API
epoll提供给用户进程的接口有如下四个,本文基于linux-5.1.4源码详细分析每个API具体做了啥工作,通过UML时序图理清内核内部的函数调用关系。
-
int epoll_create1(int size);
创建一个epfd句柄,size为0时等价于int epoll_create(0)。
-
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event);
向epfd上添加/修改/删除fd。
-
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events, int maxevents, int timeout);
返回所有就绪的fd。
内核数据结构
先上一张UML类图,从整体进行把握,图中已经标出各个数据结构所在的文件。

下面贴出各个数据结构代码,切记,实际在过代码的时候,其实我们没有必要对每一个变量和每一行代码咬文嚼字,也不建议这样去做,我们只需要重点关注主要的数据成员和那些关键的代码行,把心思和精力投入到我们最该关注的那部分,从框架层面去把握整体,抓准各个模块的核心,各个模块之间如何耦合,如何同步,如何通信等,这才是能够让你快速进步的最优路线。
/*
* Each file descriptor added to the eventpoll interface will
* have an entry of this type linked to the "rbr" RB tree.
* Avoid increasing the size of this struct, there can be many thousands
* of these on a server and we do not want this to take another cache line.
*/
struct epitem {
union {
/* RB tree node links this structure to the eventpoll RB tree */
struct rb_node rbn;
/* Used to free the struct epitem */
struct rcu_head rcu;
};
/* List header used to link this structure to the eventpoll ready list */
struct list_head rdllink;
/*
* Works together "struct eventpoll"->ovflist in keeping the
* single linked chain of items.
*/
struct epitem *next;
/* The file descriptor information this item refers to */
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
/* Number of active wait queue attached to poll operations */
int nwait;
/* List containing poll wait queues */
struct list_head pwqlist;
/* The "container" of this item */
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* List header used to link this item to the "struct file" items list */
struct list_head fllink;
/* wakeup_source used when EPOLLWAKEUP is set */
struct wakeup_source __rcu *ws;
/* The structure that describe the interested events and the source fd */
struct epoll_event event;
};
/*
* This structure is stored inside the "private_data" member of the file
* structure and represents the main data structure for the eventpoll
* interface.
*/
struct eventpoll {
/*
* This mutex is used to ensure that files are not removed
* while epoll is using them. This is held during the event
* collection loop, the file cleanup path, the epoll file exit
* code and the ctl operations.
*/
struct mutex mtx;
/* Wait queue used by sys_epoll_wait() */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
/* Wait queue used by file->poll() */
wait_queue_head_t poll_wait;
/* List of ready file descriptors */
struct list_head rdllist;
/* Lock which protects rdllist and ovflist */
rwlock_t lock;
/* RB tree root used to store monitored fd structs */
struct rb_root_cached rbr;
/*
* This is a single linked list that chains all the "struct epitem" that
* happened while transferring ready events to userspace w/out
* holding ->lock.
*/
struct epitem *ovflist;
/* wakeup_source used when ep_scan_ready_list is running */
struct wakeup_source *ws;
/* The user that created the eventpoll descriptor */
struct user_struct *user;
struct file *file;
/* used to optimize loop detection check */
int visited;
struct list_head visited_list_link;
#ifdef CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL
/* used to track busy poll napi_id */
unsigned int napi_id;
#endif
};
/* eppoll_entry主要完成epitem和epitem事件发生时的callback(ep_poll_callback)
* 函数之间的关联,并将上述两个数据结构包装成一个链表节点,
* 挂载到目标文件file的waithead中。
* Wait structure used by the poll hooks
*/
struct eppoll_entry {
/* List header used to link this structure to the "struct epitem" */
struct list_head llink;
/* The "base" pointer is set to the container "struct epitem" */
struct epitem *base;
/*
* Wait queue item that will be linked to the target file wait
* queue head.
