最近刚好需要频繁的操作一些集合对象,之前都是for循环然后查询赋值集合copy感觉有些复杂,之前看到过使用stream流,但是不会使用,抽空学习下如何使用。
一、为什么使用stream流
利用java8新特性,可以用简洁高效的代码来实现一些数据处理。
一、如何使用stream流
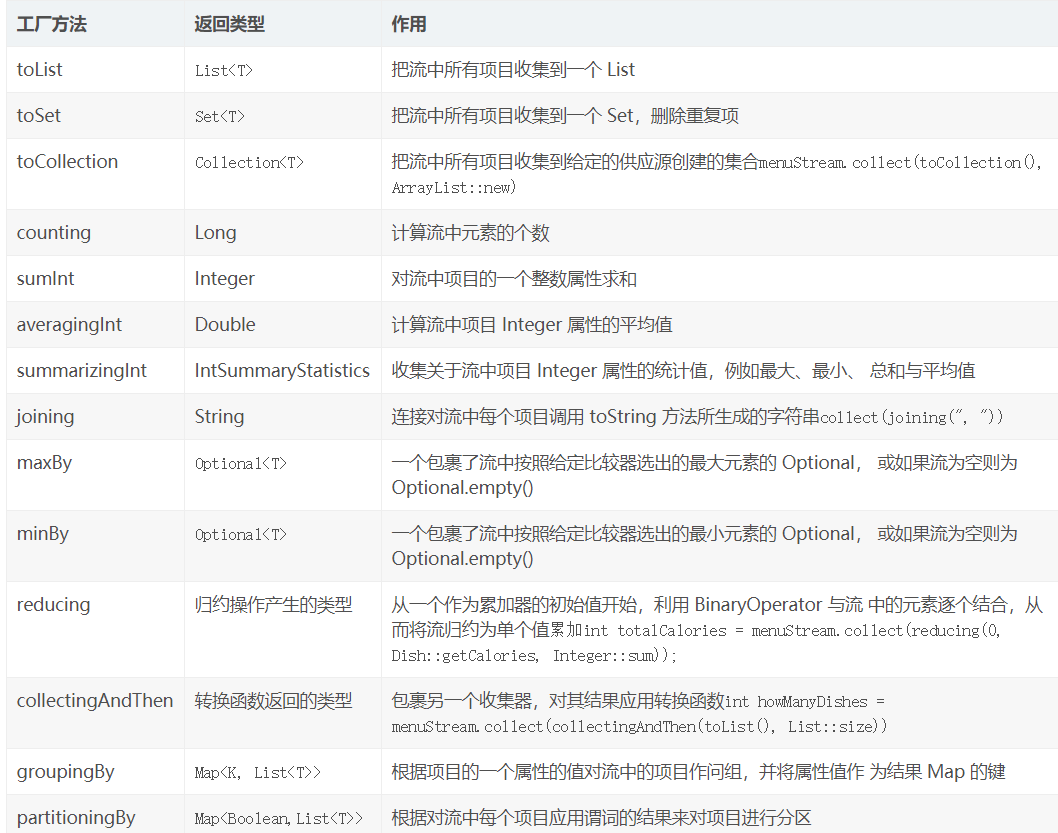
下表展示 Collectors 类的静态工厂方法。
1、定义1个phone对象:
public class Phone { private Integer id; private String name; private BigDecimal money; private Integer num; ... }
2、创建stream测试类:
package javastream; import java.math.BigDecimal; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Comparator; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.TreeSet; import java.util.stream.Collectors; /** * 学习使用java1.8的新特性使用stream流操作集合对象 * @author dell * */ public class StreamDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Phone> phoneList = new ArrayList<>();//存放apple对象集合 Phone phone1 = new Phone(1,"苹果",new BigDecimal("3.25"),10); Phone phone12 = new Phone(1,"华为",new BigDecimal("1.35"),20); Phone phone2 = new Phone(2,"小米",new BigDecimal("2.89"),30); Phone phone3 = new Phone(3,"oppo",new BigDecimal("9.99"),40); phoneList.add(phone1); phoneList.add(phone12); phoneList.add(phone2); phoneList.add(phone3); groupList(phoneList); listToMap(phoneList); filterList(phoneList); maxAndMin(phoneList); } /** * 1、分组测试 * List里面的对象元素,以某个属性来分组,例如,以id分组,将id相同的放在一起: */ public static void groupList(List<Phone> phoneList){ Map<Integer, List<Phone>> phoneMap = phoneList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Phone::getId)); System.err.println("分组测试-->List里面的对象元素"+phoneMap.toString()); } /** * 2、List转Map * id为key,apple对象为value,可以这么做: * List -> Map * 需要注意的是: * toMap 如果集合对象有重复的key,会报错Duplicate key .... * apple1,apple12的id都为1。 * 可以用 (k1,k2)->k1 来设置,如果有重复的key,则保留key1,舍弃key2 */ public static void listToMap(List<Phone> phoneList){ Map<Integer, Phone> phoneMap = phoneList.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Phone::getId, a->a,(k1,k2)->k1)); System.out.println("List转Map-->Map里面的对象元素"+phoneMap.toString()); } /** * 3、过滤Filter * 从集合中过滤出来符合条件的元素: */ public static void filterList(List<Phone> phoneList){ List<Phone> filterList = phoneList.stream().filter(p -> p.getName().equals("苹果")).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.err.println("过滤Filter-->filterList过滤后的对象元素:"+filterList); } /** * 4、将集合中的数据按照某个属性求和: */ public static void totalMoney(List<Phone> phoneList){ //计算 总金额 BigDecimal totalMoney = phoneList.stream().map(Phone::getMoney).reduce(BigDecimal.ZERO, BigDecimal::add); System.err.println("按照某个属性求和-->totalMoney:"+totalMoney); //totalMoney:17.48 } /** * 5、Collectors.maxBy 和 Collectors.minBy 来计算流中的最大或最小值。 */ public static void maxAndMin(List<Phone> phoneList){ Optional<Phone> maxPhone = phoneList.stream(). collect(Collectors.maxBy(Comparator.comparing(Phone::getMoney))); maxPhone.ifPresent(System.out::println); Optional<Phone> minPhone = phoneList.stream(). collect(Collectors.minBy(Comparator.comparing(Phone::getMoney))); minPhone.ifPresent(System.out::println); } /** * 6、根据id去重 */ public static void uniqueList(List<Phone> phoneList){ //单个字段去重 List<Phone> unique = phoneList.stream().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen( Collectors.toCollection(() -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(Phone::getId))), ArrayList<Phone>::new)); System.err.println("根据id去重-->unique:"+unique); //多个字段去重 List<Phone> unique2 = phoneList.stream() .collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen( Collectors.toCollection( () -> new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparing(p -> p.getId() + ";" + p.getName()))), ArrayList<Phone>::new)); System.err.println("多个字段去重-->unique2:"+unique2); } }