Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this 18 // pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node. 19 next_[n].Release_Store(x); 20 } 21 22 // No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations. 23 Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) { 24 assert(n >= 0); 25 return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load()); 26 } 27 void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) { 28 assert(n >= 0); 29 next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x); 30 } 31 32 private: 33 // Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link. 34 port::AtomicPointer next_[1]; 35 }; 36 37 template<typename Key, class Comparator> 38 typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* 39 SkipList<Key,Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) { 40 char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned( 41 sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - 1)); 42 return new (mem) Node(key); 43 }
抛开内存池和多线程情况下的原子操作 定义很简单
分配 获取下一个元素 设置下一个元素
template<typename Key, class Comparator>中的 key是元素类型 Comparator是元素比较大小的策略
元素插入操作如下

1 template<typename Key, class Comparator> 2 void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) { 3 // TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual() 4 // here since Insert() is externally synchronized. 5 Node* prev[kMaxHeight]; 6 Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev); 7 8 assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key)); 9 10 int height = RandomHeight(); 11 if (height > GetMaxHeight()) { 12 for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) { 13 prev[i] = head_; 14 } 15 //fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d ", max_height_, height); 16 17 // It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization 18 // with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes 19 // the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of 20 // new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in 21 // the loop below. In the former case the reader will 22 // immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all 23 // keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node. 24 max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height)); 25 } 26 27 x = NewNode(key, height); 28 for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) { 29 // NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when 30 // we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i]. 31 x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i)); 32 prev[i]->SetNext(i, x); 33 } 34 }
插入元素的层级是随机的 并且获取当前最大层级数并未使用原子操作 因为根据逻辑并无影响 不使用原子操作也是性能上的一种考虑
元素读取操作如下

1 template<typename Key, class Comparator> 2 typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev) 3 const { 4 Node* x = head_; 5 int level = GetMaxHeight() - 1; 6 while (true) { 7 Node* next = x->Next(level); 8 if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) { 9 // Keep searching in this list 10 x = next; 11 } else { 12 if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x; 13 if (level == 0) { 14 return next; 15 } else { 16 // Switch to next list 17 level--; 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 }

find
查找方法为
1 起点为最高层第一个元素 若元素小于查找值 则查找该元素的后继值
2 若元素大于查找值 则降低层级再次查找
3 若该元素的后继值 为NULL或者大于该值 ,则降低层数再次查找
4 直到查找成功或者达到表的最底层且无元素可查找
图示中查找 17
起点为最高层第一个元素 6 6<17 6的下一个元素为null 则在元素6中降低层级
再次查找6的下一个元素 是25 降低层级
再次查找6的下一个元素 是9
再次查找9的下一个元素 是25 降低层级
再次查找9的下一个元素 是12
再次查找12的下一个元素 是19 此处为最低层级 则未查找到(进行插入)


