1、“Content-Security-Policy”头缺失
在网上查了关于这个响应头的说明,CSP相当于前台的白名单,用来限制网站内部一些资源获取的来源,如限制CSS、JS、图片或者第三方链接等。
CSP的设置可以在一定程度上限制XSS攻击,有2种方式可以设置。第一种通过设置HTTP响应头,另一种通过HTML的<meta>标签。
具体的设置和说明请参考: http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/09/csp.html
Content Security Policy 入门教程
跨域脚本攻击 XSS 是最常见、危害最大的网页安全漏洞

为了防止它们,要采取很多编程措施,非常麻烦。很多人提出,能不能根本上解决问题,浏览器自动禁止外部注入恶意脚本?
这就是"网页安全政策"(Content Security Policy,缩写 CSP)的来历。本文详细介绍如何使用 CSP 防止 XSS 攻击。

一、简介
CSP 的实质就是白名单制度,开发者明确告诉客户端,哪些外部资源可以加载和执行,等同于提供白名单。它的实现和执行全部由浏览器完成,开发者只需提供配置。
CSP 大大增强了网页的安全性。攻击者即使发现了漏洞,也没法注入脚本,除非还控制了一台列入了白名单的可信主机。
两种方法可以启用 CSP。一种是通过 HTTP 头信息的Content-Security-Policy的字段。

Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self'; object-src 'none'; style-src cdn.example.org third-party.org; child-src https:
另一种是通过网页的<meta>标签。
<meta http-equiv="Content-Security-Policy" content="script-src 'self'; object-src 'none'; style-src cdn.example.org third-party.org; child-src https:">
上面代码中,CSP 做了如下配置。
- 脚本:只信任当前域名
- <object>标签:不信任任何URL,即不加载任何资源
- 样式表:只信任cdn.example.org和third-party.org
- 框架(frame):必须使用HTTPS协议加载
- 其他资源:没有限制
启用后,不符合 CSP 的外部资源就会被阻止加载。
Chrome 的报错信息。

Firefox 的报错信息。

二、限制选项
CSP 提供了很多限制选项,涉及安全的各个方面。
2.1 资源加载限制
以下选项限制各类资源的加载。
- script-src:外部脚本
- style-src:样式表
- img-src:图像
- media-src:媒体文件(音频和视频)
- font-src:字体文件
- object-src:插件(比如 Flash)
- child-src:框架
- frame-ancestors:嵌入的外部资源(比如<frame>、<iframe>、<embed>和<applet>)
- connect-src:HTTP 连接(通过 XHR、WebSockets、EventSource等)
- worker-src:worker脚本
- manifest-src:manifest 文件
2.2 default-src
default-src用来设置上面各个选项的默认值。
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'
上面代码限制所有的外部资源,都只能从当前域名加载。
如果同时设置某个单项限制(比如font-src)和default-src,前者会覆盖后者,即字体文件会采用font-src的值,其他资源依然采用default-src的值。
2.3 URL 限制
有时,网页会跟其他 URL 发生联系,这时也可以加以限制。
- frame-ancestors:限制嵌入框架的网页
- base-uri:限制<base#href>
- form-action:限制<form#action>
2.4 其他限制
其他一些安全相关的功能,也放在了 CSP 里面。
block-all-mixed-content:HTTPS 网页不得加载 HTTP 资源(浏览器已经默认开启)upgrade-insecure-requests:自动将网页上所有加载外部资源的 HTTP 链接换成 HTTPS 协议plugin-types:限制可以使用的插件格式sandbox:浏览器行为的限制,比如不能有弹出窗口等。
2.5 report-uri
有时,我们不仅希望防止 XSS,还希望记录此类行为。report-uri就用来告诉浏览器,应该把注入行为报告给哪个网址。
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; ...; report-uri /my_amazing_csp_report_parser;
上面代码指定,将注入行为报告给/my_amazing_csp_report_parser这个 URL。
浏览器会使用POST方法,发送一个JSON对象,下面是一个例子。
{
"csp-report": {
"document-uri": "http://example.org/page.html",
"referrer": "http://evil.example.com/",
"blocked-uri": "http://evil.example.com/evil.js",
"violated-directive": "script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com",
"original-policy": "script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com; report-uri http://example.org/my_amazing_csp_report_parser"
}
}

三、Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only
除了Content-Security-Policy,还有一个Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only字段,表示不执行限制选项,只是记录违反限制的行为。
它必须与report-uri选项配合使用。
Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only: default-src 'self'; ...; report-uri /my_amazing_csp_report_parser;
四、选项值
每个限制选项可以设置以下几种值,这些值就构成了白名单。
- 主机名:
example.org,https://example.com:443- 路径名:
example.org/resources/js/- 通配符:
*.example.org,*://*.example.com:*(表示任意协议、任意子域名、任意端口)- 协议名:
https:、data:- 关键字
'self':当前域名,需要加引号- 关键字
'none':禁止加载任何外部资源,需要加引号
多个值也可以并列,用空格分隔。
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'self' https://apis.google.com
如果同一个限制选项使用多次,只有第一次会生效。
# 错误的写法 script-src https://host1.com; script-src https://host2.com # 正确的写法 script-src https://host1.com https://host2.com
如果不设置某个限制选项,就是默认允许任何值。
五、script-src 的特殊值
除了常规值,script-src还可以设置一些特殊值。注意,下面这些值都必须放在单引号里面。
'unsafe-inline':允许执行页面内嵌的<script>标签和事件监听函数unsafe-eval:允许将字符串当作代码执行,比如使用eval、setTimeout、setInterval和Function等函数。- nonce值:每次HTTP回应给出一个授权token,页面内嵌脚本必须有这个token,才会执行
- hash值:列出允许执行的脚本代码的Hash值,页面内嵌脚本的哈希值只有吻合的情况下,才能执行。
nonce值的例子如下,服务器发送网页的时候,告诉浏览器一个随机生成的token。
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'nonce-EDNnf03nceIOfn39fn3e9h3sdfa'
页面内嵌脚本,必须有这个token才能执行。
<script nonce=EDNnf03nceIOfn39fn3e9h3sdfa> // some code </script>
hash值的例子如下,服务器给出一个允许执行的代码的hash值。
Content-Security-Policy: script-src 'sha256-qznLcsROx4GACP2dm0UCKCzCG-HiZ1guq6ZZDob_Tng='
下面的代码就会允许执行,因为hash值相符。
<script>alert('Hello, world.');</script>
注意,计算hash值的时候,<script>标签不算在内。
除了script-src选项,nonce值和hash值还可以用在style-src选项,控制页面内嵌的样式表。
六、注意点
(1)script-src和object-src是必设的,除非设置了default-src。
因为攻击者只要能注入脚本,其他限制都可以规避。而object-src必设是因为 Flash 里面可以执行外部脚本。
(2)script-src不能使用unsafe-inline关键字(除非伴随一个nonce值),也不能允许设置data:URL。
下面是两个恶意攻击的例子。
<img src="x" onerror="evil()"> <script src="data:text/javascript,evil()"></script>
(3)必须特别注意 JSONP 的回调函数。
<script src="/path/jsonp?callback=alert(document.domain)//"> </script>
上面的代码中,虽然加载的脚本来自当前域名,但是通过改写回调函数,攻击者依然可以执行恶意代码。
七、参考链接
- CSP Is Dead, Long Live CSP! , by Lukas Weichselbaum
- An Introduction to Content Security Policy, by Mike West
Spring 代码修改内容
我是在自定义的拦截器中加了CSP设置,后面2个关于响应头的设置也是在这里加的。
public class YourInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor { @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { //your code //…… //设置CSP response.addHeader("Content-Security-Policy","default-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval';"); response.addHeader("X-Content-Type-Options","nosniff"); response.addHeader("X-XSS-Protection","1"); //your code return true; } @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { //your code } @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { //your code } }
2、“X-Content-Type-Options”头缺失或不安全
响应头缺失,按照扫描要求设置,具体设置请参照第一点。如果不知道具体的属性值,可以参考官方的API或者去网上找一找别人的说明。
这是别人写的,大家有需要的话可以参考一下:https://www.cnblogs.com/vekair/p/11233649.html
销售“安全记分卡”的公司正在崛起,并已开始成为企业销售的一个因素。这些公司组合使用 HTTP 安全报头和 IP 信誉来进行评级。不过,在很大程度上,公司的得分取决于对外开放网站上设置的安全响应报头。本文介绍了常用的安全响应报头及对应的推荐安全值,并给出了示例。
销售“安全记分卡”的公司正在崛起,并已开始成为企业销售的一个因素。我从客户那里了解到,他们对从评级低的供应商那里的采购很不放心,至少有案例表明,他们依据最初的评级改变了采购决策。
我调查了这些评级公司是如何计算公司安全性得分的,结果发现他们组合使用了 HTTP 安全报头和 IP 信誉。
IP 信誉基于的是黑名单和垃圾邮件列表,再加上公共 IP 所有权数据。只要你的公司没有垃圾邮件,并且能够快速检测和阻止恶意软件感染,那么通常这些软件应该就是干净的。HTTP 安全报头使用的计算方式与Mozilla Observatory的工作方式类似。
因此,对于大多数公司来说,在很大程度上,他们的得分取决于对外开放的网站上设置的安全响应报头。
设置正确的响应报头可以快速实现(通常不需要进行大量测试),并能提高网站的安全性,现在还可以帮助我们赢得具有安全意识的客户。
我对这种测试方法的价值以及这些公司提出的过高的定价方案持怀疑态度。我不认为它与真正的产品安全性有那么大的关联。然而,这无疑增加了设置响应报头并维护其正确性的重要性,值得为此投入时间。
在本文中,我将介绍常用的评估响应报头,及每个报头的推荐安全值,并给出一个响应报头设置的示例。在本文的最后,还将给出常见的应用程序和 Web 服务器的设置示例。
重要的安全响应报头
Content-Security-Policy(CSP)
CSP 通过指定允许加载哪些资源的形式,来防止跨站脚本注入。在本文所列的安全响应报头中,正确地设置和维护 CSP,可能是最耗时的,也是最容易出现风险的。在开发 CSP 的过程中,要谨慎充分地测试它——以“合法”的方式阻塞站点使用的内容源会破坏站点的功能。
创建 CSP 初稿的一个很好的工具是Mozilla 实验室的 CSP 浏览器扩展。在浏览器中安装此扩展程序,首先充分地浏览要为其设置 CSP 的站点,然后在站点中使用生成的 CSP。理想情况下,还可以重构 JavaScript,使其没有残留的任何内联脚本,从而使我们可以删除“unsafe inline”指令设置。
CSP 的指令设置可能比较复杂,也很混乱,因此,如果你想更深入的了解 CSP,请访问其官方网站。
一个好的 CSP 开始可能是如下这样的(在真正的站点上使用时,可能需要进行大量的修改)。在包含该站点的每个部分中都添加域名。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' https://i.imgur.com; object-src 'none'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; base-uri 'self'; form-action 'self';
|
Strict-Transport-Security(HSTS)
该响应报头告诉浏览器,只能通过 HTTPS 访问网站——如果网站启用过 HTTPS,它将会一直生效。如果使用子域名,还建议在任何使用过的子域名对此加以强制。
|
|
X-Content-Type-Options
该响应报头确保浏览器遵守应用程序设置的 MIME 类型。这有助于防止某些类型的跨站脚本注入攻击。
它还能减少浏览器“猜测”某些内容不正确时的意外应用程序行为,例如,当开发人员将某个页面标记为“HTML”,但浏览器认为它更像 JavaScript,并试图将其渲染为 JavaScript 时。该响应报头能确保浏览器始终遵守服务端设置的 MIME 类型。
|
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
|
Cache-Control(缓存控制)
这个响应报头比其他的要稍微复杂一些,因为我们可能需要根据内容类型的不同而使用不同的缓存策略。
任何具有敏感数据的页面,如用户页面或客户结算页面,都应该设置成无缓存。其中一个原因是,防止共享计算机上的某个人按回退按钮或浏览历史记录又能查看到个人信息。
但是,对于像静态资产(图像、CSS 文件和 JS 文件)等很少变更的页面,很适合使用缓存。既可以通过逐页设置的方式来实现,也可以通过在服务端配置使用正则表达式的方式来实现。
|
# 默认情况不使用缓存
|
|
|
Header set Cache-Control no-cache
|
|
|
# 静态资产设置成缓存 1 天
|
|
|
<filesMatch ".(css|jpg|jpeg|png|gif|js|ico)$">
|
|
|
Header set Cache-Control "max-age=86400, public"
|
|
|
</filesMatch>
|
Expires(过期时间)
该响应报头能设置当前请求缓存的过期时间。如果设置了 Cache-Control 的 max-age 响应报头,它将会被忽略,因此,在不考虑使用 Cache-Control 而进行本地缓存测试时,才设置它。
为了安全起见,我们假定浏览器不应该缓存任何内容,因此,我们可以把过期时间设置为一个总表示过期的数值。
|
Expires: 0
|
X-Frame-Options
该响应报头用来表明站点是否允许在 iFrame 中展示。
如果恶意站点将我们的网站嵌套在 iFrame 中,那么恶意站点就可以通过运行一些 JavaScript 来执行点击劫持攻击,这些 JavaScript 能够捕获 iFrame 上的鼠标点击事件,然后代表用户与该站点进行交互(不必单击需要单击它们的地方!)。
应该始终将它设置为 deny(拒绝),除非特别需要使用内嵌,在这种情况下,应将其设置为 same-origin(同源)。如果需要在页面中内嵌其他的站点,也可以在此处以白名单的形式列举其他的域名。
还应该注意的是,这个响应报头已经被 CSP 的 frame-ancestors 指令所取代。目前,我仍然建议设置该响应报头来兼容不同的工具,但将来它可能会被逐步淘汰。
|
X-Frame-Options: deny
|
Access-Control-Allow-Origin
通过该响应报头可以告诉浏览器,允许哪些其他站点的前端 JavaScript 代码对页面发出请求。除非需要设置此响应报头,否则通常默认值就是正确的设置。
例如,如果站点 A 使用了一些 JavaScript,该 JavaScript 想要向站点 B 发出请求,那么站点 B 必须使用指定了允许站点 A 发出此请求的报头来提供响应。如果需要设置多个源,请参见MDN 上的详情介绍页面。
这可能有点难以理解,因此,我画了一个图表来说明这个响应报头是如何工作的:
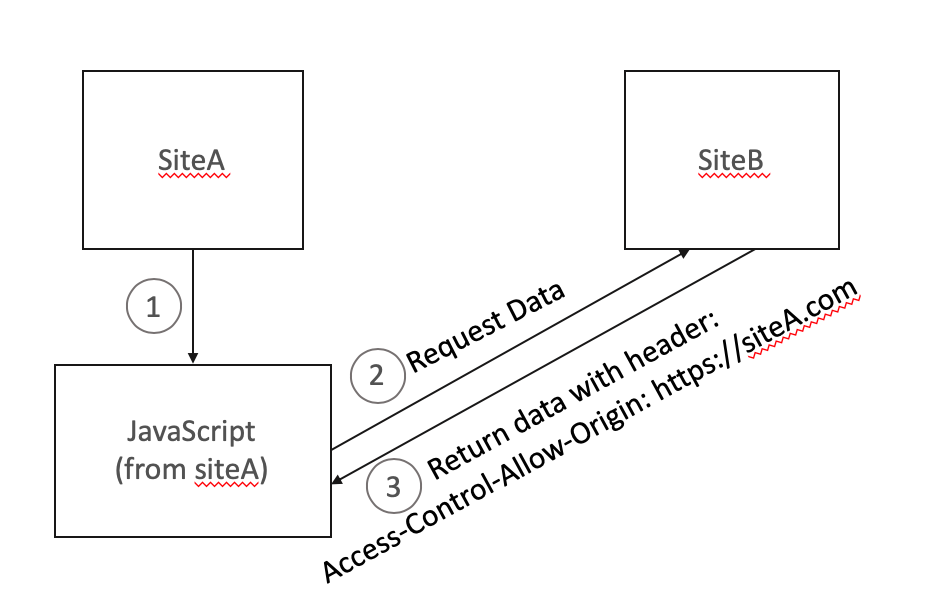
``` Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.one.site.com ```
Set-Cookie
确保 cookie 仅能通过 HTTPS(加密)传送,并且不能通过 JavaScript 访问。如果站点也支持 HTTPS(站点应该支持 HTTPS),那么就只能发送 HTTPS cookie。我们通常需要设置如下标志:
-
Secure
-
HttpOnly
一个定义 Cookie 的示例:
|
Set-Cookie: <cookie-name>=<cookie-value>; Domain=<domain-value>; Secure; HttpOnly
|
请参阅Mozilla 文档中的 cookies 部分以了解更多相关信息。
X-XSS-Protection
该响应报头用来指示浏览器停止执行跨站脚本攻击检测。一般来说,设置它的风险很低,但在投入生产前仍需要进行测试。
|
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
|
Web 服务器的配置示例
通常,最好在服务器配置中添加站点范围内的响应报头。在此,cookie 是一个例外,因为它们通常是在应用程序内定义的。
在将任何响应报头添加到站点之前,我建议首先检查 Observatory 或手动查看响应报头,以查看已经设置了哪些响应报头。有些框架和服务器会自动设置其中一些响应报头,因此,我们只需设置我们需要的或想要变更的响应报头即可。
Apache 配置
.htaccess 中的 Apache 设置示例:
|
<IfModule mod_headers.c>
|
|
|
## CSP
|
|
|
Header set Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' https://i.imgur.com; object-src 'none'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; base-uri 'self'; form-action 'self';
|
|
|
## 通用的安全响应报头
|
|
|
Header set X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
|
|
|
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.one.site.com
|
|
|
Header set X-Frame-Options: deny
|
|
|
Header set X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
|
|
|
Header set Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=3600; includeSubDomains
|
|
|
## 缓存策略
|
|
|
# 默认情况下不使用缓存
|
|
|
Header set Cache-Control no-cache
|
|
|
Header set Expires: 0
|
|
|
# 设置静态资产缓存 1 天
|
|
|
<filesMatch ".(ico|css|js|gif|jpeg|jpg|png|svg|woff|ttf|eot)$">
|
|
|
Header set Cache-Control "max-age=86400, public"
|
|
|
</filesMatch>
|
|
|
</IfModule>
|
Nginx 设置
|
## CSP
|
|
|
add_header Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self'; img-src 'self' https://i.imgur.com; object-src 'none'; script-src 'self'; style-src 'self'; frame-ancestors 'self'; base-uri 'self'; form-action 'self';
|
|
|
## 通用的安全响应报头
|
|
|
add_header X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block;
|
|
|
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin: http://www.one.site.com;
|
|
|
add_header X-Frame-Options: deny;
|
|
|
add_header X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff;
|
|
|
add_header Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=3600; includeSubDomains;
|
|
|
## 缓存策略
|
|
|
** 默认不使用缓存 **
|
|
|
add_header Cache-Control no-cache;
|
|
|
add_header Expires: 0;
|
|
|
** 设置静态资产缓存 1 天 **
|
|
|
location ~* \.(?:ico|css|js|gif|jpe?g|png|svg|woff|ttf|eot)$ {
|
|
|
try_files $uri @rewriteapp;
|
|
|
add_header Cache-Control "max-age=86400, public";
|
|
|
}
|
应用程序级的响应报头设置
如果我们没有访问 Web 服务器的权限,或者需要设置复杂的响应报头,那么我们就可能需要在应用程序内设置这些响应报头了。这通常可以在整个站点的框架中间件中实现,也可以在每次响应的基础上进行一次性的报头设置。
为了简便起见,在示例中,只包含了一个响应报头。所需的全部响应报头都是以相同的方式通过该方法来添加的。
Node 及 express:
添加一个全局挂载路径:
|
app.use(function(req, res, next) {
|
|
|
res.header('X-XSS-Protection', 1; mode=block);
|
|
|
next();
|
|
|
});
|
Java 及 Spring:
我没有太多的 Spring 实践经验,但Baeldung对在 Spring 中如何设置响应报头提供了很好的指导。
PHP:
我对各种 PHP 框架不是很熟悉。查找了能够处理请求的中间件。对于单个响应,它的设置非常简单。
|
header("X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block");
|
Python 及 Django
Django 包含可配置的安全中间件,通过该中间件来处理所有响应报头的设置。首先启用它们。
对于特定页面,可以将响应视为字典。Django 有一个处理缓存的特殊方法,如果试图以这种方式设置缓存响应报头,那么就应该调研后再使用。
|
response = HttpResponse()
|
|
|
response["X-XSS-Protection"] = "1; mode=block"
|
总结
设置响应报头相对来说比较简单快捷。在数据保护、跨站脚本注入和点击劫持方面,站点安全性将会有相当大的提高。
还可以确保我们不会因为依赖此信息的公司安全评级而失去未来的业务交易。这种做法似乎越来越多,我希望在未来几年,它能继续在企业销售中发挥作用。
如果以上有所遗漏,你认为还应该包含其他的安全响应报头,请留言回复。
英文原文:https://nullsweep.com/http-security-headers-a-complete-guide
3、“X-XSS-Protection”头缺失或不安全
响应头缺失,按照扫描要求设置,具体设置请参照前2点。
4、查询中接受的主体参数
这个就是禁用GET请求,但是由于系统内部需要用到,所以只需要对携带数据传递的请求设置为POST方式。

5、启用了不安全的“OPTIONS”HTTP 方法
这个在网上有很多方法可以参考,如果服务器有Nginx,可以直接在Nginx中配置,如果没有可以配置在Tomcat上。我这里是配置在Tomcat上的。
Tomcat的web.xml文件进行修改(修改前请先记得备份哦)
<!-- 限制HTTP请求方法配置,开始 --> <!-- 先注释掉原来的引入文件 --> <!-- <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> --> <!-- 添加新的引入文件 --> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5"> <!-- 过滤掉DELETE、HEAD、PUT等请求方式 --> <security-constraint> <web-resource-collection> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <http-method>PUT</http-method> <http-method>DELETE</http-method> <http-method>HEAD</http-method> <http-method>OPTIONS</http-method> <http-method>TRACE</http-method> <http-method>PATCH</http-method> </web-resource-collection> <auth-constraint></auth-constraint> </security-constraint> <login-config> <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> </login-config> <!--限制HTTP请求方法配置,结束 --> <!-- 限制HTTP请求方法配置,开始 --> <!-- 先注释掉原来的引入文件 --> <!-- <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_1.xsd" version="3.1"> --> <!-- 添加新的引入文件 --> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" version="2.5"> <!-- 过滤掉DELETE、HEAD、PUT等请求方式 --> <security-constraint> <web-resource-collection> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <http-method>PUT</http-method> <http-method>DELETE</http-method> <http-method>HEAD</http-method> <http-method>OPTIONS</http-method> <http-method>TRACE</http-method> <http-method>PATCH</http-method> </web-resource-collection> <auth-constraint></auth-constraint> </security-constraint> <login-config> <auth-method>BASIC</auth-method> </login-config> <!--限制HTTP请求方法配置,结束 -->
6、发现数据库错误模式
这个就是说不允许用户在前台看到有关数据库的报错,就是不能在前台看到下图这样类型的报错。

所以这里就对数据库后台的查询进行拦截,做一个统一的异常处理,使前台看不到这种报错,类似下图这种,具体的样式可以自己设计。

后端需要自定义一个异常处理类,继承HandlerExceptionResolver,重写resolveException()方法,在方法里面对异常信息进行处理即可。我这里直接简单写了几句话,返回给前台页面,加上了时间是便于排查问题。要记得把这个类注入进去。
@Component public class WebExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver { private static transient Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WebExceptionResolver.class); @Override public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) { logger.error("WebExceptionResolver:{}", ex); // if json boolean isJson = false; HandlerMethod method = (HandlerMethod) handler; ResponseBody responseBody = method.getMethodAnnotation(ResponseBody.class); if (responseBody != null) { isJson = true; } // error result Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("errorCode", "500"); map.put("errorMsg", "出错了,请联系管理员"); map.put("errorDate", DateUtil.getToday19()); String errorResult = JSONObject.toJSONString(map); // response ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); if (isJson) { try { response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8"); response.getWriter().print(errorResult); } catch (IOException e) { logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } return mv; } else { mv.addObject("exceptionMsg",map.get("errorMsg")); mv.addObject("date", DateUtil.getToday19()); mv.setViewName("sys/errorPage"); return mv; } } }
