对单链表排序,通常有两种方法。(PS:考察一个程序员的C语言编程功底,通常看他是否能娴熟地操作链表就知道了。当然,实际C编程中我们并不需要去重新实现链表,无论是Linux还是Solaris, 都有双向循环链表的标准实现。)
- 方法1:将每一个结点的内存地址保存到额外的数组中(也就是将链式存储转化为顺序存储),对数组进行排序,然后根据有序的数组重新构建链表。
- 方法2:直接对链表进行插入排序,但是实现起来比较复杂一些。
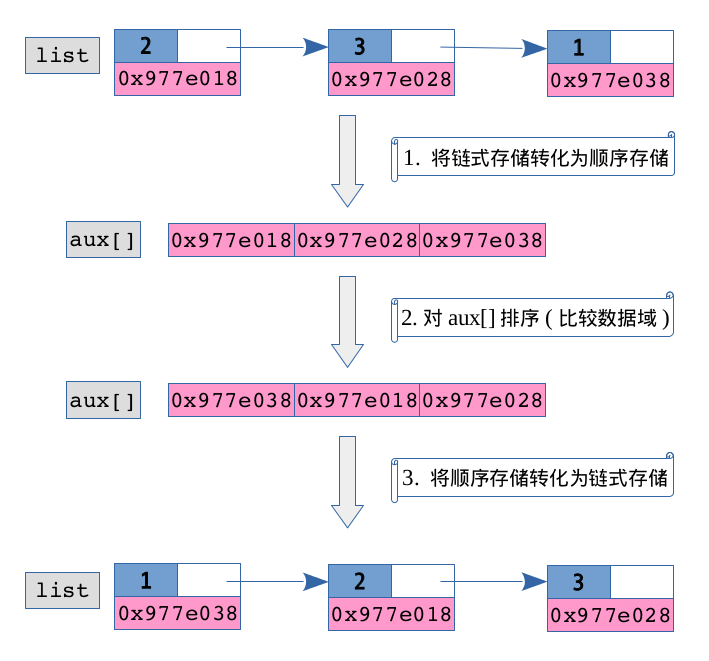
显然,方法1最为简单,因为将链式存储L先转化为顺序存储a[],对顺序存储a[]排序,就避免了较为复杂的链接指针操作。一旦对顺序存储a[]排好序后,根据a[]重新构建一个链表易如反掌。例如:设单链表list有3个结点,结点的内存地址分别为{0x977e018, 0x977e028, 0x977e038}, 结点的数据域分别为{2, 3, 1}, 于是,可用图模拟方法1之排序过程如下:
1. 单链表的定义
typedef struct list_s { int data; struct list_s *next; } list_t;
2. 方法1(对aux[]排序使用的算法是简单插入排序)
1 /* 2 * Insert a[n] before a[m] 3 * .-----------. 4 * | | 5 * o Input : a[m-1], a[m], a[m+1], ..., a[n-1], a[n], a[n+1] | 6 * | 7 * o Output: a[m-1], a[n], a[m], a[m+1], ..., a[n-1], a[n+1] | 8 * \____________________________________/ 9 */ 10 static void 11 insert(list_t *a[], int m, int n) 12 { 13 list_t *t = a[n]; 14 for (int i = n; i > m; i--) 15 a[i] = a[i-1]; 16 a[m] = t; 17 } 18 19 /* 20 * Straight Insertion Sort (sisort in short) 21 * 22 * NOTES: 23 * 1. a[i .. n-1] is not sorted and 24 * a[0 .. i-1] is sorted 25 * 2. walk a[0 .. i-1], if a[i] < a[j], insert a[i] before a[j] 26 */ 27 static void 28 sisort(list_t *a[], size_t n) 29 { 30 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { 31 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 32 if (a[i]->data < a[j]->data) { 33 insert(a, j, i); 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 40 static void 41 list_sort(list_t **head) 42 { 43 if (head == NULL || *head == NULL) 44 return; 45 46 /* get total number of nodes in the single linked list */ 47 int len = 0; 48 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 49 len++; 50 51 /* malloc aux[] */ 52 list_t **aux = (list_t **)malloc(sizeof (list_t *) * len); 53 if (aux == NULL) /* error */ 54 return; 55 56 /* save addr of per node to aux[] */ 57 int k = 0; 58 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 59 aux[k++] = p; 60 61 /* sort aux[] via straight insertion sorting algorithm */ 62 sisort(aux, len); 63 64 /* rebuild the single linked list by walking aux[] */ 65 *head = aux[0]; 66 for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) 67 aux[i]->next = aux[i+1]; 68 aux[len-1]->next = NULL; 69 70 free(aux); 71 }
3. 方法2
实现链式插入排序的关键有两点:
- 在遍历单链表的过程中,从单链表上把某个结点p摘下来存入q,把q插入到已经有序的链表上,然后将p指针向后移(p = p->next); (注意: 要将q断开(q->next = NULL), 必须先执行p = p->next)
- 遍历已经有序的链表,计算出待插入结点p的前驱和后继指针。 (PS: 下面的两个函数大约花了我1个半小时的时间,嘿费脑壳Orz)
1 static void 2 list_insert(list_t **head, list_t *node) 3 { 4 if (*head == NULL) { 5 *head = node; 6 return; 7 } 8 9 /* get both prev and next of the node to insert */ 10 list_t *node_prev = *head; 11 list_t *node_next = NULL; 12 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) { 13 if (p->data < node->data) { 14 node_prev = p; 15 continue; 16 } 17 18 node_next = p; 19 break; 20 } 21 22 if (node_next == NULL) { /* append node to the tail */ 23 node_prev->next = node; 24 } else { 25 if (node_next == node_prev) { /* == *head */ 26 node->next = *head; 27 *head = node; 28 return; 29 } 30 31 /* node_prev -> node -> node_next */ 32 node_prev->next = node; 33 node->next = node_next; 34 } 35 } 36 37 static void 38 list_sort(list_t **head) 39 { 40 if (*head == NULL) 41 return; 42 43 list_t *headp = *head; /* copy *head to headp before snip headp->next */ 44 list_t *p = headp->next; /* init p (move forward) before cut-off */ 45 headp->next = NULL; /* now cut off headp->next */ 46 47 while (p != NULL) { 48 list_t *this = p; /* copy p to this before snip this->next */ 49 p = p->next; /* move p forward before cut-off */ 50 this->next = NULL; /* now cut off this->next */ 51 list_insert(&headp, this); /* insert this node to list headp */ 52 } 53 54 *head = headp; /* always save headp back even if headp == *head */ 55 }
4. 完整的C代码实现(戳这里)
o sort.c
1 /* 2 * Single Linked List Sorting 3 * 4 * 1. convert a[] to a single linked list L 5 * e.g. int a[] = {9, 8, 7, 7} 6 * ==> L = 9->8->7->7->NULL 7 * 2. sort list L via straight insertion sorting 8 * ==> L = 7->7->8->9->NULL 9 * 3. convert list L back to a[] 10 * ==> a[] = {7, 7, 8, 9} 11 * 12 * Note there are two solutions, 13 * (a) Use aux[] to save addr of per node in list L, then sort aux[] via 14 * straight insertion sorting algorithm, and rebuild list L by walking 15 * sorted aux[] 16 * (b) Don't use aux[] but directly sort the single liked list L 17 * 18 * To implement the two solutions above, (a) is very easy and (b) is a bit 19 * difficult. Please also keep in mind that performance of (b) is good. 20 */ 21 22 #include <stdio.h> 23 #include <stdlib.h> 24 #include <string.h> 25 26 typedef enum bool_s {false, true} bool_t; 27 28 bool_t g_isint = true; 29 30 typedef struct list_s { 31 int data; 32 struct list_s *next; 33 } list_t; 34 35 #ifdef _USE_AUX /* solution (a) */ 36 static void 37 list_init(list_t **head, list_t *node) 38 { 39 static list_t *tail = NULL; 40 41 if (*head == NULL) { 42 *head = node; 43 tail = node; 44 return; 45 } 46 47 tail->next = node; 48 tail = node; 49 } 50 #else 51 static void 52 list_init(list_t **head, list_t *node) 53 { 54 if (*head == NULL) { 55 *head = node; 56 return; 57 } 58 59 list_t *q = *head; 60 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 61 q = p; 62 q->next = node; 63 } 64 #endif 65 66 static void 67 list_show(list_t *head) 68 { 69 if (head == NULL) 70 return; 71 72 for (list_t *p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 73 printf("%d ", p->data); 74 printf(" "); 75 } 76 77 static void 78 list_fini(list_t *head) 79 { 80 list_t *p = head; 81 while (p != NULL) { 82 list_t *q = p; 83 p = p->next; 84 free(q); 85 } 86 } 87 88 #ifdef _USE_AUX /* solution (a) */ 89 /* 90 * Insert a[n] before a[m] 91 * .-----------. 92 * | | 93 * o Input : a[m-1], a[m], a[m+1], ..., a[n-1], a[n], a[n+1] | 94 * | 95 * o Output: a[m-1], a[n], a[m], a[m+1], ..., a[n-1], a[n+1] | 96 * \____________________________________/ 97 */ 98 static void 99 insert(list_t *a[], int m, int n) 100 { 101 list_t *t = a[n]; 102 for (int i = n; i > m; i--) 103 a[i] = a[i-1]; 104 a[m] = t; 105 } 106 107 /* 108 * Straight Insertion Sort (sisort in short) 109 * 110 * NOTES: 111 * 1. a[i .. n-1] is not sorted and 112 * a[0 .. i-1] is sorted 113 * 2. walk a[0 .. i-1], if a[i] < a[j], insert a[i] before a[j] 114 */ 115 static void 116 sisort(list_t *a[], size_t n) 117 { 118 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { 119 