下面这个学习,把List<T>转换为Datatable。

class Ay { private int _ID; public int ID { get { return _ID; } set { _ID = value; } } private string _Account; public string Account { get { return _Account; } set { _Account = value; } } private string _Email; public string Email { get { return _Email; } set { _Email = value; } } public Ay() { } public Ay(int id,string account,string email) { this._ID = id; this._Account = account; this._Email = email; } }

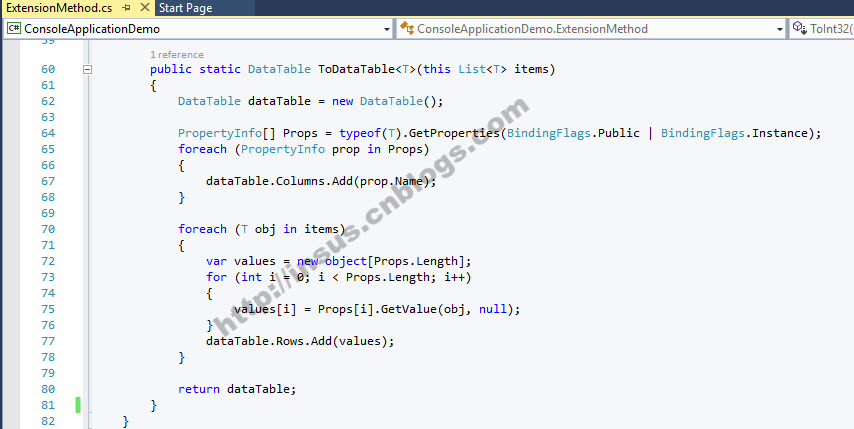
public static DataTable ToDataTable<T>(this List<T> items) { DataTable dataTable = new DataTable(); PropertyInfo[] Props = typeof(T).GetProperties(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Instance); foreach (PropertyInfo prop in Props) { dataTable.Columns.Add(prop.Name); } foreach (T obj in items) { var values = new object[Props.Length]; for (int i = 0; i < Props.Length; i++) { values[i] = Props[i].GetValue(obj, null); } dataTable.Rows.Add(values); } return dataTable; }
下面,我们在List<T>添加几笔记录,然后使用上面的扩展方法,把List<T> 转换为DataTable.
为了看到结果,再把DataTable打印至控制台上:

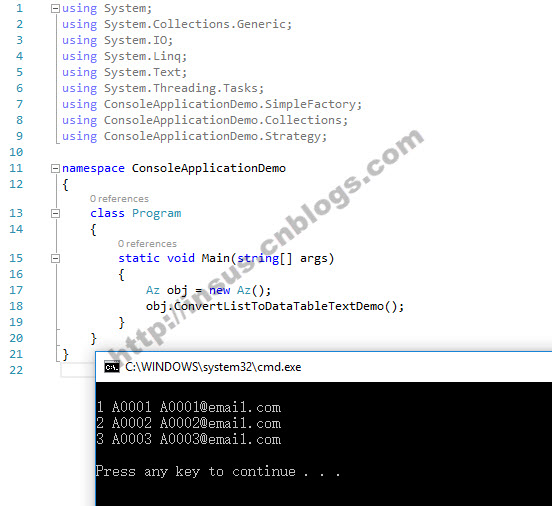
class Az { public void ConvertListToDataTableTextDemo() { List<Ay> ays = new List<Ay>() { new Ay() { ID=1,Account="A0001",Email="A0001@email.com" }, new Ay() { ID=2,Account="A0002",Email="A0002@email.com"}, new Ay() {ID=3,Account="A0003",Email="A0003@email.com" } }; DataTable dt = ays.ToDataTable(); foreach (DataRow row in dt.Rows) { Console.WriteLine(); for (int x = 0; x < dt.Columns.Count; x++) { Console.Write(row[x].ToString() + " "); } } Console.WriteLine(" "); } }