1.基础指令:
- v-show
- v-if
- v-else
- v-for
- v-bind 简用(:) vue会在实例过程中添加setter getter方法去监听值得变化
- v-click 简用(@)
2.vue中监听window事件:
感谢 smallW
根据窗口的变化去变化 canvas 的宽度?
解决方法一很常见:
- 在data初始化等时候定义一个记录宽度的属性
data: { screenWidth: document.body.clientWidth // 这里是给到了一个默认值 (这个很重要) } - 在vue钩子函数mounted里面挂载resize方法
mounted () { const that = this window.onresize = () => { return (() => { window.screenWidth = document.body.clientWidth that.screenWidth = window.screenWidth })() } } - 监听变化,不断改变大小
watch: { screenWidth (val) { if (!this.timer) { this.screenWidth = val this.timer = true let that = this setTimeout(function () { that.screenWidth = that.$store.state.canvasWidth console.log(that.screenWidth) that.init() that.timer = false }, 400) } } }
解决方法二:
mounted时监听(快,但是一般新人会选择第一种)
3.vue的源码讲了一些什么:
- 生命周期
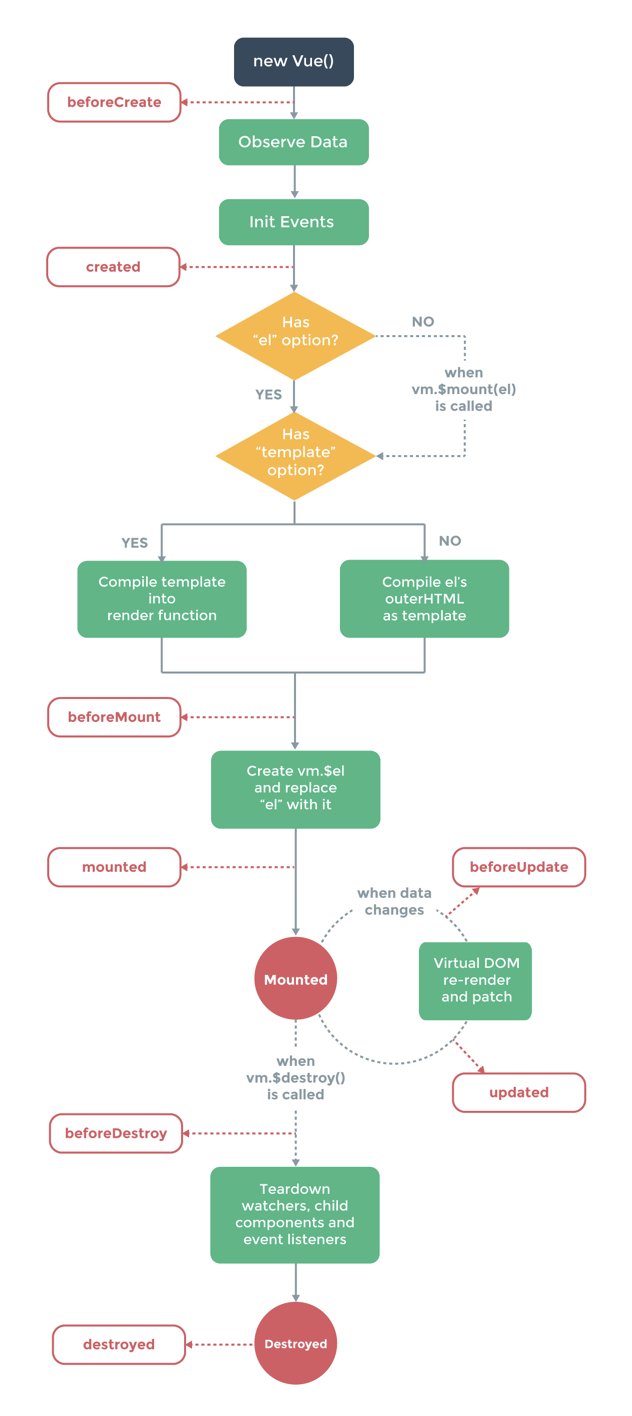
- vue中的new做了哪些事?
- new一个新对象
- 将这个新对象的prototype指向构造函数的prototype成员对象
- 将构造函数的this指向这个new的对象
- 返回新对象
拓展:new一个新对象,到底干了什么?(面试题)
- 不用手动新建一个obj ,new会帮你创建
- 不用把新建的obj的__proto__指向构造函数Common的prototype,new会帮你做。
- 构造函数this的作用域会指向实例本身。
- 不用手动return新建的obj,new会帮你return。
- new出来的实例的__proto__会指向构造函数的prototype。构造函数的方法,实例可以直接调用。
- vue实例化的构造函数在哪?
项目的 vue 文件夹下 core / instance / index.js ( 感谢 smallW)

-
Vue 2.0 为什么选用 Flow 进行静态代码检查而不是直接使用 TypeScript?
- vue源码的三要素vm,compiler,watcher
- 核心代码init初始化了什么?
- 生命周期initLifecycle
- 事件initEvents
- 初始化渲染initRender(vm)
- initInjections
- initState
具体参考:vue.js源码解析四
- Vue实现数据监听以及单向数据流的主要方式:
export function defineReactive(obj, key, val, customSetter, shallow) {
const dep = new Dep();
const property = Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, key);
if (property && property.configurable === false) {
return;
}
// cater for pre-defined getter/setters
const getter = property && property.get;
const setter = property && property.set;
if ((!getter || setter) && arguments.length === 2) {
val = obj[key];
}
let childOb = !shallow && observe(val);
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function reactiveGetter() {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
if (Dep.target) {
dep.depend();
if (childOb) {
childOb.dep.depend();
if (Array.isArray(value)) {
dependArray(value);
}
}
}
return value;
},
set: function reactiveSetter(newVal) {
const value = getter ? getter.call(obj) : val;
/* eslint-disable no-self-compare */
if (newVal === value || newVal !== newVal && value !== value) {
return;
}
/* eslint-enable no-self-compare */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && customSetter) {
customSetter();
}
if (setter) {
setter.call(obj, newVal);
} else {
val = newVal;
}
childOb = !shallow && observe(newVal);
dep.notify();
}
});
}
4.vue源码中的神奇用法:
-
判断是否为 undefined
let isUndef = function(v) { return v === undefined || v === null } -
判断是否不为空
let isDef = function(v) { return v !== undefined && v !== null } -
判断是否为原始数据类型
let isPrimitive = function(value) { return typeof value === 'string' || typeof value === 'number' || typeof value === 'symbol' || typeof value === 'boolean'; } -
判断是否为 Object 类型
let isPrimitive = function(value) { return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object'; } -
判断是否为原始对象
const _toString = Object.prototype.toString; // 继承对象的原始方法 let isPlainObject = function(obj) { return _toString.call(obj) === '[object Object]'; } -
判断是否为正则对象
const _toString = Object.prototype.toString; // 继承对象的原始方法 let isRegExp= function(v) { return _toString.call(v) === '[object RegExp]'; }
5.React 和 Vue 的方法类似, 在路由跳转前先做拦截操作。加上需要在页面中加入的方法和统计代码即可。