for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) { 120 if (a[i]->data < a[j]->data) { 121 insert(a, j, i); 122 break; 123 } 124 } 125 } 126 } 127 128 static void 129 list_sort(list_t **head) 130 { 131 if (head == NULL || *head == NULL) 132 return; 133 134 /* get total number of nodes in the single linked list */ 135 int len = 0; 136 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 137 len++; 138 139 /* malloc aux[] */ 140 list_t **aux = (list_t **)malloc(sizeof (list_t *) * len); 141 if (aux == NULL) /* error */ 142 return; 143 144 /* save addr of per node to aux[] */ 145 int k = 0; 146 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) 147 aux[k++] = p; 148 149 /* sort aux[] via straight insertion sorting algorithm */ 150 sisort(aux, len); 151 152 /* rebuild the single linked list by walking aux[] */ 153 *head = aux[0]; 154 for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) 155 aux[i]->next = aux[i+1]; 156 aux[len-1]->next = NULL; 157 158 free(aux); 159 } 160 #else 161 static void 162 list_insert(list_t **head, list_t *node) 163 { 164 if (*head == NULL) { 165 *head = node; 166 return; 167 } 168 169 /* get both prev and next of the node to insert */ 170 list_t *node_prev = *head; 171 list_t *node_next = NULL; 172 for (list_t *p = *head; p != NULL; p = p->next) { 173 if (p->data < node->data) { 174 node_prev = p; 175 continue; 176 } 177 178 node_next = p; 179 break; 180 } 181 182 if (node_next == NULL) { /* append node to the tail */ 183 node_prev->next = node; 184 } else { 185 if (node_next == node_prev) { /* == *head */ 186 node->next = *head; 187 *head = node; 188 return; 189 } 190 191 /* node_prev -> node -> node_next */ 192 node_prev->next = node; 193 node->next = node_next; 194 } 195 } 196 197 static void 198 list_sort(list_t **head) 199 { 200 if (*head == NULL) 201 return; 202 203 list_t *headp = *head; /* copy *head to headp before snip headp->next */ 204 list_t *p = headp->next; /* init p (move forward) before cut-off */ 205 headp->next = NULL; /* now cut off headp->next */ 206 207 while (p != NULL) { 208 list_t *this = p; /* copy p to this before snip this->next */ 209 p = p->next; /* move p forward before cut-off */ 210 this->next = NULL; /* now cut off this->next */ 211 list_insert(&headp, this); /* insert this node to list headp */ 212 } 213 214 *head = headp; /* always save headp back even if headp == *head */ 215 } 216 #endif 217 218 static void 219 show(int a[], size_t n) 220 { 221 if (g_isint) { 222 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 223 printf("%-2d ", a[i]); 224 } else { 225 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 226 printf("%-2c ", a[i]); 227 } 228 printf(" "); 229 } 230 231 static void 232 a2l_init(list_t **head, int a[], size_t n) 233 { 234 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { 235 list_t *nodep = NULL; 236 nodep = (list_t *)malloc(sizeof (list_t)); 237 if (nodep == NULL) /* error: failed to malloc */ 238 return; 239 240 nodep->data = a[i]; 241 nodep->next = NULL; 242 243 list_init(head, nodep); 244 245 printf("Append a[%x]=%d: ", i, nodep->data); list_show(*head); 246 } 247 248 } 249 250 static void 251 a2l_fini(list_t *head, int a[], size_t n) 252 { 253 if (head == NULL) 254 return; 255 256 int k = 0; 257 for (list_t *p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) { 258 a[k++] = p->data; 259 260 if (k >= n) 261 break; 262 } 263 264 list_fini(head); 265 } 266 267 int 268 main(int argc, char *argv[]) 269 { 270 if (argc < 2) { 271 fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <C1> [C2] ... ", argv[0]); 272 return -1; 273 } 274 275 argc--; 276 argv++; 277 278 int n = argc; 279 int *a = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * n); 280 #define VALIDATE(p) do { if (p == NULL) return -1; } while (0) 281 VALIDATE(a); 282 283 char *s = getenv("ISINT"); 284 if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "true", 4) == 0) 285 g_isint = true; 286 else if (s != NULL && strncmp(s, "false", 4) == 0) 287 g_isint = false; 288 289 if (g_isint) { 290 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 291 *(a+i) = atoi(argv[i]); 292 } else { 293 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 294 *(a+i) = argv[i][0]; 295 } 296 297 printf(" "); 298 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) 299 printf("%-2x ", i); 300 printf(" "); 301 302 printf("Before sorting: "); show(a, n); 303 list_t *head = NULL; 304 a2l_init(&head, a, n); 305 list_sort(&head); 306 a2l_fini(head, a, n); 307 printf("After sorting: "); show(a, n); 308 309 #define FREE(p) do { free(p); p = NULL; } while (0) 310 FREE(a); 311 return 0; 312 }
o 编译并测试
$ gcc -g -Wall -m32 -std=c99 -D_USE_AUX -o sort sort.c $ ./sort 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b Before sorting: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 Append a[0]=9: 9 Append a[1]=8: 9 8 Append a[2]=7: 9 8 7 Append a[3]=6: 9 8 7 6 Append a[4]=5: 9 8 7 6 5 Append a[5]=4: 9 8 7 6 5 4 Append a[6]=3: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 Append a[7]=2: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Append a[8]=1: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Append a[9]=0: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Append a[a]=10: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 Append a[b]=1: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 After sorting: 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $ gcc -g -Wall -m32 -std=c99 -o sort sort.c $ ./sort 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b Before sorting: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 Append a[0]=9: 9 Append a[1]=8: 9 8 Append a[2]=7: 9 8 7 Append a[3]=6: 9 8 7 6 Append a[4]=5: 9 8 7 6 5 Append a[5]=4: 9 8 7 6 5 4 Append a[6]=3: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 Append a[7]=2: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 Append a[8]=1: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Append a[9]=0: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 Append a[a]=10: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 Append a[b]=1: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 10 1 After sorting: 0 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
小结: 链式存储排序显然比顺序存储排序节省了较大存储空间,同时时间效率也不错,只是实现起来较为复杂。关于Linux/Solaris中有关通用双向循环链表(本质上是"侵入式"链表)的实现,请参见其源码。
- Linux: linux/types.h, linux/list.h
- Solaris: list_impl.h, list.h, list.c