*/
wait_queue_entry_t wait;
/* The wait queue head that linked the "wait" wait queue item */
wait_queue_head_t *whead;
};
/* ep_pqueue主要完成epitem和callback函数的关联。
* 然后通过目标文件的poll函数调用callback函数ep_ptable_queue_proc。
* Poll函数一般由设备驱动提供,以网络设备为例,
* 他的poll函数为sock_poll然后根据sock类型调用不同的poll函数如:
* packet_poll。packet_poll在通过datagram_poll调用sock_poll_wait,
* 最后在poll_wait实际调用callback函数(ep_ptable_queue_proc)
* Wrapper struct used by poll queueing
*/
struct ep_pqueue {
poll_table pt;
struct epitem *epi;
};
/* Used by the ep_send_events() function as callback private data */
struct ep_send_events_data {
int maxevents;
struct epoll_event __user *events;
int res;
};
struct fd {
struct file *file;
unsigned int flags;
};
全局调用关系
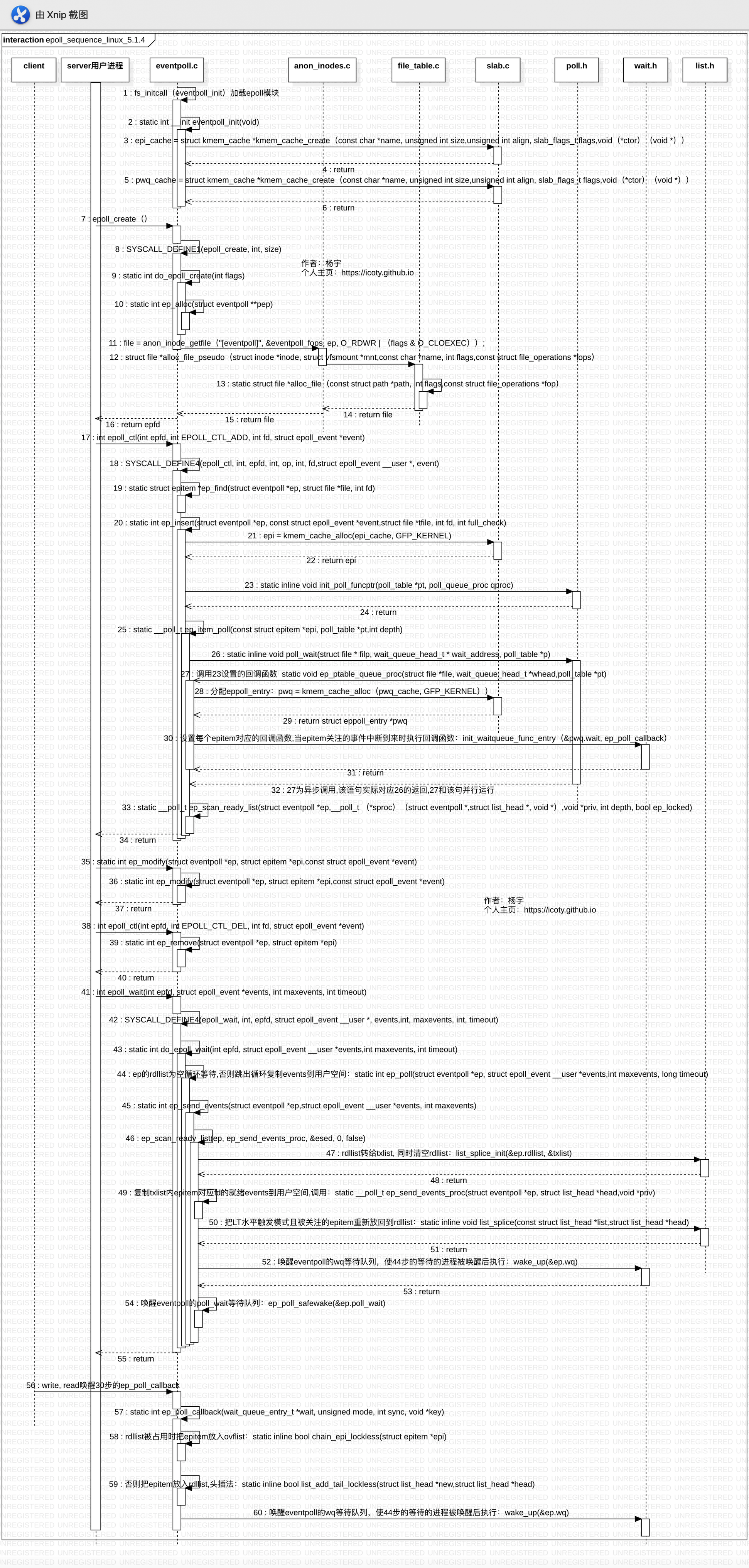
再贴一张各个API从用户进程陷入到内核态并执行系统调用的详细过程,以及client发数据过来时触发ep_poll_callback回调函数的执行流程。
epoll模块初始化&内存池开辟
epoll是内核的一个module,内核启动时会初始化这个module。
// fs/eventpoll.c
static int __init eventpoll_init(void)
{
struct sysinfo si;
si_meminfo(&si);
/*
* Allows top 4% of lomem to be allocated for epoll watches (per user).