6、具有不安全、不正确或缺少 SameSite 属性的 Cookie
基于 Shiro 框架作为 Cookie管理器模式
这个就是要求对Cookie设置SameSite属性,防止跨域和XSS攻击的。因为我这里使用了Shiro框架作为Cookie管理器,要从Shiro的角度处理。
从Shiro的配置文件可以看到,默认使用的是DefaultSessionManager。
<!--Session集群配置 --> <bean id="sessionManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.session.mgt.DefaultWebSessionManager"> <property name="globalSessionTimeout" value="${globalSessionTimeout}" /> <property name="sessionDAO" ref="shiroSessionDAO" /> <property name="sessionValidationScheduler" ref="sessionValidationScheduler" /> <property name="sessionValidationSchedulerEnabled" value="true" /> <property name="sessionIdCookie" ref="wapsession" /> </bean>
因为Shiro版本问题(1.2.3),去查官网文档发现这个版本的cookie是没有SameSite属性的。1.7.1及以上版本才添加了这个属性,所以现在要么就把Shiro升级版本,要么就重写这个类。由于考虑到Shiro与Spring的兼容问题,所以我这里直接重写DefaultWebSessionManager。
看源码我们可以看到,在DefaultWebSessionManager这个类有2个属性,其中有一个就是Cookie,它的构造方法可以去改变cookie的值,从而给cookie加上SameSite属性。

但是仔细观察构造方法,可以看到这个Cookie是一个SimpleCookie,也就是说我们想要给cookie加上一个新的属性,还需要自定义SimpleCookie。
除此之外,还有一点很重要,除了构造方法以外,还要关注cookie是什么时候生成的。这个onStart()方法很重要,是存储session的核心方法。

观察完毕之后,可以动手写我们自己的WebSessionManager和SimpleCookie了。
(1)自定义WebSessionManager:MyDefaultWebSessionManager
public class MyDefaultWebSessionManager extends DefaultWebSessionManager { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MyDefaultWebSessionManager.class); @Override protected void onStart(Session session, SessionContext context) { super.onStart(session, context); if (!WebUtils.isHttp(context)) { log.debug("SessionContext argument is not HTTP compatible or does not have an HTTP request/response pair. No session ID cookie will be set."); } else { HttpServletRequest request = WebUtils.getHttpRequest(context); HttpServletResponse response = WebUtils.getHttpResponse(context); if (this.isSessionIdCookieEnabled()) { Serializable sessionId = session.getId(); //重写父类方法,使用我们自己定义的cookie this.storeSessionId(sessionId, request, response); } else { log.debug("Session ID cookie is disabled. No cookie has been set for new session with id {}", session.getId()); } request.removeAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_ID_SOURCE); request.setAttribute(ShiroHttpServletRequest.REFERENCED_SESSION_IS_NEW, Boolean.TRUE); } } private void storeSessionId(Serializable currentId, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { if (currentId == null) { String msg = "sessionId cannot be null when persisting for subsequent requests."; throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg); } else { Cookie cookie = this.getSessionIdCookie(); //Cookie cookie = new MySimpleCookie(template); String idString = currentId.toString(); cookie.setValue(idString); //这一行决定自定义的cookie中的属性 cookie.saveTo(request, response); log.trace("Set session ID cookie for session with id {}", idString); } } }
(2)自定义SimpleCookie:MySimpleCookie
public class MySimpleCookie extends SimpleCookie { private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MySimpleCookie.class); //自定义的属性sameSite private String sameSite; //重写该方法,添加SameSite属性 @Override public void saveTo(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { String name = this.getName(); String value = this.getValue(); String comment = this.getComment(); String domain = this.getDomain(); String path = this.calculatePath(request); int maxAge = this.getMaxAge(); int version = this.getVersion(); boolean secure = this.isSecure(); boolean httpOnly = this.isHttpOnly(); String s = this.addCookieHeader(name, value, comment, domain, path, maxAge, version, secure, httpOnly); //在原来的基础上添加SameSite属性 String headerValue = appendtSameSite(s, sameSite); response.addHeader("Set-Cookie", headerValue); } private String addCookieHeader(String name, String value, String comment, String domain, String path, int maxAge, int version, boolean secure, boolean httpOnly) { String headerValue = this.buildHeaderValue(name, value, comment, domain, path, maxAge, version, secure, httpOnly); if (log.isDebugEnabled()) { log.debug("Added HttpServletResponse Cookie [{}]", headerValue); } return headerValue; } private String calculatePath(HttpServletRequest request) { String path = StringUtils.clean(this.getPath()); if (!StringUtils.hasText(path)) { path = StringUtils.clean(request.getContextPath()); } if (path == null) { path = "/"; } log.trace("calculated path: {}", path); return path; } //这里只拼接一个字符串,没用StringBuilder,不考虑效率问题 private String appendtSameSite(String s, String sameSite) { if (org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils.isNotBlank(sameSite)) { s += ("; "); s += ("SameSite=") + sameSite; } return s; } public String getSameSite() { return sameSite; } public void setSameSite(String sameSite) { this.sameSite = sameSite; } public MySimpleCookie(String name, String sameSite) { super(name); this.sameSite = sameSite; } }
(3)调整自己的配置文件,使WebSessionManager指向自定义的类。
<!--Session集群配置 --> <bean id="sessionManager" class="com.mytest.common.sys.service.realm.MyDefaultWebSessionManager"> <property name="globalSessionTimeout" value="${globalSessionTimeout}" /> <property name="sessionDAO" ref="shiroSessionDAO" /> <property name="sessionValidationScheduler" ref="sessionValidationScheduler" /> <property name="sessionValidationSchedulerEnabled" value="true" /> <property name="sessionIdCookie" ref="wapsession" /> </bean> <!-- 指定本系统SESSIONID, 默认为: JSESSIONID 问题: 与SERVLET容器名冲突, 如JETTY, TOMCAT 等默认JSESSIONID--> <bean id="wapsession" class="com.mytest.common.sys.service.realm.MySimpleCookie"> <property name="secure" value="${cookieIsSecure}"/> <constructor-arg name="name" value="${cookieName}"/> <constructor-arg name="sameSite" value="${sameSite}"/> </bean>
(4)最后呈现的效果

基于Spring 正常的 一般管理模式


import com.google.common.net.HttpHeaders; import java.io.IOException; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Set; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.apache.commons.collections.CollectionUtils; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseCookie; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping; import org.springframework.web.util.UrlPathHelper; public class XssFilter implements Filter { public XssFilter() { } @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } @Override public void destroy() { } @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest = (HttpServletRequest) request; HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response; //方法体里增加代码: //20220616 处理:“具有不安全、不正确或缺少 SameSite 属性的 Cookie” httpServletResponse.setHeader("Set-Cookie", ((HttpServletRequest) request).getHeader("Set-Cookie")+",SameSite=strict"); ResponseCookie cookie = ResponseCookie.from("myCookie", "myCookieValue") // key & value .httpOnly(true) // 禁止js读取 .secure(false) // 在http下也传输 .domain("localhost")// 域名 .path("/") // path .maxAge(Duration.ofHours(1)) // 1个小时候过期 .sameSite("Lax") // 大多数情况也是不发送第三方 Cookie,但是导航到目标网址的 Get 请求除外 .Samesite 有两个属性值,分别是 Strict 、Lax和None。 .build() ; // 设置Cookie Header httpServletResponse.setHeader(HttpHeaders.SET_COOKIE, cookie.toString());
chain.doFilter(new XssHttpServletRequestWrapper(httpServletRequest), response);
} }
/* * Copyright 2002-2021 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.http; import java.time.Duration; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * An {@code HttpCookie} subclass with the additional attributes allowed in * the "Set-Cookie" response header. To build an instance use the {@link #from} * static method. * * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @author Brian Clozel * @since 5.0 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265">RFC 6265</a> */ public final class ResponseCookie extends HttpCookie { private final Duration maxAge; @Nullable private final String domain; @Nullable private final String path; private final boolean secure; private final boolean httpOnly; @Nullable private final String sameSite; /** * Private constructor. See {@link #from(String, String)}. */ private ResponseCookie(String name, String value, Duration maxAge, @Nullable String domain, @Nullable String path, boolean secure, boolean httpOnly, @Nullable String sameSite) { super(name, value); Assert.notNull(maxAge, "Max age must not be null"); this.maxAge = maxAge; this.domain = domain; this.path = path; this.secure = secure; this.httpOnly = httpOnly; this.sameSite = sameSite; Rfc6265Utils.validateCookieName(name); Rfc6265Utils.validateCookieValue(value); Rfc6265Utils.validateDomain(domain); Rfc6265Utils.validatePath(path); } /** * Return the cookie "Max-Age" attribute in seconds. * <p>A positive value indicates when the cookie expires relative to the * current time. A value of 0 means the cookie should expire immediately. * A negative value means no "Max-Age" attribute in which case the cookie * is removed when the browser is closed. */ public Duration getMaxAge() { return this.maxAge; } /** * Return the cookie "Domain" attribute, or {@code null} if not set. */ @Nullable public String getDomain() { return this.domain; } /** * Return the cookie "Path" attribute, or {@code null} if not set. */ @Nullable public String getPath() { return this.path; } /** * Return {@code true} if the cookie has the "Secure" attribute. */ public boolean isSecure() { return this.secure; } /** * Return {@code true} if the cookie has the "HttpOnly" attribute. * @see <a href="https://www.owasp.org/index.php/HTTPOnly">https://www.owasp.org/index.php/HTTPOnly</a> */ public boolean isHttpOnly() { return this.httpOnly; } /** * Return the cookie "SameSite" attribute, or {@code null} if not set. * <p>This limits the scope of the cookie such that it will only be attached to * same site requests if {@code "Strict"} or cross-site requests if {@code "Lax"}. * @since 5.1 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-rfc6265bis#section-4.1.2.7">RFC6265 bis</a> */ @Nullable public String getSameSite() { return this.sameSite; } @Override public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) { if (this == other) { return true; } if (!(other instanceof ResponseCookie)) { return false; } ResponseCookie otherCookie = (ResponseCookie) other; return (getName().equalsIgnoreCase(otherCookie.getName()) && ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.path, otherCookie.getPath()) && ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.domain, otherCookie.getDomain())); } @Override public int hashCode() { int result = super.hashCode(); result = 31 * result + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.domain); result = 31 * result + ObjectUtils.nullSafeHashCode(this.path); return result; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(getName()).append('=').append(getValue()); if (StringUtils.hasText(getPath())) { sb.append("; Path=").append(getPath()); } if (StringUtils.hasText(this.domain)) { sb.append("; Domain=").append(this.domain); } if (!this.maxAge.isNegative()) { sb.append("; Max-Age=").append(this.maxAge.getSeconds()); sb.append("; Expires="); long millis = this.maxAge.getSeconds() > 0 ? System.currentTimeMillis() + this.maxAge.toMillis() : 0; sb.append(HttpHeaders.formatDate(millis)); } if (this.secure) { sb.append("; Secure"); } if (this.httpOnly) { sb.append("; HttpOnly"); } if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sameSite)) { sb.append("; SameSite=").append(this.sameSite); } return sb.toString(); } /** * Factory method to obtain a builder for a server-defined cookie that starts * with a name-value pair and may also include attributes. * @param name the cookie name * @param value the cookie value * @return a builder to create the cookie with */ public static ResponseCookieBuilder from(final String name, final String value) { return from(name, value, false); } /** * Factory method to obtain a builder for a server-defined cookie. Unlike * {@link #from(String, String)} this option assumes input from a remote * server, which can be handled more leniently, e.g. ignoring a empty domain * name with double quotes. * @param name the cookie name * @param value the cookie value * @return a builder to create the cookie with * @since 5.2.5 */ public static ResponseCookieBuilder fromClientResponse(final String name, final String value) { return from(name, value, true); } private static ResponseCookieBuilder from(final String name, final String value, boolean lenient) { return new ResponseCookieBuilder() { private Duration maxAge = Duration.ofSeconds(-1); @Nullable private String domain; @Nullable private String path; private boolean secure; private boolean httpOnly; @Nullable private String sameSite; @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder maxAge(Duration maxAge) { this.maxAge = maxAge; return this; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder maxAge(long maxAgeSeconds) { this.maxAge = maxAgeSeconds >= 0 ? Duration.ofSeconds(maxAgeSeconds) : Duration.ofSeconds(-1); return this; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder domain(String domain) { this.domain = initDomain(domain); return this; } @Nullable private String initDomain(String domain) { if (lenient && StringUtils.hasLength(domain)) { String str = domain.trim(); if (str.startsWith("\"") && str.endsWith("\"")) { if (str.substring(1, str.length() - 1).trim().isEmpty()) { return null; } } } return domain; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder path(String path) { this.path = path; return this; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder secure(boolean secure) { this.secure = secure; return this; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder httpOnly(boolean httpOnly) { this.httpOnly = httpOnly; return this; } @Override public ResponseCookieBuilder sameSite(@Nullable String sameSite) { this.sameSite = sameSite; return this; } @Override public ResponseCookie build() { return new ResponseCookie(name, value, this.maxAge, this.domain, this.path, this.secure, this.httpOnly, this.sameSite); } }; } /** * A builder for a server-defined HttpCookie with attributes. */ public interface ResponseCookieBuilder { /** * Set the cookie "Max-Age" attribute. * * <p>A positive value indicates when the cookie should expire relative * to the current time. A value of 0 means the cookie should expire * immediately. A negative value results in no "Max-Age" attribute in * which case the cookie is removed when the browser is closed. */ ResponseCookieBuilder maxAge(Duration maxAge); /** * Variant of {@link #maxAge(Duration)} accepting a value in seconds. */ ResponseCookieBuilder maxAge(long maxAgeSeconds); /** * Set the cookie "Path" attribute. */ ResponseCookieBuilder path(String path); /** * Set the cookie "Domain" attribute. */ ResponseCookieBuilder domain(String domain); /** * Add the "Secure" attribute to the cookie. */ ResponseCookieBuilder secure(boolean secure); /** * Add the "HttpOnly" attribute to the cookie. * @see <a href="https://www.owasp.org/index.php/HTTPOnly">https://www.owasp.org/index.php/HTTPOnly</a> */ ResponseCookieBuilder httpOnly(boolean httpOnly); /** * Add the "SameSite" attribute to the cookie. * <p>This limits the scope of the cookie such that it will only be * attached to same site requests if {@code "Strict"} or cross-site * requests if {@code "Lax"}. * @since 5.1 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-httpbis-rfc6265bis#section-4.1.2.7">RFC6265 bis</a> */ ResponseCookieBuilder sameSite(@Nullable String sameSite); /** * Create the HttpCookie. */ ResponseCookie build(); } private static class Rfc6265Utils { private static final String SEPARATOR_CHARS = new String(new char[] { '(', ')', '<', '>', '@', ',', ';', ':', '\\', '"', '/', '[', ']', '?', '=', '{', '}', ' ' }); private static final String DOMAIN_CHARS = "0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ.-"; public static void validateCookieName(String name) { for (int i = 0; i < name.length(); i++) { char c = name.charAt(i); // CTL = <US-ASCII control chars (octets 0 - 31) and DEL (127)> if (c <= 0x1F || c == 0x7F) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( name + ": RFC2616 token cannot have control chars"); } if (SEPARATOR_CHARS.indexOf(c) >= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( name + ": RFC2616 token cannot have separator chars such as '" + c + "'"); } if (c >= 0x80) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( name + ": RFC2616 token can only have US-ASCII: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(c)); } } } public static void validateCookieValue(@Nullable String value) { if (value == null) { return; } int start = 0; int end = value.length(); if (end > 1 && value.charAt(0) == '"' && value.charAt(end - 1) == '"') { start = 1; end--; } for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { char c = value.charAt(i); if (c < 0x21 || c == 0x22 || c == 0x2c || c == 0x3b || c == 0x5c || c == 0x7f) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "RFC2616 cookie value cannot have '" + c + "'"); } if (c >= 0x80) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "RFC2616 cookie value can only have US-ASCII chars: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(c)); } } } public static void validateDomain(@Nullable String domain) { if (!StringUtils.hasLength(domain)) { return; } int char1 = domain.charAt(0); int charN = domain.charAt(domain.length() - 1); if (char1 == '-' || charN == '.' || charN == '-') { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid first/last char in cookie domain: " + domain); } for (int i = 0, c = -1; i < domain.length(); i++) { int p = c; c = domain.charAt(i); if (DOMAIN_CHARS.indexOf(c) == -1 || (p == '.' && (c == '.' || c == '-')) || (p == '-' && c == '.')) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(domain + ": invalid cookie domain char '" + c + "'"); } } } public static void validatePath(@Nullable String path) { if (path == null) { return; } for (int i = 0; i < path.length(); i++) { char c = path.charAt(i); if (c < 0x20 || c > 0x7E || c == ';') { throw new IllegalArgumentException(path + ": Invalid cookie path char '" + c + "'"); } } } } }
/* * Copyright 2002-2021 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.http; import com.sun.xml.internal.messaging.saaj.packaging.mime.internet.ContentDisposition; import java.io.Serializable; import java.net.InetSocketAddress; import java.net.URI; import java.nio.charset.Charset; import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.text.DecimalFormat; import java.text.DecimalFormatSymbols; import java.time.Duration; import java.time.Instant; import java.time.ZoneId; import java.time.ZonedDateTime; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import java.time.format.DateTimeParseException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Base64; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.EnumSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.StringJoiner; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils; import org.springframework.util.LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap; import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap; import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * A data structure representing HTTP request or response headers, mapping String header names * to a list of String values, also offering accessors for common application-level data types. * * <p>In addition to the regular methods defined by {@link Map}, this class offers many common * convenience methods, for example: * <ul> * <li>{@link #getFirst(String)} returns the first value associated with a given header name</li> * <li>{@link #add(String, String)} adds a header value to the list of values for a header name</li> * <li>{@link #set(String, String)} sets the header value to a single string value</li> * </ul> * * <p>Note that {@code HttpHeaders} generally treats header names in a case-insensitive manner. * * @author Arjen Poutsma * @author Sebastien Deleuze * @author Brian Clozel * @author Juergen Hoeller * @author Josh Long * @author Sam Brannen * @since 3.0 */ public class HttpHeaders implements MultiValueMap<String, String>, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8578554704772377436L; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.3.2">Section 5.3.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT = "Accept"; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept-Charset} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.3.3">Section 5.3.3 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT_CHARSET = "Accept-Charset"; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept-Encoding} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.3.4">Section 5.3.4 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT_ENCODING = "Accept-Encoding"; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept-Language} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.3.5">Section 5.3.5 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT_LANGUAGE = "Accept-Language"; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept-Patch} header field name. * @since 5.3.6 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5789#section-3.1">Section 3.1 of RFC 5789</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT_PATCH = "Accept-Patch"; /** * The HTTP {@code Accept-Ranges} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-2.3">Section 5.3.5 of RFC 7233</a> */ public static final String ACCEPT_RANGES = "Accept-Ranges"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Allow-Credentials} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS = "Access-Control-Allow-Credentials"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Allow-Headers} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_HEADERS = "Access-Control-Allow-Headers"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Allow-Methods} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_METHODS = "Access-Control-Allow-Methods"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Allow-Origin} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_ORIGIN = "Access-Control-Allow-Origin"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Expose-Headers} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_EXPOSE_HEADERS = "Access-Control-Expose-Headers"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Max-Age} response header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_MAX_AGE = "Access-Control-Max-Age"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Request-Headers} request header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS = "Access-Control-Request-Headers"; /** * The CORS {@code Access-Control-Request-Method} request header field name. * @see <a href="https://www.w3.org/TR/cors/">CORS W3C recommendation</a> */ public static final String ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD = "Access-Control-Request-Method"; /** * The HTTP {@code Age} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.1">Section 5.1 of RFC 7234</a> */ public static final String AGE = "Age"; /** * The HTTP {@code Allow} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.1">Section 7.4.1 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String ALLOW = "Allow"; /** * The HTTP {@code Authorization} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-4.2">Section 4.2 of RFC 7235</a> */ public static final String AUTHORIZATION = "Authorization"; /** * The HTTP {@code Cache-Control} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2">Section 5.2 of RFC 7234</a> */ public static final String CACHE_CONTROL = "Cache-Control"; /** * The HTTP {@code Connection} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-6.1">Section 6.1 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String CONNECTION = "Connection"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Encoding} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-3.1.2.2">Section 3.1.2.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_ENCODING = "Content-Encoding"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Disposition} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6266">RFC 6266</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_DISPOSITION = "Content-Disposition"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Language} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-3.1.3.2">Section 3.1.3.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_LANGUAGE = "Content-Language"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Length} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-3.3.2">Section 3.3.2 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_LENGTH = "Content-Length"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Location} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-3.1.4.2">Section 3.1.4.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_LOCATION = "Content-Location"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Range} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-4.2">Section 4.2 of RFC 7233</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_RANGE = "Content-Range"; /** * The HTTP {@code Content-Type} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-3.1.1.5">Section 3.1.1.5 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String CONTENT_TYPE = "Content-Type"; /** * The HTTP {@code Cookie} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2109#section-4.3.4">Section 4.3.4 of RFC 2109</a> */ public static final String COOKIE = "Cookie"; /** * The HTTP {@code Date} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.1.2">Section 7.1.1.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String DATE = "Date"; /** * The HTTP {@code ETag} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-2.3">Section 2.3 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String ETAG = "ETag"; /** * The HTTP {@code Expect} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.1.1">Section 5.1.1 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String EXPECT = "Expect"; /** * The HTTP {@code Expires} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.3">Section 5.3 of RFC 7234</a> */ public static final String EXPIRES = "Expires"; /** * The HTTP {@code From} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.5.1">Section 5.5.1 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String FROM = "From"; /** * The HTTP {@code Host} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-5.4">Section 5.4 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String HOST = "Host"; /** * The HTTP {@code If-Match} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-3.1">Section 3.1 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String IF_MATCH = "If-Match"; /** * The HTTP {@code If-Modified-Since} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-3.3">Section 3.3 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String IF_MODIFIED_SINCE = "If-Modified-Since"; /** * The HTTP {@code If-None-Match} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-3.2">Section 3.2 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String IF_NONE_MATCH = "If-None-Match"; /** * The HTTP {@code If-Range} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-3.2">Section 3.2 of RFC 7233</a> */ public static final String IF_RANGE = "If-Range"; /** * The HTTP {@code If-Unmodified-Since} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-3.4">Section 3.4 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE = "If-Unmodified-Since"; /** * The HTTP {@code Last-Modified} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-2.2">Section 2.2 of RFC 7232</a> */ public static final String LAST_MODIFIED = "Last-Modified"; /** * The HTTP {@code Link} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5988">RFC 5988</a> */ public static final String LINK = "Link"; /** * The HTTP {@code Location} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.2">Section 7.1.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String LOCATION = "Location"; /** * The HTTP {@code Max-Forwards} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.1.2">Section 5.1.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String MAX_FORWARDS = "Max-Forwards"; /** * The HTTP {@code Origin} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6454">RFC 6454</a> */ public static final String ORIGIN = "Origin"; /** * The HTTP {@code Pragma} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.4">Section 5.4 of RFC 7234</a> */ public static final String PRAGMA = "Pragma"; /** * The HTTP {@code Proxy-Authenticate} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-4.3">Section 4.3 of RFC 7235</a> */ public static final String PROXY_AUTHENTICATE = "Proxy-Authenticate"; /** * The HTTP {@code Proxy-Authorization} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-4.4">Section 4.4 of RFC 7235</a> */ public static final String PROXY_AUTHORIZATION = "Proxy-Authorization"; /** * The HTTP {@code Range} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7233#section-3.1">Section 3.1 of RFC 7233</a> */ public static final String RANGE = "Range"; /** * The HTTP {@code Referer} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.5.2">Section 5.5.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String REFERER = "Referer"; /** * The HTTP {@code Retry-After} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.3">Section 7.1.3 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String RETRY_AFTER = "Retry-After"; /** * The HTTP {@code Server} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.4.2">Section 7.4.2 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String SERVER = "Server"; /** * The HTTP {@code Set-Cookie} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2109#section-4.2.2">Section 4.2.2 of RFC 2109</a> */ public static final String SET_COOKIE = "Set-Cookie"; /** * The HTTP {@code Set-Cookie2} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2965">RFC 2965</a> */ public static final String SET_COOKIE2 = "Set-Cookie2"; /** * The HTTP {@code TE} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-4.3">Section 4.3 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String TE = "TE"; /** * The HTTP {@code Trailer} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-4.4">Section 4.4 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String TRAILER = "Trailer"; /** * The HTTP {@code Transfer-Encoding} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-3.3.1">Section 3.3.1 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String TRANSFER_ENCODING = "Transfer-Encoding"; /** * The HTTP {@code Upgrade} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-6.7">Section 6.7 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String UPGRADE = "Upgrade"; /** * The HTTP {@code User-Agent} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-5.5.3">Section 5.5.3 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String USER_AGENT = "User-Agent"; /** * The HTTP {@code Vary} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.4">Section 7.1.4 of RFC 7231</a> */ public static final String VARY = "Vary"; /** * The HTTP {@code Via} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7230#section-5.7.1">Section 5.7.1 of RFC 7230</a> */ public static final String VIA = "Via"; /** * The HTTP {@code Warning} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.5">Section 5.5 of RFC 7234</a> */ public static final String WARNING = "Warning"; /** * The HTTP {@code WWW-Authenticate} header field name. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7235#section-4.1">Section 4.1 of RFC 7235</a> */ public static final String WWW_AUTHENTICATE = "WWW-Authenticate"; /** * An empty {@code HttpHeaders} instance (immutable). * @since 5.0 */ // public static final HttpHeaders EMPTY = new ReadOnlyHttpHeaders(new LinkedMultiValueMap<>()); /** * Pattern matching ETag multiple field values in headers such as "If-Match", "If-None-Match". * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7232#section-2.3">Section 2.3 of RFC 7232</a> */ private static final Pattern ETAG_HEADER_VALUE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("\\*|\\s*((W\\/)?(\"[^\"]*\"))\\s*,?"); private static final DecimalFormatSymbols DECIMAL_FORMAT_SYMBOLS = new DecimalFormatSymbols(Locale.ENGLISH); private static final ZoneId GMT = ZoneId.of("GMT"); /** * Date formats with time zone as specified in the HTTP RFC to use for formatting. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.1.1">Section 7.1.1.1 of RFC 7231</a> */ private static final DateTimeFormatter DATE_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss zzz", Locale.US).withZone(GMT); /** * Date formats with time zone as specified in the HTTP RFC to use for parsing. * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7231#section-7.1.1.1">Section 7.1.1.1 of RFC 7231</a> */ private static final DateTimeFormatter[] DATE_PARSERS = new DateTimeFormatter[] { DateTimeFormatter.RFC_1123_DATE_TIME, DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("EEEE, dd-MMM-yy HH:mm:ss zzz", Locale.US), DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("EEE MMM dd HH:mm:ss yyyy", Locale.US).withZone(GMT) }; final MultiValueMap<String, String> headers; /** * Construct a new, empty instance of the {@code HttpHeaders} object. * <p>This is the common constructor, using a case-insensitive map structure. */ public HttpHeaders() { this(CollectionUtils.toMultiValueMap(new LinkedCaseInsensitiveMap<>(8, Locale.ENGLISH))); } /** * Construct a new {@code HttpHeaders} instance backed by an existing map. * <p>This constructor is available as an optimization for adapting to existing * headers map structures, primarily for internal use within the framework. * @param headers the headers map (expected to operate with case-insensitive keys) * @since 5.1 */ public HttpHeaders(MultiValueMap<String, String> headers) { Assert.notNull(headers, "MultiValueMap must not be null"); this.headers = headers; } /** * Get the list of header values for the given header name, if any. * @param headerName the header name * @return the list of header values, or an empty list * @since 5.2 */ public List<String> getOrEmpty(Object headerName) { List<String> values = get(headerName); return (values != null ? values : Collections.emptyList()); } /** * Set the list of acceptable {@linkplain MediaType media types}, * as specified by the {@code Accept} header. */ public void setAccept(List<MediaType> acceptableMediaTypes) { set(ACCEPT, MediaType.toString(acceptableMediaTypes)); } /** * Return the list of acceptable {@linkplain MediaType media types}, * as specified by the {@code Accept} header. * <p>Returns an empty list when the acceptable media types are unspecified. */ /* public List<MediaType> getAccept() { return MediaType.parseMediaTypes(get(ACCEPT)); }*/ /** * Set the acceptable language ranges, as specified by the * {@literal Accept-Language} header. * @since 5.0 */ public void setAcceptLanguage(List<Locale.LanguageRange> languages) { Assert.notNull(languages, "LanguageRange List must not be null"); DecimalFormat decimal = new DecimalFormat("0.0", DECIMAL_FORMAT_SYMBOLS); List<String> values = languages.stream() .map(range -> range.getWeight() == Locale.LanguageRange.MAX_WEIGHT ? range.getRange() : range.getRange() + ";q=" + decimal.format(range.getWeight())) .collect(Collectors.toList()); set(ACCEPT_LANGUAGE, toCommaDelimitedString(values)); } /** * Return the language ranges from the {@literal "Accept-Language"} header. * <p>If you only need sorted, preferred locales only use * {@link #getAcceptLanguageAsLocales()} or if you need to filter based on * a list of supported locales you can pass the returned list to * {@link Locale#filter(List, Collection)}. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value cannot be converted to a language range * @since 5.0 */ public List<Locale.LanguageRange> getAcceptLanguage() { String value = getFirst(ACCEPT_LANGUAGE); return (StringUtils.hasText(value) ? Locale.LanguageRange.parse(value) : Collections.emptyList()); } /** * Variant of {@link #setAcceptLanguage(List)} using {@link Locale}'s. * @since 5.0 */ public void setAcceptLanguageAsLocales(List<Locale> locales) { setAcceptLanguage(locales.stream() .map(locale -> new Locale.LanguageRange(locale.toLanguageTag())) .collect(Collectors.toList())); } /** * A variant of {@link #getAcceptLanguage()} that converts each * {@link java.util.Locale.LanguageRange} to a {@link Locale}. * @return the locales or an empty list * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value cannot be converted to a locale * @since 5.0 */ public List<Locale> getAcceptLanguageAsLocales() { List<Locale.LanguageRange> ranges = getAcceptLanguage(); if (ranges.isEmpty()) { return Collections.emptyList(); } return ranges.stream() .map(range -> Locale.forLanguageTag(range.getRange())) .filter(locale -> StringUtils.hasText(locale.getDisplayName())) .collect(Collectors.toList()); } /** * Set the list of acceptable {@linkplain MediaType media types} for * {@code PATCH} methods, as specified by the {@code Accept-Patch} header. * @since 5.3.6 */ public void setAcceptPatch(List<MediaType> mediaTypes) { set(ACCEPT_PATCH, MediaType.toString(mediaTypes)); } /** * Return the list of acceptable {@linkplain MediaType media types} for * {@code PATCH} methods, as specified by the {@code Accept-Patch} header. * <p>Returns an empty list when the acceptable media types are unspecified. * @since 5.3.6 */ /*public List<MediaType> getAcceptPatch() { return MediaType.parseMediaTypes(get(ACCEPT_PATCH)); }*/ /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Credentials} response header. */ public void setAccessControlAllowCredentials(boolean allowCredentials) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS, Boolean.toString(allowCredentials)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Credentials} response header. */ public boolean getAccessControlAllowCredentials() { return Boolean.parseBoolean(getFirst(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS)); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Headers} response header. */ public void setAccessControlAllowHeaders(List<String> allowedHeaders) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_HEADERS, toCommaDelimitedString(allowedHeaders)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Headers} response header. */ public List<String> getAccessControlAllowHeaders() { return getValuesAsList(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_HEADERS); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Methods} response header. */ public void setAccessControlAllowMethods(List<HttpMethod> allowedMethods) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_METHODS, StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(allowedMethods)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Methods} response header. */ /* public List<HttpMethod> getAccessControlAllowMethods() { List<HttpMethod> result = new ArrayList<>(); String value = getFirst(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_METHODS); if (value != null) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(value, ","); for (String token : tokens) { HttpMethod resolved = HttpMethod.resolve(token); if (resolved != null) { result.add(resolved); } } } return result; }*/ /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Origin} response header. */ public void setAccessControlAllowOrigin(@Nullable String allowedOrigin) { setOrRemove(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_ORIGIN, allowedOrigin); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Allow-Origin} response header. */ @Nullable public String getAccessControlAllowOrigin() { return getFieldValues(ACCESS_CONTROL_ALLOW_ORIGIN); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Expose-Headers} response header. */ public void setAccessControlExposeHeaders(List<String> exposedHeaders) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_EXPOSE_HEADERS, toCommaDelimitedString(exposedHeaders)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Expose-Headers} response header. */ public List<String> getAccessControlExposeHeaders() { return getValuesAsList(ACCESS_CONTROL_EXPOSE_HEADERS); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Max-Age} response header. * @since 5.2 */ public void setAccessControlMaxAge(Duration maxAge) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_MAX_AGE, Long.toString(maxAge.getSeconds())); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Max-Age} response header. */ public void setAccessControlMaxAge(long maxAge) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_MAX_AGE, Long.toString(maxAge)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Max-Age} response header. * <p>Returns -1 when the max age is unknown. */ public long getAccessControlMaxAge() { String value = getFirst(ACCESS_CONTROL_MAX_AGE); return (value != null ? Long.parseLong(value) : -1); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Request-Headers} request header. */ public void setAccessControlRequestHeaders(List<String> requestHeaders) { set(ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS, toCommaDelimitedString(requestHeaders)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Request-Headers} request header. */ public List<String> getAccessControlRequestHeaders() { return getValuesAsList(ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_HEADERS); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Access-Control-Request-Method} request header. */ public void setAccessControlRequestMethod(@Nullable HttpMethod requestMethod) { setOrRemove(ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD, (requestMethod != null ? requestMethod.name() : null)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Access-Control-Request-Method} request header. */ /* @Nullable public HttpMethod getAccessControlRequestMethod() { return HttpMethod.resolve(getFirst(ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD)); }*/ /** * Set the list of acceptable {@linkplain Charset charsets}, * as specified by the {@code Accept-Charset} header. */ public void setAcceptCharset(List<Charset> acceptableCharsets) { StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(", "); for (Charset charset : acceptableCharsets) { joiner.add(charset.name().toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH)); } set(ACCEPT_CHARSET, joiner.toString()); } /** * Return the list of acceptable {@linkplain Charset charsets}, * as specified by the {@code Accept-Charset} header. */ public List<Charset> getAcceptCharset() { String value = getFirst(ACCEPT_CHARSET); if (value != null) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(value, ","); List<Charset> result = new ArrayList<>(tokens.length); for (String token : tokens) { int paramIdx = token.indexOf(';'); String charsetName; if (paramIdx == -1) { charsetName = token; } else { charsetName = token.substring(0, paramIdx); } if (!charsetName.equals("*")) { result.add(Charset.forName(charsetName)); } } return result; } else { return Collections.emptyList(); } } /** * Set the set of allowed {@link HttpMethod HTTP methods}, * as specified by the {@code Allow} header. */ public void setAllow(Set<HttpMethod> allowedMethods) { set(ALLOW, StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(allowedMethods)); } /** * Return the set of allowed {@link HttpMethod HTTP methods}, * as specified by the {@code Allow} header. * <p>Returns an empty set when the allowed methods are unspecified. */ /*public Set<HttpMethod> getAllow() { String value = getFirst(ALLOW); if (StringUtils.hasLength(value)) { String[] tokens = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(value, ","); List<HttpMethod> result = new ArrayList<>(tokens.length); for (String token : tokens) { HttpMethod resolved = HttpMethod.resolve(token); if (resolved != null) { result.add(resolved); } } return EnumSet.copyOf(result); } else { return EnumSet.noneOf(HttpMethod.class); } }*/ /** * Set the value of the {@linkplain #AUTHORIZATION Authorization} header to * Basic Authentication based on the given username and password. * <p>Note that this method only supports characters in the * {@link StandardCharsets#ISO_8859_1 ISO-8859-1} character set. * @param username the username * @param password the password * @throws IllegalArgumentException if either {@code user} or * {@code password} contain characters that cannot be encoded to ISO-8859-1 * @since 5.1 * @see #setBasicAuth(String) * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see #encodeBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7617">RFC 7617</a> */ public void setBasicAuth(String username, String password) { setBasicAuth(username, password, null); } /** * Set the value of the {@linkplain #AUTHORIZATION Authorization} header to * Basic Authentication based on the given username and password. * @param username the username * @param password the password * @param charset the charset to use to convert the credentials into an octet * sequence. Defaults to {@linkplain StandardCharsets#ISO_8859_1 ISO-8859-1}. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code username} or {@code password} * contains characters that cannot be encoded to the given charset * @since 5.1 * @see #setBasicAuth(String) * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String) * @see #encodeBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7617">RFC 7617</a> */ public void setBasicAuth(String username, String password, @Nullable Charset charset) { setBasicAuth(encodeBasicAuth(username, password, charset)); } /** * Set the value of the {@linkplain #AUTHORIZATION Authorization} header to * Basic Authentication based on the given {@linkplain #encodeBasicAuth * encoded credentials}. * <p>Favor this method over {@link #setBasicAuth(String, String)} and * {@link #setBasicAuth(String, String, Charset)} if you wish to cache the * encoded credentials. * @param encodedCredentials the encoded credentials * @throws IllegalArgumentException if supplied credentials string is * {@code null} or blank * @since 5.2 * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String) * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see #encodeBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7617">RFC 7617</a> */ public void setBasicAuth(String encodedCredentials) { Assert.hasText(encodedCredentials, "'encodedCredentials' must not be null or blank"); set(AUTHORIZATION, "Basic " + encodedCredentials); } /** * Set the value of the {@linkplain #AUTHORIZATION Authorization} header to * the given Bearer token. * @param token the Base64 encoded token * @since 5.1 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6750">RFC 6750</a> */ public void setBearerAuth(String token) { set(AUTHORIZATION, "Bearer " + token); } /** * Set a configured {@link CacheControl} instance as the * new value of the {@code Cache-Control} header. * @since 5.0.5 */ /*public void setCacheControl(CacheControl cacheControl) { setOrRemove(CACHE_CONTROL, cacheControl.getHeaderValue()); }*/ /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Cache-Control} header. */ public void setCacheControl(@Nullable String cacheControl) { setOrRemove(CACHE_CONTROL, cacheControl); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Cache-Control} header. */ @Nullable public String getCacheControl() { return getFieldValues(CACHE_CONTROL); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Connection} header. */ public void setConnection(String connection) { set(CONNECTION, connection); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Connection} header. */ public void setConnection(List<String> connection) { set(CONNECTION, toCommaDelimitedString(connection)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Connection} header. */ public List<String> getConnection() { return getValuesAsList(CONNECTION); } /** * Set the {@code Content-Disposition} header when creating a * {@code "multipart/form-data"} request. * <p>Applications typically would not set this header directly but * rather prepare a {@code MultiValueMap<String, Object>}, containing an * Object or a {@link org.springframework.core.io.Resource} for each part, * and then pass that to the {@code RestTemplate} or {@code WebClient}. * @param name the control name * @param filename the filename (may be {@code null}) * @see #getContentDisposition() */ /* public void setContentDispositionFormData(String name, @Nullable String filename) { Assert.notNull(name, "Name must not be null"); ContentDisposition.Builder disposition = ContentDisposition.formData().name(name); if (StringUtils.hasText(filename)) { disposition.filename(filename); } setContentDisposition(disposition.build()); }*/ /** * Set the {@literal Content-Disposition} header. * <p>This could be used on a response to indicate if the content is * expected to be displayed inline in the browser or as an attachment to be * saved locally. * <p>It can also be used for a {@code "multipart/form-data"} request. * For more details see notes on {@link #set ContentDispositionFormData}. * @since 5.0 * @see #get ContentDisposition() */ public void setContentDisposition(ContentDisposition contentDisposition) { set(CONTENT_DISPOSITION, contentDisposition.toString()); } /** * Return a parsed representation of the {@literal Content-Disposition} header. * @since 5.0 * @see #setContentDisposition(C ontentDisposition) */ /* public ContentDisposition getContentDisposition() { String contentDisposition = getFirst(CONTENT_DISPOSITION); if (StringUtils.hasText(contentDisposition)) { return ContentDisposition.parse(contentDisposition); } return ContentDisposition.empty(); }*/ /** * Set the {@link Locale} of the content language, * as specified by the {@literal Content-Language} header. * <p>Use {@code put(CONTENT_LANGUAGE, list)} if you need * to set multiple content languages.</p> * @since 5.0 */ public void setContentLanguage(@Nullable Locale locale) { setOrRemove(CONTENT_LANGUAGE, (locale != null ? locale.toLanguageTag() : null)); } /** * Get the first {@link Locale} of the content languages, as specified by the * {@code Content-Language} header. * <p>Use {@link #getValuesAsList(String)} if you need to get multiple content * languages. * @return the first {@code Locale} of the content languages, or {@code null} * if unknown * @since 5.0 */ @Nullable public Locale getContentLanguage() { return getValuesAsList(CONTENT_LANGUAGE) .stream() .findFirst() .map(Locale::forLanguageTag) .orElse(null); } /** * Set the length of the body in bytes, as specified by the * {@code Content-Length} header. */ public void setContentLength(long contentLength) { set(CONTENT_LENGTH, Long.toString(contentLength)); } /** * Return the length of the body in bytes, as specified by the * {@code Content-Length} header. * <p>Returns -1 when the content-length is unknown. */ public long getContentLength() { String value = getFirst(CONTENT_LENGTH); return (value != null ? Long.parseLong(value) : -1); } /** * Set the {@linkplain MediaType media type} of the body, * as specified by the {@code Content-Type} header. */ public void setContentType(@Nullable MediaType mediaType) { if (mediaType != null) { Assert.isTrue(!mediaType.isWildcardType(), "Content-Type cannot contain wildcard type '*'"); Assert.isTrue(!mediaType.isWildcardSubtype(), "Content-Type cannot contain wildcard subtype '*'"); set(CONTENT_TYPE, mediaType.toString()); } else { remove(CONTENT_TYPE); } } /** * Return the {@linkplain MediaType media type} of the body, as specified * by the {@code Content-Type} header. * <p>Returns {@code null} when the content-type is unknown. */ @Nullable public MediaType getContentType() { String value = getFirst(CONTENT_TYPE); return (StringUtils.hasLength(value) ? MediaType.parseMediaType(value) : null); } /** * Set the date and time at which the message was created, as specified * by the {@code Date} header. * @since 5.2 */ public void setDate(ZonedDateTime date) { setZonedDateTime(DATE, date); } /** * Set the date and time at which the message was created, as specified * by the {@code Date} header. * @since 5.2 */ public void setDate(Instant date) { setInstant(DATE, date); } /** * Set the date and time at which the message was created, as specified * by the {@code Date} header. * <p>The date should be specified as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. */ public void setDate(long date) { setDate(DATE, date); } /** * Return the date and time at which the message was created, as specified * by the {@code Date} header. * <p>The date is returned as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. Returns -1 when the date is unknown. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if the value cannot be converted to a date */ public long getDate() { return getFirstDate(DATE); } /** * Set the (new) entity tag of the body, as specified by the {@code ETag} header. */ public void setETag(@Nullable String etag) { if (etag != null) { Assert.isTrue(etag.startsWith("\"") || etag.startsWith("W/"), "Invalid ETag: does not start with W/ or \""); Assert.isTrue(etag.endsWith("\""), "Invalid ETag: does not end with \""); set(ETAG, etag); } else { remove(ETAG); } } /** * Return the entity tag of the body, as specified by the {@code ETag} header. */ @Nullable public String getETag() { return getFirst(ETAG); } /** * Set the duration after which the message is no longer valid, * as specified by the {@code Expires} header. * @since 5.0.5 */ public void setExpires(ZonedDateTime expires) { setZonedDateTime(EXPIRES, expires); } /** * Set the date and time at which the message is no longer valid, * as specified by the {@code Expires} header. * @since 5.2 */ public void setExpires(Instant expires) { setInstant(EXPIRES, expires); } /** * Set the date and time at which the message is no longer valid, * as specified by the {@code Expires} header. * <p>The date should be specified as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. */ public void setExpires(long expires) { setDate(EXPIRES, expires); } /** * Return the date and time at which the message is no longer valid, * as specified by the {@code Expires} header. * <p>The date is returned as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. Returns -1 when the date is unknown. * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String) */ public long getExpires() { return getFirstDate(EXPIRES, false); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Host} header. * <p>If the given {@linkplain InetSocketAddress#getPort() port} is {@code 0}, * the host header will only contain the * {@linkplain InetSocketAddress#getHostString() host name}. * @since 5.0 */ public void setHost(@Nullable InetSocketAddress host) { if (host != null) { String value = host.getHostString(); int port = host.getPort(); if (port != 0) { value = value + ":" + port; } set(HOST, value); } else { remove(HOST, null); } } /** * Return the value of the {@code Host} header, if available. * <p>If the header value does not contain a port, the * {@linkplain InetSocketAddress#getPort() port} in the returned address will * be {@code 0}. * @since 5.0 */ @Nullable public InetSocketAddress getHost() { String value = getFirst(HOST); if (value == null) { return null; } String host = null; int port = 0; int separator = (value.startsWith("[") ? value.indexOf(':', value.indexOf(']')) : value.lastIndexOf(':')); if (separator != -1) { host = value.substring(0, separator); String portString = value.substring(separator + 1); try { port = Integer.parseInt(portString); } catch (NumberFormatException ex) { // ignore } } if (host == null) { host = value; } return InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(host, port); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code If-Match} header. * @since 4.3 */ public void setIfMatch(String ifMatch) { set(IF_MATCH, ifMatch); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code If-Match} header. * @since 4.3 */ public void setIfMatch(List<String> ifMatchList) { set(IF_MATCH, toCommaDelimitedString(ifMatchList)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code If-Match} header. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if parsing fails * @since 4.3 */ public List<String> getIfMatch() { return getETagValuesAsList(IF_MATCH); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setIfModifiedSince(ZonedDateTime ifModifiedSince) { setZonedDateTime(IF_MODIFIED_SINCE, ifModifiedSince.withZoneSameInstant(GMT)); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setIfModifiedSince(Instant ifModifiedSince) { setInstant(IF_MODIFIED_SINCE, ifModifiedSince); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code If-Modified-Since} header. * <p>The date should be specified as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. */ public void setIfModifiedSince(long ifModifiedSince) { setDate(IF_MODIFIED_SINCE, ifModifiedSince); } /** * Return the value of the {@code If-Modified-Since} header. * <p>The date is returned as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. Returns -1 when the date is unknown. * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String) */ public long getIfModifiedSince() { return getFirstDate(IF_MODIFIED_SINCE, false); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code If-None-Match} header. */ public void setIfNoneMatch(String ifNoneMatch) { set(IF_NONE_MATCH, ifNoneMatch); } /** * Set the (new) values of the {@code If-None-Match} header. */ public void setIfNoneMatch(List<String> ifNoneMatchList) { set(IF_NONE_MATCH, toCommaDelimitedString(ifNoneMatchList)); } /** * Return the value of the {@code If-None-Match} header. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if parsing fails */ public List<String> getIfNoneMatch() { return getETagValuesAsList(IF_NONE_MATCH); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setIfUnmodifiedSince(ZonedDateTime ifUnmodifiedSince) { setZonedDateTime(IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE, ifUnmodifiedSince.withZoneSameInstant(GMT)); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setIfUnmodifiedSince(Instant ifUnmodifiedSince) { setInstant(IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE, ifUnmodifiedSince); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code If-Unmodified-Since} header. * <p>The date should be specified as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. * @since 4.3 */ public void setIfUnmodifiedSince(long ifUnmodifiedSince) { setDate(IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE, ifUnmodifiedSince); } /** * Return the value of the {@code If-Unmodified-Since} header. * <p>The date is returned as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. Returns -1 when the date is unknown. * @since 4.3 * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String) */ public long getIfUnmodifiedSince() { return getFirstDate(IF_UNMODIFIED_SINCE, false); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setLastModified(ZonedDateTime lastModified) { setZonedDateTime(LAST_MODIFIED, lastModified.withZoneSameInstant(GMT)); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setLastModified(Instant lastModified) { setInstant(LAST_MODIFIED, lastModified); } /** * Set the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * <p>The date should be specified as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. */ public void setLastModified(long lastModified) { setDate(LAST_MODIFIED, lastModified); } /** * Return the time the resource was last changed, as specified by the * {@code Last-Modified} header. * <p>The date is returned as the number of milliseconds since * January 1, 1970 GMT. Returns -1 when the date is unknown. * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String) */ public long getLastModified() { return getFirstDate(LAST_MODIFIED, false); } /** * Set the (new) location of a resource, * as specified by the {@code Location} header. */ public void setLocation(@Nullable URI location) { setOrRemove(LOCATION, (location != null ? location.toASCIIString() : null)); } /** * Return the (new) location of a resource * as specified by the {@code Location} header. * <p>Returns {@code null} when the location is unknown. */ @Nullable public URI getLocation() { String value = getFirst(LOCATION); return (value != null ? URI.create(value) : null); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Origin} header. */ public void setOrigin(@Nullable String origin) { setOrRemove(ORIGIN, origin); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Origin} header. */ @Nullable public String getOrigin() { return getFirst(ORIGIN); } /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Pragma} header. */ public void setPragma(@Nullable String