前言
多线程共用进程的内存空间导致数据共享,但有时候也有线程数据隔离的需求,本文介绍了线程私有数据
正文
例子&&使用
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_key_t key; //定义一个key
void *pthread1(void *arg){
int a = 1;
pthread_setspecific(key, &a);//在线程1中,将这个key关联其私有数据
printf("thread1: %d
", *(int *)pthread_getspecific(key)); //获取其私有数据
}
void *pthread2(void *arg){
int a = 2;
pthread_setspecific(key, &a); //在线程2中,将这个key关联其私有数据
printf("thread2: %d
", *(int *)pthread_getspecific(key)); //获取其私有数据
}
int main()
{
pthread_key_create(&key, NULL); //创建一个key
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, &pthread1, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, &pthread2, NULL);
pthread_join(tid1, NULL);
pthread_join(tid2, NULL);
return 0;
}
如上述的例子,通过定义一个pthread_key_t类型变量, 使用pthread_key_create()去初始化它,不同的线程通过pthread_setspecific()将key与自己的私有数据进行绑定,当需要使用数据的时候,通过pthread_getspecific()获取数据
原理
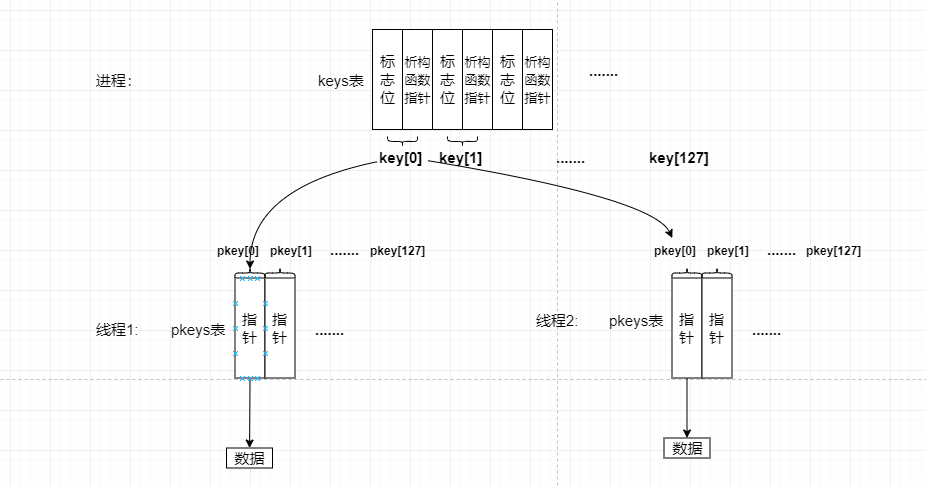
如上图所示,进程中维护了一张keys表,与之关联线程中也存在一张pkeys表,使用pthread_key_create()初始化一个key的时候,首先从进程中的keys表找到一个未使用的key(通过标志位判断)的下标(pthread_key_t的实际类型是unsigned int), 然后,线程就通过这个下标对应的pkey对象去维护要存取的数据