https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/How-it-works
1. 配置各种规则,然后通过aspectj解析注解然后看是否可以通过各种校验
@Aspect public class SentinelResourceAspect extends AbstractSentinelAspectSupport { @Pointcut("@annotation(com.qxwz.sentinel.annotation.SentinelResource)") public void sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut() { } @Around("sentinelResourceAnnotationPointcut()") public Object invokeResourceWithSentinel(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { Method originMethod = resolveMethod(pjp); SentinelResource annotation = originMethod.getAnnotation(SentinelResource.class); if (annotation == null) { // Should not go through here. throw new IllegalStateException("Wrong state for SentinelResource annotation"); } String resourceName = getResourceName(annotation.value(), originMethod); EntryType entryType = annotation.entryType(); Entry entry = null; try { entry = SphU.entry(resourceName, entryType, 1, pjp.getArgs()); Object result = pjp.proceed(); return result; } catch (BlockException ex) { return handleBlockException(pjp, annotation, ex); } catch (Throwable ex) { Class<? extends Throwable>[] exceptionsToIgnore = annotation.exceptionsToIgnore(); // The ignore list will be checked first. if (exceptionsToIgnore.length > 0 && exceptionBelongsTo(ex, exceptionsToIgnore)) { throw ex; } if (exceptionBelongsTo(ex, annotation.exceptionsToTrace())) { traceException(ex, annotation); return handleFallback(pjp, annotation, ex); } // No fallback function can handle the exception, so throw it out. throw ex; } finally { if (entry != null) { entry.exit(1, pjp.getArgs()); } } } }
2. FlowRuleManager 动态规则(基于观察者模式)构建及监控(定时任务地调度metricTimerListener)
private static final Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, List<FlowRule>>(); private static final FlowPropertyListener LISTENER = new FlowPropertyListener(); private static SentinelProperty<List<FlowRule>> currentProperty = new DynamicSentinelProperty<List<FlowRule>>(); @SuppressWarnings("PMD.ThreadPoolCreationRule") private static final ScheduledExecutorService SCHEDULER = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1, new NamedThreadFactory("sentinel-metrics-record-task", true)); static { currentProperty.addListener(LISTENER); SCHEDULER.scheduleAtFixedRate(new MetricTimerListener(), 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS); }
3. 规则生效方法 - 基于滑动窗口的判断

4. 处理单元组织
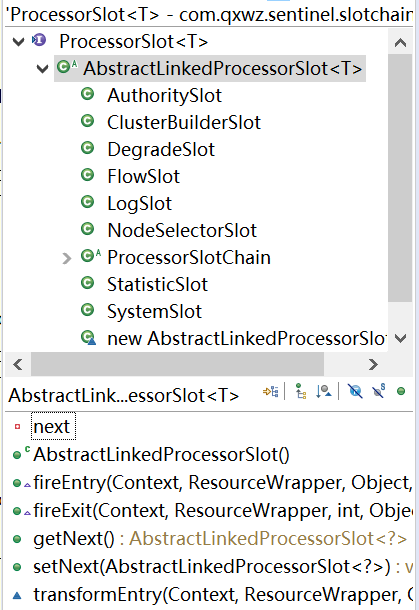
FlowSlot 会根据预设的规则,结合前面 NodeSelectorSlot、ClusterNodeBuilderSlot、StatisticSlot 统计出来的实时信息进行流量控制,遍历所有限流规则,直到有规则触发限流或者所有规则遍历完毕。
5. 处理链条

6. 简单调用关系
SentinelResourceAspect.invokeResourceWithSentinel -> SphU.entry -> CtSph...lookProcessChain -> FlowSlot(checkFlow/fireEntry) -> DefaultController(canpass)