*/
max_user_watches = (((si.totalram - si.totalhigh) / 25) << PAGE_SHIFT) /
EP_ITEM_COST;
BUG_ON(max_user_watches < 0);
/*
* Initialize the structure used to perform epoll file descriptor
* inclusion loops checks.
*/
ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_loop_ncalls);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC
/* Initialize the structure used to perform safe poll wait head wake ups */
ep_nested_calls_init(&poll_safewake_ncalls);
#endif
/*
* We can have many thousands of epitems, so prevent this from
* using an extra cache line on 64-bit (and smaller) CPUs
*/
BUILD_BUG_ON(sizeof(void *) <= 8 && sizeof(struct epitem) > 128);
// 提前开辟eventpoll_epi内存池,UML时序图的第21步alloc时直接从内存池里取,
// 而不是重新调用malloc,效率得以提高
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct epitem" items */
epi_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_epi",
sizeof(struct epitem),0, placehold_flag, 0);
// 提前开辟eventpoll_pwq内存池,UML时序图的第28步alloc时直接从内存池里取
// 而不是重新调用malloc,效率得以提高
/* Allocates slab cache used to allocate "struct eppoll_entry" */
pwq_cache = kmem_cache_create("eventpoll_pwq",
sizeof(struct eppoll_entry), 0, SLAB_PANIC|SLAB_ACCOUNT, NULL);
return 0;
}
fs_initcall(eventpoll_init);
epoll_create
用户空间调用epoll_create(0)或epoll_create1(int),其实质就是在名为"eventpollfs"的文件系统里创建了一个新文件,同时为该文件申请一个fd,绑定一个inode,最后返回该文件句柄。
epoll_create/epoll_create1陷入内核
// fs/eventpoll.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create1, int, flags)
{
return do_epoll_create(flags);
}
SYSCALL_DEFINE1(epoll_create, int, size)
{
if (size <= 0)
return -EINVAL;
return do_epoll_create(0);
}
do_epoll_create/ep_alloc
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c
* Open an eventpoll file descriptor.
*/
static int do_epoll_create(int flags)
{
int error, fd;
struct eventpoll *ep = NULL;
struct file *file;
/* Check the EPOLL_* constant for consistency. */
BUILD_BUG_ON(EPOLL_CLOEXEC != O_CLOEXEC);
if (flags & ~EPOLL_CLOEXEC)
return -EINVAL;
/*
* 申请一个struct eventpoll内存空间,执行初始化后赋给ep
* Create the internal data structure ("struct eventpoll").
*/
error = ep_alloc(&ep);
if (error < 0)
return error;
/*
* 获取一个未使用的fd句柄
* Creates all the items needed to setup an eventpoll file. That is,
* a file structure and a free file descriptor.