pragma) { setOrRemove(PRAGMA, pragma); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Pragma} header. */ @Nullable public String getPragma() { return getFirst(PRAGMA); } /** * Sets the (new) value of the {@code Range} header. */ /*public void setRange(List<HttpRange> ranges) { String value = HttpRange.toString(ranges); set(RANGE, value); }*/ /** * Return the value of the {@code Range} header. * <p>Returns an empty list when the range is unknown. */ /* public List<HttpRange> getRange() { String value = getFirst(RANGE); return HttpRange.parseRanges(value); }*/ /** * Set the (new) value of the {@code Upgrade} header. */ public void setUpgrade(@Nullable String upgrade) { setOrRemove(UPGRADE, upgrade); } /** * Return the value of the {@code Upgrade} header. */ @Nullable public String getUpgrade() { return getFirst(UPGRADE); } /** * Set the request header names (e.g. "Accept-Language") for which the * response is subject to content negotiation and variances based on the * value of those request headers. * @param requestHeaders the request header names * @since 4.3 */ public void setVary(List<String> requestHeaders) { set(VARY, toCommaDelimitedString(requestHeaders)); } /** * Return the request header names subject to content negotiation. * @since 4.3 */ public List<String> getVary() { return getValuesAsList(VARY); } /** * Set the given date under the given header name after formatting it as a string * using the RFC-1123 date-time formatter. The equivalent of * {@link #set(String, String)} but for date headers. * @since 5.0 */ public void setZonedDateTime(String headerName, ZonedDateTime date) { set(headerName, DATE_FORMATTER.format(date)); } /** * Set the given date under the given header name after formatting it as a string * using the RFC-1123 date-time formatter. The equivalent of * {@link #set(String, String)} but for date headers. * @since 5.1.4 */ public void setInstant(String headerName, Instant date) { setZonedDateTime(headerName, ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(date, GMT)); } /** * Set the given date under the given header name after formatting it as a string * using the RFC-1123 date-time formatter. The equivalent of * {@link #set(String, String)} but for date headers. * @since 3.2.4 * @see #setZonedDateTime(String, ZonedDateTime) */ public void setDate(String headerName, long date) { setInstant(headerName, Instant.ofEpochMilli(date)); } /** * Parse the first header value for the given header name as a date, * return -1 if there is no value, or raise {@link IllegalArgumentException} * if the value cannot be parsed as a date. * @param headerName the header name * @return the parsed date header, or -1 if none * @since 3.2.4 * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String) */ public long getFirstDate(String headerName) { return getFirstDate(headerName, true); } /** * Parse the first header value for the given header name as a date, * return -1 if there is no value or also in case of an invalid value * (if {@code rejectInvalid=false}), or raise {@link IllegalArgumentException} * if the value cannot be parsed as a date. * @param headerName the header name * @param rejectInvalid whether to reject invalid values with an * {@link IllegalArgumentException} ({@code true}) or rather return -1 * in that case ({@code false}) * @return the parsed date header, or -1 if none (or invalid) * @see #getFirstZonedDateTime(String, boolean) */ private long getFirstDate(String headerName, boolean rejectInvalid) { ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = getFirstZonedDateTime(headerName, rejectInvalid); return (zonedDateTime != null ? zonedDateTime.toInstant().toEpochMilli() : -1); } /** * Parse the first header value for the given header name as a date, * return {@code null} if there is no value, or raise {@link IllegalArgumentException} * if the value cannot be parsed as a date. * @param headerName the header name * @return the parsed date header, or {@code null} if none * @since 5.0 */ @Nullable public ZonedDateTime getFirstZonedDateTime(String headerName) { return getFirstZonedDateTime(headerName, true); } /** * Parse the first header value for the given header name as a date, * return {@code null} if there is no value or also in case of an invalid value * (if {@code rejectInvalid=false}), or raise {@link IllegalArgumentException} * if the value cannot be parsed as a date. * @param headerName the header name * @param rejectInvalid whether to reject invalid values with an * {@link IllegalArgumentException} ({@code true}) or rather return {@code null} * in that case ({@code false}) * @return the parsed date header, or {@code null} if none (or invalid) */ @Nullable private ZonedDateTime getFirstZonedDateTime(String headerName, boolean rejectInvalid) { String headerValue = getFirst(headerName); if (headerValue == null) { // No header value sent at all return null; } if (headerValue.length() >= 3) { // Short "0" or "-1" like values are never valid HTTP date headers... // Let's only bother with DateTimeFormatter parsing for long enough values. // See https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12626699/if-modified-since-http-header-passed-by-ie9-includes-length int parametersIndex = headerValue.indexOf(';'); if (parametersIndex != -1) { headerValue = headerValue.substring(0, parametersIndex); } for (DateTimeFormatter dateFormatter : DATE_PARSERS) { try { return ZonedDateTime.parse(headerValue, dateFormatter); } catch (DateTimeParseException ex) { // ignore } } } if (rejectInvalid) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot parse date value \"" + headerValue + "\" for \"" + headerName + "\" header"); } return null; } /** * Return all values of a given header name, * even if this header is set multiple times. * @param headerName the header name * @return all associated values * @since 4.3 */ public List<String> getValuesAsList(String headerName) { List<String> values = get(headerName); if (values != null) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); for (String value : values) { if (value != null) { Collections.addAll(result, StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(value, ",")); } } return result; } return Collections.emptyList(); } /** * Remove the well-known {@code "Content-*"} HTTP headers. * <p>Such headers should be cleared from the response if the intended * body can't be written due to errors. * @since 5.2.3 */ public void clearContentHeaders() { this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_DISPOSITION); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_ENCODING); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LANGUAGE); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LENGTH); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_LOCATION); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE); this.headers.remove(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_TYPE); } /** * Retrieve a combined result from the field values of the ETag header. * @param headerName the header name * @return the combined result * @throws IllegalArgumentException if parsing fails * @since 4.3 */ protected List<String> getETagValuesAsList(String headerName) { List<String> values = get(headerName); if (values != null) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); for (String value : values) { if (value != null) { Matcher matcher = ETAG_HEADER_VALUE_PATTERN.matcher(value); while (matcher.find()) { if ("*".equals(matcher.group())) { result.add(matcher.group()); } else { result.add(matcher.group(1)); } } if (result.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Could not parse header '" + headerName + "' with value '" + value + "'"); } } } return result; } return Collections.emptyList(); } /** * Retrieve a combined result from the field values of multi-valued headers. * @param headerName the header name * @return the combined result * @since 4.3 */ @Nullable protected String getFieldValues(String headerName) { List<String> headerValues = get(headerName); return (headerValues != null ? toCommaDelimitedString(headerValues) : null); } /** * Turn the given list of header values into a comma-delimited result. * @param headerValues the list of header values * @return a combined result with comma delimitation */ protected String toCommaDelimitedString(List<String> headerValues) { StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(", "); for (String val : headerValues) { if (val != null) { joiner.add(val); } } return joiner.toString(); } /** * Set the given header value, or remove the header if {@code null}. * @param headerName the header name * @param headerValue the header value, or {@code null} for none */ private void setOrRemove(String headerName, @Nullable String headerValue) { if (headerValue != null) { set(headerName, headerValue); } else { remove(headerName); } } // MultiValueMap implementation /** * Return the first header value for the given header name, if any. * @param headerName the header name * @return the first header value, or {@code null} if none */ @Override @Nullable public String getFirst(String headerName) { return this.headers.getFirst(headerName); } /** * Add the given, single header value under the given name. * @param headerName the header name * @param headerValue the header value * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if adding headers is not supported * @see #put(String, List) * @see #set(String, String) */ @Override public void add(String headerName, @Nullable String headerValue) { this.headers.add(headerName, headerValue); } /* @Override public void addAll(String key, List<? extends String> values) { this.headers.addAll(key, values); } @Override public void addAll(MultiValueMap<String, String> values) { this.headers.addAll(values); }*/ /** * Set the given, single header value under the given name. * @param headerName the header name * @param headerValue the header value * @throws UnsupportedOperationException if adding headers is not supported * @see #put(String, List) * @see #add(String, String) */ @Override public void set(String headerName, @Nullable String headerValue) { this.headers.set(headerName, headerValue); } @Override public void setAll(Map<String, String> values) { this.headers.setAll(values); } @Override public Map<String, String> toSingleValueMap() { return this.headers.toSingleValueMap(); } // Map implementation @Override public int size() { return this.headers.size(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return this.headers.isEmpty(); } @Override public boolean containsKey(Object key) { return this.headers.containsKey(key); } @Override public boolean containsValue(Object value) { return this.headers.containsValue(value); } @Override @Nullable public List<String> get(Object key) { return this.headers.get(key); } @Override public List<String> put(String key, List<String> value) { return this.headers.put(key, value); } @Override public List<String> remove(Object key) { return this.headers.remove(key); } @Override public void putAll(Map<? extends String, ? extends List<String>> map) { this.headers.putAll(map); } @Override public void clear() { this.headers.clear(); } @Override public Set<String> keySet() { return this.headers.keySet(); } @Override public Collection<List<String>> values() { return this.headers.values(); } @Override public Set<Entry<String, List<String>>> entrySet() { return this.headers.entrySet(); } @Override public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) { if (this == other) { return true; } if (!(other instanceof HttpHeaders)) { return false; } return unwrap(this).equals(unwrap((HttpHeaders) other)); } private static MultiValueMap<String, String> unwrap(HttpHeaders headers) { while (headers.headers instanceof HttpHeaders) { headers = (HttpHeaders) headers.headers; } return headers.headers; } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.headers.hashCode(); } @Override public String toString() { return formatHeaders(this.headers); } /** * Apply a read-only {@code HttpHeaders} wrapper around the given headers, if necessary. * <p>Also caches the parsed representations of the "Accept" and "Content-Type" headers. * @param headers the headers to expose * @return a read-only variant of the headers, or the original headers as-is * (in case it happens to be a read-only {@code HttpHeaders} instance already) * @since 5.3 */ /* public static HttpHeaders readOnlyHttpHeaders(MultiValueMap<String, String> headers) { return (headers instanceof HttpHeaders ? readOnlyHttpHeaders((HttpHeaders) headers) : new ReadOnlyHttpHeaders(headers)); }*/ /** * Apply a read-only {@code HttpHeaders} wrapper around the given headers, if necessary. * <p>Also caches the parsed representations of the "Accept" and "Content-Type" headers. * @param headers the headers to expose * @return a read-only variant of the headers, or the original headers as-is */ /* public static HttpHeaders readOnlyHttpHeaders(HttpHeaders headers) { Assert.notNull(headers, "HttpHeaders must not be null"); return (headers instanceof ReadOnlyHttpHeaders ? headers : new ReadOnlyHttpHeaders(headers.headers)); }*/ /** * Remove any read-only wrapper that may have been previously applied around * the given headers via {@link #readOnlyHttpHeaders(HttpHeaders)}. * @param headers the headers to expose * @return a writable variant of the headers, or the original headers as-is * @since 5.1.1 */ /*public static HttpHeaders writableHttpHeaders(HttpHeaders headers) { Assert.notNull(headers, "HttpHeaders must not be null"); if (headers == EMPTY) { return new HttpHeaders(); } return (headers instanceof ReadOnlyHttpHeaders ? new HttpHeaders(headers.headers) : headers); }*/ /** * Helps to format HTTP header values, as HTTP header values themselves can * contain comma-separated values, can become confusing with regular * {@link Map} formatting that also uses commas between entries. * @param headers the headers to format * @return the headers to a String * @since 5.1.4 */ public static String formatHeaders(MultiValueMap<String, String> headers) { return headers.entrySet().stream() .map(entry -> { List<String> values = entry.getValue(); return entry.getKey() + ":" + (values.size() == 1 ? "\"" + values.get(0) + "\"" : values.stream().map(s -> "\"" + s + "\"").collect(Collectors.joining(", "))); }) .collect(Collectors.joining(", ", "[", "]")); } /** * Encode the given username and password into Basic Authentication credentials. * <p>The encoded credentials returned by this method can be supplied to * {@link #setBasicAuth(String)} to set the Basic Authentication header. * @param username the username * @param password the password * @param charset the charset to use to convert the credentials into an octet * sequence. Defaults to {@linkplain StandardCharsets#ISO_8859_1 ISO-8859-1}. * @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code username} or {@code password} * contains characters that cannot be encoded to the given charset * @since 5.2 * @see #setBasicAuth(String) * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String) * @see #setBasicAuth(String, String, Charset) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7617">RFC 7617</a> */ public static String encodeBasicAuth(String username, String password, @Nullable Charset charset) { Assert.notNull(username, "Username must not be null"); Assert.doesNotContain(username, ":", "Username must not contain a colon"); Assert.notNull(password, "Password must not be null"); if (charset == null) { charset = StandardCharsets.ISO_8859_1; } CharsetEncoder encoder = charset.newEncoder(); if (!encoder.canEncode(username) || !encoder.canEncode(password)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Username or password contains characters that cannot be encoded to " + charset.displayName()); } String credentialsString = username + ":" + password; byte[] encodedBytes = Base64.getEncoder().encode(credentialsString.getBytes(charset)); return new String(encodedBytes, charset); } // Package-private: used in ResponseCookie static String formatDate(long date) { Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochMilli(date); ZonedDateTime time = ZonedDateTime.ofInstant(instant, GMT); return DATE_FORMATTER.format(time); } }
