感觉迭代法也挺巧妙的
题目
给你单链表的头节点 head ,请你反转链表,并返回反转后的链表。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 3:
输入:head = []
输出:[]
提示:
链表中节点的数目范围是 [0, 5000]
-5000 <= Node.val <= 5000
进阶:链表可以选用迭代或递归方式完成反转。你能否用两种方法解决这道题?
作者:力扣 (LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/top-interview-questions-easy/xnnhm6/
code
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
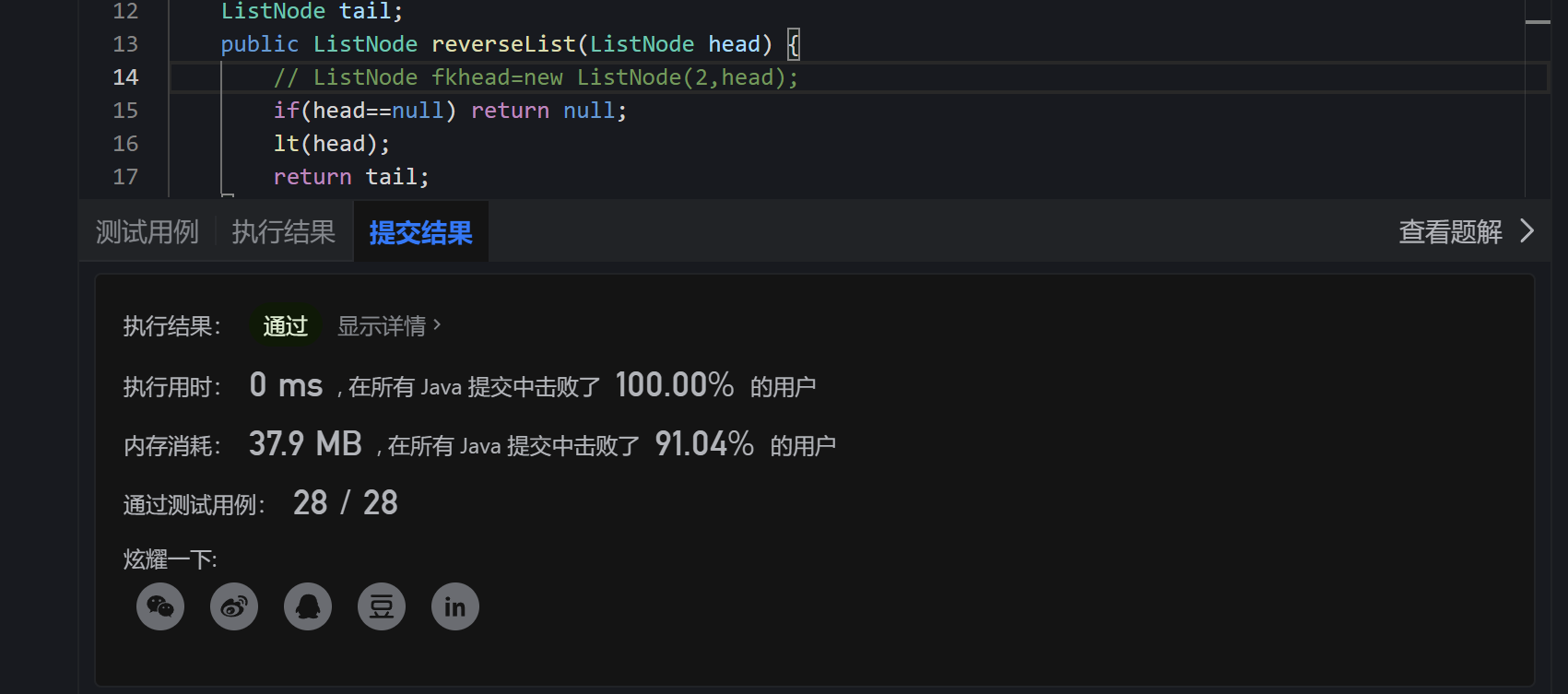
class Solution {
ListNode tail;
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// ListNode fkhead=new ListNode(2,head);
if(head==null) return null;
lt(head);
return tail;
}
public ListNode lt(ListNode t) {
if(t.next==null) {
tail=t;
return tail;
}
lt(t.next).next=t;
t.next=null;//防止最后一位出不去
return t;
}
}
迭代求解法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
//新链表
ListNode newHead = null;
while (head != null) {
ListNode temp = head.next;//新节点
head.next = newHead;//避免成环,处理上一步的头
newHead = head;//元元头,下一步用
head = temp;
}
//返回新链表
return newHead;
}
}
其他递归
因为递归调用之后head.next节点就会成为reverse节点的尾结点,我们可以直接让head.next.next = head;,这样代码会更简洁一些,看下代码
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode reverse = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return reverse;
}
这种递归往下传递的时候基本上没有逻辑处理,当往回反弹的时候才开始处理,也就是从链表的尾端往前开始处理的。我们还可以再来改一下,在链表递归的时候从前往后处理,处理完之后直接返回递归的结果,这就是所谓的尾递归,这种运行效率要比上一种好很多
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverseListInt(head, null);
}
private ListNode reverseListInt(ListNode head, ListNode newHead) {
if (head == null)
return newHead;
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = newHead;
return reverseListInt(next, head);
}
作者:数据结构和算法
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/leetbook/read/top-interview-questions-easy/xnnhm6/?discussion=0NDu5u