*/
fd = get_unused_fd_flags(O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (fd < 0) {
error = fd;
goto out_free_ep;
}
file = anon_inode_getfile("[eventpoll]", &eventpoll_fops, ep,
O_RDWR | (flags & O_CLOEXEC));
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
error = PTR_ERR(file);
goto out_free_fd;
}
ep->file = file;
// 绑定fd和file
fd_install(fd, file);
// 这个fd就是epfd句柄,返回给用户进程的
return fd;
out_free_fd:
put_unused_fd(fd);
out_free_ep:
ep_free(ep);
return error;
}
// fs/eventpoll.c
// 形参是一个二级指针,该接口就是简单的分配一个struct eventpoll,然后执行初始化工作
static int ep_alloc(struct eventpoll **pep)
{
int error;
struct user_struct *user;
struct eventpoll *ep;
user = get_current_user();
error = -ENOMEM;
ep = kzalloc(sizeof(*ep), GFP_KERNEL);
if (unlikely(!ep))
goto free_uid;
mutex_init(&ep->mtx);
rwlock_init(&ep->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->wq);
init_waitqueue_head(&ep->poll_wait);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&ep->rdllist);
ep->rbr = RB_ROOT_CACHED;
ep->ovflist = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
ep->user = user;
*pep = ep;
return 0;
free_uid:
free_uid(user);
return error;
}
anon_inode_getfile/alloc_file_pseudo/alloc_file
/**
* fs/anon_inodes.c
* anon_inode_getfile - creates a new file instance by hooking it up to an
* anonymous inode, and a dentry that describe the "class"
* of the file
*
* @name: [in] name of the "class" of the new file
* @fops: [in] file operations for the new file
* @priv: [in] private data for the new file (will be file's private_data)
* @flags: [in] flags
*
* Creates a new file by hooking it on a single inode. This is useful for files
* that do not need to have a full-fledged inode in order to operate correctly.
* All the files created with anon_inode_getfile() will share a single inode,
* hence saving memory and avoiding code duplication for the file/inode/dentry
* setup. Returns the newly created file* or an error pointer.
* 在一个inode上挂接一个新文件,这对于不需要完整inode才能正确操作的文件非常有用。
* 使用anon_inode_getfile()创建的所有文件都将共享一个inode,
* 因此可以节省内存并避免文件/inode/dentry设置的代码重复。
* 返回新创建的文件*或错误指针。
*/
struct file *anon_inode_getfile(const char *name,const struct file_operations *fops,void *priv, int flags)
{
struct file *file;
if (IS_ERR(anon_inode_inode))
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
if (fops->owner && !try_module_get(fops->owner))
return ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/*
* We know the anon_inode inode count is always greater than zero,
* so ihold() is safe.
*/
ihold(anon_inode_inode);
// 创建一个名字为“[eventpoll]”的eventpollfs文件描述符
file = alloc_file_pseudo(anon_inode_inode, anon_inode_mnt, name,
flags & (O_ACCMODE | O_NONBLOCK), fops);
if (IS_ERR(file))
goto err;
file->f_mapping = anon_inode_inode->i_mapping;
// file->private_data指向传进来的priv( = struct eventpoll *ep)
file->private_data = priv;
return file;
err:
iput(anon_inode_inode);
module_put(fops->owner);
return file;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(anon_inode_getfile);
// fs/file_table.c
struct file *alloc_file_pseudo(struct inode *inode, struct vfsmount *mnt,
const char *name, int flags,const struct file_operations *fops)
{
static const struct dentry_operations anon_ops = {
.d_dname = simple_dname
};
struct qstr this = QSTR_INIT(name, strlen(name));
struct path path;
struct file *file;
// 挂载名为“[eventpoll]”的eventpollfs文件系统
path.dentry = d_alloc_pseudo(mnt->mnt_sb, &this);
if (!path.dentry)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
if (!mnt->mnt_sb->s_d_op)
d_set_d_op(path.dentry, &anon_ops);
path.mnt = mntget(mnt);
d_instantiate(path.dentry, inode);
// inode和file绑定,返回绑定后的file结构
file = alloc_file(&path, flags, fops);
if (IS_ERR(file)) {
ihold(inode);
path_put(&path);
}
return file;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(alloc_file_pseudo);
/**
* fs/file_table.c