/* * Copyright 2002-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.http; import com.sun.istack.internal.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.Assert; /** * Represents an HTTP cookie as a name-value pair consistent with the content of * the "Cookie" request header. The {@link ResponseCookie} sub-class has the * additional attributes expected in the "Set-Cookie" response header. * * @author Rossen Stoyanchev * @since 5.0 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6265">RFC 6265</a> */ public class HttpCookie { private final String name; private final String value; public HttpCookie(String name, @com.sun.istack.internal.Nullable String value) { Assert.hasLength(name, "'name' is required and must not be empty."); this.name = name; this.value = (value != null ? value : ""); } /** * Return the cookie name. */ public String getName() { return this.name; } /** * Return the cookie value or an empty string (never {@code null}). */ public String getValue() { return this.value; } @Override public int hashCode() { return this.name.hashCode(); } @Override public boolean equals(@Nullable Object other) { if (this == other) { return true; } if (!(other instanceof HttpCookie)) { return false; } HttpCookie otherCookie = (HttpCookie) other; return (this.name.equalsIgnoreCase(otherCookie.getName())); } @Override public String toString() { return this.name + '=' + this.value; } }
/* * Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.http; import java.time.Duration; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.springframework.lang.Nullable; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * A builder for creating "Cache-Control" HTTP response headers. * * <p>Adding Cache-Control directives to HTTP responses can significantly improve the client * experience when interacting with a web application. This builder creates opinionated * "Cache-Control" headers with response directives only, with several use cases in mind. * * <ul> * <li>Caching HTTP responses with {@code CacheControl cc = CacheControl.maxAge(1, TimeUnit.HOURS)} * will result in {@code Cache-Control: "max-age=3600"}</li> * <li>Preventing cache with {@code CacheControl cc = CacheControl.noStore()} * will result in {@code Cache-Control: "no-store"}</li> * <li>Advanced cases like {@code CacheControl cc = CacheControl.maxAge(1, TimeUnit.HOURS).noTransform().cachePublic()} * will result in {@code Cache-Control: "max-age=3600, no-transform, public"}</li> * </ul> * * <p>Note that to be efficient, Cache-Control headers should be written along HTTP validators * such as "Last-Modified" or "ETag" headers. * * @author Brian Clozel * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 4.2 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2">rfc7234 section 5.2.2</a> * @see <a href="https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/optimizing-content-efficiency/http-caching"> * HTTP caching - Google developers reference</a> * @see <a href="https://www.mnot.net/cache_docs/">Mark Nottingham's cache documentation</a> */ public class CacheControl { @Nullable private Duration maxAge; private boolean noCache = false; private boolean noStore = false; private boolean mustRevalidate = false; private boolean noTransform = false; private boolean cachePublic = false; private boolean cachePrivate = false; private boolean proxyRevalidate = false; @Nullable private Duration staleWhileRevalidate; @Nullable private Duration staleIfError; @Nullable private Duration sMaxAge; /** * Create an empty CacheControl instance. * @see #empty() */ protected CacheControl() { } /** * Return an empty directive. * <p>This is well suited for using other optional directives without "max-age", * "no-cache" or "no-store". * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining */ public static CacheControl empty() { return new CacheControl(); } /** * Add a "max-age=" directive. * <p>This directive is well suited for publicly caching resources, knowing that * they won't change within the configured amount of time. Additional directives * can be also used, in case resources shouldn't be cached ({@link #cachePrivate()}) * or transformed ({@link #noTransform()}) by shared caches. * <p>In order to prevent caches to reuse the cached response even when it has * become stale (i.e. the "max-age" delay is passed), the "must-revalidate" * directive should be set ({@link #mustRevalidate()} * @param maxAge the maximum time the response should be cached * @param unit the time unit of the {@code maxAge} argument * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see #maxAge(Duration) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.8">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.8</a> */ public static CacheControl maxAge(long maxAge, TimeUnit unit) { return maxAge(Duration.ofSeconds(unit.toSeconds(maxAge))); } /** * Add a "max-age=" directive. * <p>This directive is well suited for publicly caching resources, knowing that * they won't change within the configured amount of time. Additional directives * can be also used, in case resources shouldn't be cached ({@link #cachePrivate()}) * or transformed ({@link #noTransform()}) by shared caches. * <p>In order to prevent caches to reuse the cached response even when it has * become stale (i.e. the "max-age" delay is passed), the "must-revalidate" * directive should be set ({@link #mustRevalidate()} * @param maxAge the maximum time the response should be cached * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @since 5.2 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.8">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.8</a> */ public static CacheControl maxAge(Duration maxAge) { CacheControl cc = new CacheControl(); cc.maxAge = maxAge; return cc; } /** * Add a "no-cache" directive. * <p>This directive is well suited for telling caches that the response * can be reused only if the client revalidates it with the server. * This directive won't disable cache altogether and may result with clients * sending conditional requests (with "ETag", "If-Modified-Since" headers) * and the server responding with "304 - Not Modified" status. * <p>In order to disable caching and minimize requests/responses exchanges, * the {@link #noStore()} directive should be used instead of {@code #noCache()}. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.2">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.2</a> */ public static CacheControl noCache() { CacheControl cc = new CacheControl(); cc.noCache = true; return cc; } /** * Add a "no-store" directive. * <p>This directive is well suited for preventing caches (browsers and proxies) * to cache the content of responses. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.3">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.3</a> */ public static CacheControl noStore() { CacheControl cc = new CacheControl(); cc.noStore = true; return cc; } /** * Add a "must-revalidate" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that once it has become stale, a cache MUST NOT * use the response to satisfy subsequent requests without successful validation * on the origin server. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.1">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.1</a> */ public CacheControl mustRevalidate() { this.mustRevalidate = true; return this; } /** * Add a "no-transform" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that intermediaries (caches and others) should * not transform the response content. This can be useful to force caches and * CDNs not to automatically gzip or optimize the response content. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.4">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.4</a> */ public CacheControl noTransform() { this.noTransform = true; return this; } /** * Add a "public" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that any cache MAY store the response, * even if the response would normally be non-cacheable or cacheable * only within a private cache. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.5">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.5</a> */ public CacheControl cachePublic() { this.cachePublic = true; return this; } /** * Add a "private" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that the response message is intended * for a single user and MUST NOT be stored by a shared cache. * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.6">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.6</a> */ public CacheControl cachePrivate() { this.cachePrivate = true; return this; } /** * Add a "proxy-revalidate" directive. * <p>This directive has the same meaning as the "must-revalidate" directive, * except that it does not apply to private caches (i.e. browsers, HTTP clients). * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.7">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.7</a> */ public CacheControl proxyRevalidate() { this.proxyRevalidate = true; return this; } /** * Add an "s-maxage" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that, in shared caches, the maximum age specified * by this directive overrides the maximum age specified by other directives. * @param sMaxAge the maximum time the response should be cached * @param unit the time unit of the {@code sMaxAge} argument * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see #sMaxAge(Duration) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.9">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.9</a> */ public CacheControl sMaxAge(long sMaxAge, TimeUnit unit) { return sMaxAge(Duration.ofSeconds(unit.toSeconds(sMaxAge))); } /** * Add an "s-maxage" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that, in shared caches, the maximum age specified * by this directive overrides the maximum age specified by other directives. * @param sMaxAge the maximum time the response should be cached * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @since 5.2 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7234#section-5.2.2.9">rfc7234 section 5.2.2.9</a> */ public CacheControl sMaxAge(Duration sMaxAge) { this.sMaxAge = sMaxAge; return this; } /** * Add a "stale-while-revalidate" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that caches MAY serve the response in which it * appears after it becomes stale, up to the indicated number of seconds. * If a cached response is served stale due to the presence of this extension, * the cache SHOULD attempt to revalidate it while still serving stale responses * (i.e. without blocking). * @param staleWhileRevalidate the maximum time the response should be used while being revalidated * @param unit the time unit of the {@code staleWhileRevalidate} argument * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see #staleWhileRevalidate(Duration) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5861#section-3">rfc5861 section 3</a> */ public CacheControl staleWhileRevalidate(long staleWhileRevalidate, TimeUnit unit) { return staleWhileRevalidate(Duration.ofSeconds(unit.toSeconds(staleWhileRevalidate))); } /** * Add a "stale-while-revalidate" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that caches MAY serve the response in which it * appears after it becomes stale, up to the indicated number of seconds. * If a cached response is served stale due to the presence of this extension, * the cache SHOULD attempt to revalidate it while still serving stale responses * (i.e. without blocking). * @param staleWhileRevalidate the maximum time the response should be used while being revalidated * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @since 5.2 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5861#section-3">rfc5861 section 3</a> */ public CacheControl staleWhileRevalidate(Duration staleWhileRevalidate) { this.staleWhileRevalidate = staleWhileRevalidate; return this; } /** * Add a "stale-if-error" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that when an error is encountered, a cached stale response * MAY be used to satisfy the request, regardless of other freshness information. * @param staleIfError the maximum time the response should be used when errors are encountered * @param unit the time unit of the {@code staleIfError} argument * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @see #staleIfError(Duration) * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5861#section-4">rfc5861 section 4</a> */ public CacheControl staleIfError(long staleIfError, TimeUnit unit) { return staleIfError(Duration.ofSeconds(unit.toSeconds(staleIfError))); } /** * Add a "stale-if-error" directive. * <p>This directive indicates that when an error is encountered, a cached stale response * MAY be used to satisfy the request, regardless of other freshness information. * @param staleIfError the maximum time the response should be used when errors are encountered * @return {@code this}, to facilitate method chaining * @since 5.2 * @see <a href="https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5861#section-4">rfc5861 section 4</a> */ public CacheControl staleIfError(Duration staleIfError) { this.staleIfError = staleIfError; return this; } /** * Return the "Cache-Control" header value, if any. * @return the header value, or {@code null} if no directive was added */ @Nullable public String getHeaderValue() { String headerValue = toHeaderValue(); return (StringUtils.hasText(headerValue) ? headerValue : null); } /** * Return the "Cache-Control" header value. * @return the header value (potentially empty) */ private String toHeaderValue() { StringBuilder headerValue = new StringBuilder(); if (this.maxAge != null) { appendDirective(headerValue, "max-age=" + this.maxAge.getSeconds()); } if (this.noCache) { appendDirective(headerValue, "no-cache"); } if (this.noStore) { appendDirective(headerValue, "no-store"); } if (this.mustRevalidate) { appendDirective(headerValue, "must-revalidate"); } if (this.noTransform) { appendDirective(headerValue, "no-transform"); } if (this.cachePublic) { appendDirective(headerValue, "public"); } if (this.cachePrivate) { appendDirective(headerValue, "private"); } if (this.proxyRevalidate) { appendDirective(headerValue, "proxy-revalidate"); } if (this.sMaxAge != null) { appendDirective(headerValue, "s-maxage=" + this.sMaxAge.getSeconds()); } if (this.staleIfError != null) { appendDirective(headerValue, "stale-if-error=" + this.staleIfError.getSeconds()); } if (this.staleWhileRevalidate != null) { appendDirective(headerValue, "stale-while-revalidate=" + this.staleWhileRevalidate.getSeconds()); } return headerValue.toString(); } private void appendDirective(StringBuilder builder, String value) { if (builder.length() > 0) { builder.append(", "); } builder.append(value); } @Override public String toString() { return "CacheControl [" + toHeaderValue() + "]"; } }
/* * Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.lang; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import javax.annotation.Nonnull; import javax.annotation.meta.TypeQualifierNickname; import javax.annotation.meta.When; /** * A common Spring annotation to declare that annotated elements can be {@code null} under * some circumstance. * * <p>Leverages JSR-305 meta-annotations to indicate nullability in Java to common * tools with JSR-305 support and used by Kotlin to infer nullability of Spring API. * * <p>Should be used at parameter, return value, and field level. Methods override should * repeat parent {@code @Nullable} annotations unless they behave differently. * * <p>Can be used in association with {@code @NonNullApi} or {@code @NonNullFields} to * override the default non-nullable semantic to nullable. * * @author Sebastien Deleuze * @author Juergen Hoeller * @since 5.0 * @see N on NullApi * @see N on NullFields * @see N on Null */ @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Nonnull(when = When.MAYBE) @TypeQualifierNickname public @interface Nullable { }
package javax.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import javax.annotation.meta.TypeQualifier; import javax.annotation.meta.TypeQualifierValidator; import javax.annotation.meta.When; @Documented @TypeQualifier @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface Nonnull { When when() default When.ALWAYS; static class Checker implements TypeQualifierValidator<Nonnull> { @Override public When forConstantValue(Nonnull qualifierqualifierArgument, Object value) { if (value == null) { return When.NEVER; } return When.ALWAYS; } } }
package javax.annotation.meta; /** * Used to describe the relationship between a qualifier T and the set of values * S possible on an annotated element. * * In particular, an issues should be reported if an ALWAYS or MAYBE value is * used where a NEVER value is required, or if a NEVER or MAYBE value is used * where an ALWAYS value is required. * * */ public enum When { /** S is a subset of T */ ALWAYS, /** nothing definitive is known about the relation between S and T */ UNKNOWN, /** S intersection T is non empty and S - T is nonempty */ MAYBE, /** S intersection T is empty */ NEVER; }
package javax.annotation.meta; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation; import javax.annotation.Nonnull; public interface TypeQualifierValidator<A extends Annotation> { /** * Given a type qualifier, check to see if a known specific constant value * is an instance of the set of values denoted by the qualifier. * * @param annotation * the type qualifier * @param value * the value to check * @return a value indicating whether or not the value is an member of the * values denoted by the type qualifier */ public @Nonnull When forConstantValue(@Nonnull A annotation, Object value); }
package javax.annotation.meta; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * * This annotation is applied to a annotation, and marks the annotation as being * a qualifier nickname. Applying a nickname annotation X to a element Y should * be interpreted as having the same meaning as applying all of annotations of X * (other than QualifierNickname) to Y. * * <p> * Thus, you might define a qualifier SocialSecurityNumber as follows: * </p> * * * <code> @Documented @TypeQualifierNickname @Pattern("[0-9]{3}-[0-9]{2}-[0-9]{4}") @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface SocialSecurityNumber { } </code> * * */ @Documented @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) public @interface TypeQualifierNickname { }
package javax.annotation.meta; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * This qualifier is applied to an annotation to denote that the annotation * should be treated as a type qualifier. */ @Documented @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) public @interface TypeQualifier { /** * Describes the kinds of values the qualifier can be applied to. If a * numeric class is provided (e.g., Number.class or Integer.class) then the * annotation can also be applied to the corresponding primitive numeric * types. */ Class<?> applicableTo() default Object.class; }
7、 Http 主机头注入攻击 解决方案
参考:检测到目标URL存在http host头攻击漏洞
简介
绿盟科技扫描到网站存在http host头攻击漏洞,需要对该漏洞进行修复,网站后台是用java写的,对于这种host头攻击的方式,有很多种方式避免。
如从源头考虑的话,一般网站都配置了nginx或者部署在Apache上面,可以在nginx或者Apache上拦截非法请求头的;由于我是在本机上测试的,项目是部署在tomcat上,故无法验证nginx和apache的修复方式。这里介绍一下从过滤器的层次进行拦截的方式。
过滤器拦截的方式
使用的测试工具
burpsuite,Firefox ;在火狐上面设置代理,用burpsuite拦截请求并修改host测试验证是否成功,使用burpsuite以及在火狐设置代理的方式这里就不介绍了,网上有很多详细的教程
存在漏洞的版本
这里先介绍漏洞版本的测试样例,我在火狐代理以及burpsuite上监听的端口是8081,注意burpsuite默认监听了8080,一定要取消,不然就会和tomcat启用端口重复了

火狐浏览器上访问存在漏洞的页面(实际上随便访问个网页测试结果都一样的)


在burpsuite上监听拦截到该地址,通过repeater修改host头,模拟访问请求。原来的host是10.4.0.246:8080,我们将其修改后改为10.4.0.2460:8080,修改后重新send请求过去,有响应,且响应内容为修改后的host。这就存在了host伪装的情况。

实际上这种非法的host的只要加了个拦截器最后跳回登录界面就可以了,但是可能存在通过修改host来跨域攻击以及越过普通权限攻击,这种只是有可能实际上系统架构完善了是完全可以避免的。但是既然检测出了漏洞,那么理所应当的也要对其进行相应的修复。
修复漏洞的版本
上面我们已经知道了如何测试漏洞的方法了,现在是如何使用过滤器的方式处理漏洞修复。直奔主题由于使用的是javaweb开发的网站,在web.xml下配置一个新的拦截器。
<filter> <filter-name>hostCleanFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.test.HostCleanFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>hostCleanFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
注意在这里添加的拦截器建议放到第一个,即< url-pattern> /* < /url-pattern> 放在第一个,因为一个项目可能本身的过滤器较多,当其他的过滤器起作用后可能就轮不到这个过滤器执行了,那么检测监听的时候会发现漏洞没被修复,这点也是我自己测试的时候踩的坑,当时发现有的页面修复了漏洞,有的页面没被修复,这是因为拦截器对于请求的结果可能导致了不同的去向。
配置拦截器的代码:
public class HostCleanFilter implements Filter { public static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(HostCleanFilter.class); public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { } public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; String requestHost = request.getHeader("host"); if (requestHost != null && isRightHost(requestHost)){ response.setStatus(403); return; } chain.doFilter(request,response); } public boolean isRightHost(String requestHost){ if (!StringUtils.equals(requestHost,WebConstants.HostOne) &&!StringUtils.equals(requestHost,WebConstants.HostTwo)){ //注意:该2处标红位置 内容代码缺失 //域名非法 logger.info("非法的Host:" + requestHost); return true; } logger.info("合法的Host:" + requestHost); return false; } public void destroy() { } }
上面的WebConstants.HostOne、WebConstants.HostTwo是我自己配置合法host,拦截每一个请求若检验host不对则返回403。一般网站的话只要检验两个host就可以了,一个是ip地址类型的,如我本机测试允许的是10.4.0.246:8080,假如是生产环境上的可以在HostTwo修改为 域名:port,如 baidu.com:8080 这种,根据自身的真实情况添加或修改。
以上步骤修改完后,可以开始重新测试刚刚的地址了,让我们来看下会有什么变化呢。继续访问刚才的地址,在burpsuite上监听端口并重新repeater。老规矩还是修改host为10.4.0.2460:8080,重写了host查看到返回403。

至此漏洞已经修复完毕,可以多测几个不同的网页检测下是否一致。测试时候需注意几点的是:
在本机上测试的时候ip一般是localhost或者127.0.0.1地址作为网站的访问ip地址,会与火狐浏览器默认的不代理地址冲突,导致无法正常测试,我这里的10.4.0.246是在ipconfig上查看分配给的子网ip,本地访问网站的时候使用分配的ip进行访问而不是直接访问本机ip,这么做就能成功的代理火狐浏览器上的请求。
火狐或者其他浏览器设置的代理端口尽量不要与本地tomcat或者Apache重提,所以我设置的是8081端口,burpsuite上监听的也是8081端口。
web.xml设置过滤器建议放在第一位,因为不同的项目过滤器可能执行结果不一样,比如是直接访问这个漏洞网页还是登陆用户后再访问这个漏洞网页,所返回的结果可能都会不一样,因为登录前后拦截的session不一样了。假如你熟悉你的项目那么可以设置过滤的顺序,我这次是把host头过滤放在了执行顺序第二位,不确定的话可以直接放第一位,省去一些麻烦。
本次文章的编写参考了博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/Orangesir/article/details/84999847
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43922510/article/details/99657007
参考: springboot解决目标URL存在http host头攻击漏洞
1.增加过滤器类进行host白名单过滤
package com.todaytech.pwp.core.web; import com.todaytech.pwp.core.exception.BizException; import com.todaytech.pwp.core.util.Config; import com.todaytech.pwp.core.util.lang.StringUtil; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * http host头攻击漏洞处理过滤器, 需要在配置文件添加allowed.servernames可访问host白名单, * 多个host用逗号隔开,本地开发使用127.0.0.1,localhost * * @author liufr */ @Component public class HostFilter implements Filter { /** * 自定义实现host白名单添加 */ private String ALLOWED_SERVERNAMES = null; @Override public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { // System.out.println("Filter初始化中"); } /** * host拦截 */ @Override public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse; String host = request.getHeader("host"); String serverName = request.getServerName(); System.out.println("========自定义实现host白名单添加:请求访问ip 头信息=================serverName-debug:" + serverName +";host:"+host+"===================="); if (!isEmpty(serverName)) { if (checkBlankList(serverName)) { filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } else { System.out.println("[serverName deny access tips]->" + serverName); // response.getWriter().print("host deny"); response.setStatus(403); response.flushBuffer(); } } else { filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse); } } @Override public void destroy() { // System.out.println("Filter销毁"); } /** * 校验当前host是否在白名单中 */ private boolean checkBlankList(String serverName) { ALLOWED_SERVERNAMES = Config.getConfigProperty("allowed_servernames", null); BizException.throwWhenTrue(StringUtil.isBlank(ALLOWED_SERVERNAMES), "处理“主机头注入攻击”的配置参数:allowed_servernames的ip信息不存在 "); //说明:此处代码为从配置文件了读取 参数 allowed_servernames的内容,不同的项目系统的处理方法不同。按照实际情况来处理 String[] allowdServerName = ALLOWED_SERVERNAMES.split(","); List<String> serverNameList = Arrays.asList(allowdServerName); for (String str : serverNameList) { if (!isEmpty(str) && str.equals(serverName)) { return true; } } return false; } /** * 判空 */ public boolean isEmpty(Object str) { return str == null || "".equals(str); } }
2.配置文件增加配置allowed.servernames
allowed_servernames=127.0.0.1,localhost

3.web.xml配置 该拦截器的信息
<!--处理“主机头注入攻击”网络攻击问题--> <filter> <filter-name>HostFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>com.todaytech.pwp.core.web.HostFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HostFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> <url-pattern>*.vop</url-pattern> <url-pattern>*.vopx</url-pattern> <url-pattern>*.js</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>

8、 检测到目标Referrer-Policy响应头缺失
问题展示:
项目进行安全扫描 遇到以下低危的风险需要处理~



响应头缺失 需要更新后台文件 作为一枚前端菜鸟~我就这样开始了摸索的道路
因为项目是用tomcat部署到服务器上的 所以我们需要修改后台服务的文件web.xml
在web.xml中新增一下内容 重启:
<filter> <filter-name>httpHeaderSecurity</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.catalina.filters.HttpHeaderSecurityFilter</filter-class> <async-supported>true</async-supported> <init-param> <param-name>hstsEnabled</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>hstsMaxAgeSeconds</param-name> <param-value>31536000</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>antiClickJackingEnabled</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>antiClickJackingOption</param-name> <param-value>SAMEORIGIN</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>blockContentTypeSniffingEnabled</param-name> <!-- X-Content-Type-Options 默认: true(nosniff) --> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>xssProtectionEnabled</param-name> <!-- X-XSS-Protection 默认: true(1; mode=block) --> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter>
<filter-mapping> <filter-name>httpHeaderSecurity</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher> </filter-mapping>
重启之后 我们发现响应头中

但是 如果我们要添加Content-Security-Policy 这样类似的响应头 怎么添加呢 ?我们需要在web.xml中添加过滤器 然后在过滤器中配置响应头即可,废话不多说 上代码
新建一个headerFilter.java文件:
package xx.xx.xx // 你的项目路径 import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; import javax.servlet.Filter; import javax.servlet.FilterChain; import javax.servlet.FilterConfig; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.ServletRequest; import javax.servlet.ServletResponse; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; public class headerFilter implements Filter { public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException { // System.out.println("FirstFilter init..."); } public void doFilter(ServletRequest request,ServletResponse response,FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletResponse httpResponse = (HttpServletResponse) response; // 添加响应头 httpResponse.setHeader("Content-Security-Policy","frame-ancestors 'self'"); httpResponse.setHeader("X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies","master-only"); httpResponse.setHeader("X-Download-Options","noopen"); httpResponse.setHeader("Strict-Transport-Security","max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains"); httpResponse.setHeader("Referrer-Policy","no-referrer"); chain.doFilter(request,response); } public void destroy() { } }
在web.xml中添加一下内容:
<filter>
// xx.xx.xx 为项目部署的路径
<filter-name>headerFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>xx.xx.xx.headerFilter</filter-class>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>headerFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
<dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher>
</filter-mapping>
修改完成后 重启 查看前端的network 我们可以看到响应头中已添加

http 策略之 Referrer-Policy 细节内容讲解
一、背景
说道 referer ,大家想必知道的清楚一些。referer是用来防止 CORS(跨站请求伪造)的一种最常见及有效的方式。对于自身服务器,通过客户端发来的请求中带有的referer信息,可以判断该请求是否来源于本网站。这样就可以一定程度上避免其他网站盗取自身服务器信息,或者可以通过referer来实现广告流量引流,说白了,referer是一种客户端带到服务器的客户端信息,而Referrer-Policy则是客户端对这个带信息策略的配置。
二、配置方式
1 、HTML 配置
既然是客户端策略,那么在HTML中的配置想必大家应该都清楚:
<meta name="referrer" content="origin">
或者用 <a>、<area>、<img>、<iframe>、<script> 或者 <link> 元素上的 referrerpolicy 属性为其设置独立的请求策略。
<a href="http://example.com" referrerpolicy="origin">
另外也可以在 <a>、<area> 或者 <link> 元素上将 rel属性设置为 noreferrer。
<a href="http://example.com" rel="noreferrer">
2、CSP响应头设置
CSP(Content Security Policy)
Content-Security-Policy:
referrer no-referrer|no-referrer-when-downgrade|origin|origin-when-cross-origin|unsafe-url;
三、API
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer
Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade
Referrer-Policy: origin
Referrer-Policy: origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: same-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Referrer-Policy: unsafe-url
值
no-referrer
整个 Referer 首部会被移除。访问来源信息不随着请求一起发送
no-referrer-when-downgrade (默认值)
在没有指定任何策略的情况下用户代理的默认行为。在同等安全级别的情况下,引用页面的地址会被发送(HTTPS->HTTPS),但是在降级的情况下不会被发送 (HTTPS->HTTP)。
origin
在任何情况下,仅发送文件的源作为引用地址。例如 https://example.com/page.html 会将 https://example.com/ 作为引用地址。
origin-when-cross-origin
对于同源的请求,会发送完整的URL作为引用地址,但是对于非同源请求仅发送文件的源。
same-origin
对于同源的请求会发送引用地址,但是对于非同源请求则不发送引用地址信息
strict-origin
在同等安全级别的情况下,发送文件的源作为引用地址(HTTPS->HTTPS),但是在降级的情况下不会发送 (HTTPS->HTTP)。
strict-origin-when-cross-origin
对于同源的请求,会发送完整的URL作为引用地址;在同等安全级别的情况下,发送文件的源作为引用地址(HTTPS->HTTPS);在降级的情况下不发送此首部 (HTTPS->HTTP)。
unsafe-url
无论是同源请求还是非同源请求,都发送完整的 URL(移除参数信息之后)作为引用地址。(最不安全的策略了)
四、推荐
推荐使用strict-origin-when-cross-origin 作为默认的referer策略。这是适配同源模式下,防止CSRF攻击的最佳实践