说到遍历,首先想到的是数组的遍历,方法不要太多,比如 for, forEach,map,filter,every,some等
下面来看下,用法 首先 定义一个数组:

1. for循环,需要知道数组的长度,才能遍历,
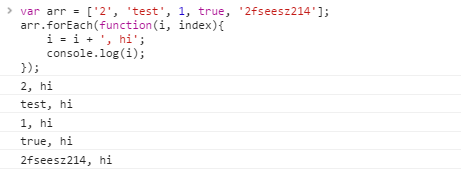
2. forEach循环,循环数组中每一个元素并采取操作, 没有返回值, 可以不用知道数组长度
3. map函数,遍历数组每个元素,并回调操作,需要返回值,返回值组成新的数组,原数组不变

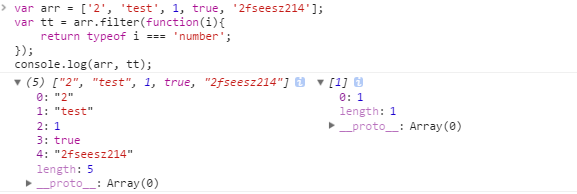
4. filter函数, 过滤通过条件的元素组成一个新数组, 原数组不变
5. some函数,遍历数组中是否有符合条件的元素,返回Boolean值

6. every函数, 遍历数组中是否每个元素都符合条件, 返回Boolean值

当然, 除了遍历数组之外,还有遍历对象,常用方法 in

in 不仅可以用来 遍历对象,还可以用来遍历数组, 不过 i 对应与数组的 key值

介绍完遍历,下面说一下工作中遇到的情况,后台传给我一个对象数组,我需要排序再显示,看到有介绍用 sort 排序的方法,如下
var arr1 = [
{name: 'te', value: 5},
{name: 'te', value: 2},
{name: 'we', value: 3},
{name: 'ee', value: 1},
{name: 'ee', value: 4}
];
var by = function(type){
return function(o,p){
console.log(o,p);
var a;
var b;
if(typeof o === 'object' && typeof p === 'object' && o && p){
a = o[type];
b = p[type];
if(a === b) {
return 0;
}
if(typeof a === typeof b){
console.log(a, b);
return a < b ? -1 : 1
}
return typeof a < typeof b ? -1 : 1;
}else {
throw('字段有误');
}
}
}
console.log(arr1.sort(by('value')));
显示如下:

总结:
排序应用场景很多 , 所以要弄清楚,明白,方可游刃有余。望小伙伴多多提意见!
补充: 后面发现, 后台传过来的数组中,每个对象按 value 排序, value > 5的按顺序排在前面,小于5排在后面
思考后, 可以在原来的的方法中这样写,将数组分成2段,大于等于5和小于5,交换位置即可
var arr1 = [
{name: 'te', value: 5},
{name: 'te', value: 2},
{name: 'we', value: 3},
{name: 'ee', value: 1},
{name: 'ee', value: 4}
];
var sortObj = function(arr, type , num){
var by = function(type){
return function(o,p){
var a;
var b;
if(typeof o === 'object' && typeof p === 'object' && o && p){
a = o[type];
b = p[type];
if(a === b) {
return 0;
}
if(typeof a === typeof b){
console.log(a, b);
return a < b ? -1 : 1
}
return typeof a < typeof b ? -1 : 1;
}else {
throw('字段有误');
}
}
};
var cacheArr = arr.sort(by('value'));
//通过num 把数组分成两段
var arrBf = cacheArr.filter(function(item){
if(item.value < num){
return item;
}
});
var arrAf = cacheArr.filter(function(item){
if(item.value >= num){
return item;
}
});
//交换位置 即可得到
var newArr = arrAf.concat(arrBf);
return newArr;
};
console.log(sortObj(arr1, 'value' , 3));