* alloc_file - allocate and initialize a 'struct file'
*
* @path: the (dentry, vfsmount) pair for the new file
* @flags: O_... flags with which the new file will be opened
* @fop: the 'struct file_operations' for the new file
*/
static struct file *alloc_file(const struct path *path, int flags,
const struct file_operations *fop)
{
struct file *file;
// 申请一个空的file结构
file = alloc_empty_file(flags, current_cred());
if (IS_ERR(file))
return file;
file->f_path = *path;
file->f_inode = path->dentry->d_inode;
file->f_mapping = path->dentry->d_inode->i_mapping;
file->f_wb_err = filemap_sample_wb_err(file->f_mapping);
if ((file->f_mode & FMODE_READ) && likely(fop->read || fop->read_iter))
file->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_READ;
if ((file->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE) && likely(fop->write || fop->write_iter))
file->f_mode |= FMODE_CAN_WRITE;
file->f_mode |= FMODE_OPENED;
file->f_op = fop;
if ((file->f_mode & (FMODE_READ | FMODE_WRITE)) == FMODE_READ)
i_readcount_inc(path->dentry->d_inode);
return file;
}
epoll_ctl
用户进程调用int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event),op可填EPOLL_CTL_ADD(注册fd到epfd)、EPOLL_CTL_MOD(修改已注册fd监听的事件)和EPOLL_CTL_DEL(从epfd中删除fd)。
epoll_ctl陷入内核
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c
* The following function implements the controller interface for
* the eventpoll file that enables the insertion/removal/change of
* file descriptors inside the interest set.
*/
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,
struct epoll_event __user *, event)
{
int error;
int full_check = 0;
struct fd f, tf;
struct eventpoll *ep;
struct epitem *epi;
struct epoll_event epds;
struct eventpoll *tep = NULL;
error = -EFAULT;
// copy_from_user将用户空间关注的event事件拷贝到内核空间
if (ep_op_has_event(op) &&
copy_from_user(&epds, event, sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
goto error_return;
error = -EBADF;
f = fdget(epfd);
if (!f.file)
goto error_return;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the target file */
tf = fdget(fd);
if (!tf.file)
goto error_fput;
/* The target file descriptor must support poll */
error = -EPERM;
if (!file_can_poll(tf.file))
goto error_tgt_fput;
/* 如果系统设置了自动休眠模式(通过/sys/power/autosleep),
* 当唤醒设备的事件发生时,设备驱动会保持唤醒状态,直到事件进入排队状态。
* 为了保持设备唤醒直到事件处理完成,必须使用epoll EPOLLWAKEUP 标记。
* 一旦给structe poll_event中的events字段设置了EPOLLWAKEUP标记,系统会在事件排队时就保持唤醒,
* 从epoll_wait调用开始,持续要下一次epoll_wait调用。
*/
/* Check if EPOLLWAKEUP is allowed */
if (ep_op_has_event(op))
ep_take_care_of_epollwakeup(&epds);
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the file descriptor
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file. And also we do not permit
* adding an epoll file descriptor inside itself.
*/
error = -EINVAL;
if (f.file == tf.file || !is_file_epoll(f.file))
goto error_tgt_fput;
/*
* epoll adds to the wakeup queue at EPOLL_CTL_ADD time only,
* so EPOLLEXCLUSIVE is not allowed for a EPOLL_CTL_MOD operation.
* Also, we do not currently supported nested exclusive wakeups.
*/
if (ep_op_has_event(op) && (epds.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)) {
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_MOD)
goto error_tgt_fput;
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD && (is_file_epoll(tf.file) ||
(epds.events & ~EPOLLEXCLUSIVE_OK_BITS)))
goto error_tgt_fput;
}
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
*/
ep = f.file->private_data;
/*
* When we insert an epoll file descriptor, inside another epoll file
* descriptor, there is the change of creating closed loops, which are
* better be handled here, than in more critical paths. While we are
* checking for loops we also determine the list of files reachable
* and hang them on the tfile_check_list, so we can check that we
* haven't created too many possible wakeup paths.
*
* We do not need to take the global 'epumutex' on EPOLL_CTL_ADD when
* the epoll file descriptor is attaching directly to a wakeup source,
* unless the epoll file descriptor is nested. The purpose of taking the
* 'epmutex' on add is to prevent complex toplogies such as loops and
* deep wakeup paths from forming in parallel through multiple
* EPOLL_CTL_ADD operations.
*/
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);
if (op == EPOLL_CTL_ADD) {
if (!list_empty(&f.file->f_ep_links) ||
is_file_epoll(tf.file)) {
full_check = 1;
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
mutex_lock(&epmutex);
if (is_file_epoll(tf.file)) {
error = -ELOOP;
if (ep_loop_check(ep, tf.file) != 0) {
clear_tfile_check_list();
goto error_tgt_fput;
}
} else
list_add(&tf.file->f_tfile_llink,
&tfile_check_list);
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, 0);
if (is_file_epoll(tf.file)) {
tep = tf.file->private_data;
mutex_lock_nested(&tep->mtx, 1);
}
}
}
/*
* Try to lookup the file inside our RB tree, Since we grabbed "mtx"
* above, we can be sure to be able to use the item looked up by
* ep_find() till we release the mutex.
* 从红黑树中寻找添加的fd是否存在,存在则返回到ep中,否则返回NULL
*/
epi = ep_find(ep, tf.file, fd);
error = -EINVAL;
switch (op) {
case EPOLL_CTL_ADD:
// 若ep为空说明红黑树中不存在,执行ep_insert添加到红黑树中
if (!epi) {
epds.events |= EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP;
// 如果不存在则添加,已经存在不重复添加
error = ep_insert(ep, &epds, tf.file, fd, full_check);
} else
error = -EEXIST;
if (full_check)
clear_tfile_check_list();
break;
// 删除fd调用ep_remove
case EPOLL_CTL_DEL:
if (epi)
error = ep_remove(ep, epi);
else
error = -ENOENT;
break;
// 修改已注册fd所监听的事件,调用ep_modify
case EPOLL_CTL_MOD:
if (epi) {
if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)) {
epds.events |= EPOLLERR | EPOLLHUP;
error = ep_modify(ep, epi, &epds);
}
} else
error = -ENOENT;
break;
}
if (tep != NULL)
mutex_unlock(&tep->mtx);
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
error_tgt_fput:
if (full_check)
mutex_unlock(&epmutex);
fdput(tf);
error_fput:
fdput(f);
error_return:
return error;
}
ep_find
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c
* Search the file inside the eventpoll tree. The RB tree operations
* are protected by the "mtx" mutex, and ep_find() must be called with
* "mtx" held.
*/
static struct epitem *ep_find(struct eventpoll *ep, struct file *file, int fd)
{
int kcmp;
struct rb_node *rbp;
struct epitem *epi, *epir = NULL;
struct epoll_filefd ffd;
ep_set_ffd(&ffd, file, fd);
// 从红黑树根节开始二分查找,判断左右子树
for (rbp = ep->rbr.rb_root.rb_node; rbp; ) {
epi = rb_entry(rbp, struct epitem, rbn);
kcmp = ep_cmp_ffd(&ffd, &epi->ffd);
if (kcmp > 0)
rbp = rbp->rb_right;
else if (kcmp < 0)
rbp = rbp->rb_left;
else {
epir = epi;
break;
}
}
return epir;
}
ep_insert
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c
* Must be called with "mtx" held.
*/
static int ep_insert(struct eventpoll *ep, const struct epoll_event *event,
struct file *tfile, int fd, int full_check)
{
int error, pwake = 0;
__poll_t revents;
long user_watches;
struct epitem *epi;
struct ep_pqueue epq;
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
user_watches = atomic_long_read(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
if (unlikely(user_watches >= max_user_watches))
return -ENOSPC;
// epi_cache内存池在epoll模块初始化时已经分配,这里根据slab直接取一个epitem
if (!(epi = kmem_cache_alloc(epi_cache, GFP_KERNEL)))
return -ENOMEM;
// 初始化 epitem
/* Item initialization follow here ... */
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->rdllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->fllink);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&epi->pwqlist);
epi->ep = ep;
ep_set_ffd(&epi->ffd, tfile, fd);
epi->event = *event;
epi->nwait = 0;
epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLWAKEUP) {
error = ep_create_wakeup_source(epi);
if (error)
goto error_create_wakeup_source;
} else {
RCU_INIT_POINTER(epi->ws, NULL);
}
// 创建一个struct ep_pqueue epq, 并与epitem(epi)关联
/* Initialize the poll table using the queue callback */
epq.epi = epi;
/* 设置epq的回调函数为ep_ptable_queue_proc,当调用poll_wait时会调用该回调函数,
* 而函数体ep_ptable_queue_proc内部所做的主要工作,
* 就是把epitem对应fd的事件到来时的回调函数设置为ep_poll_callback。
* ep_poll_callback所做的主要工作就是把就绪的fd放到就绪链表rdllist上,
* 然后唤醒epoll_wait的调用者, 被唤醒的进程再把rdllist上就绪的fd的events拷贝给用户进程,
* 完成一个闭环。
*/
init_poll_funcptr(&epq.pt, ep_ptable_queue_proc);
/*
* Attach the item to the poll hooks and get current event bits.
* We can safely use the file* here because its usage count has
* been increased by the caller of this function. Note that after
* this operation completes, the poll callback can start hitting
* the new item.
* 判断当前插入的event是否刚好发生,返回就绪事件的掩码赋给revents,
* 如果发生,那么做一个ready动作,
* 后面的if语句将epitem加入到rdlist中,并对epoll上的wait队列调用wakeup
*/
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &epq.pt, 1);
/*
* We have to check if something went wrong during the poll wait queue
* install process. Namely an allocation for a wait queue failed due
* high memory pressure.
*/
error = -ENOMEM;
if (epi->nwait < 0)
goto error_unregister;
/* Add the current item to the list of active epoll hook for this file */
spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);
// 每个文件会将所有监听自己的epitem链起来
list_add_tail_rcu(&epi->fllink, &tfile->f_ep_links);
spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);
/*
* Add the current item to the RB tree. All RB tree operations are
* protected by "mtx", and ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
* 将epitem插入到对应的eventpoll红黑树中去,红黑树用一个互斥锁进行保护
*/
ep_rbtree_insert(ep, epi);
/* now check if we've created too many backpaths */
error = -EINVAL;
if (full_check && reverse_path_check())
goto error_remove_epi;
/* We have to drop the new item inside our item list to keep track of it */
write_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
/* record NAPI ID of new item if present */
ep_set_busy_poll_napi_id(epi);
/* If the file is already "ready" we drop it inside the ready list */
if (revents && !ep_is_linked(epi)) {
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
/* Notify waiting tasks that events are available */
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
write_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
atomic_long_inc(&ep->user->epoll_watches);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return 0;
error_remove_epi:
spin_lock(&tfile->f_lock);
list_del_rcu(&epi->fllink);
spin_unlock(&tfile->f_lock);
rb_erase_cached(&epi->rbn, &ep->rbr);
error_unregister:
ep_unregister_pollwait(ep, epi);
/*
* We need to do this because an event could have been arrived on some
* allocated wait queue. Note that we don't care about the ep->ovflist
* list, since that is used/cleaned only inside a section bound by "mtx".
* And ep_insert() is called with "mtx" held.
*/
write_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
if (ep_is_linked(epi))
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
write_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
wakeup_source_unregister(ep_wakeup_source(epi));
error_create_wakeup_source:
kmem_cache_free(epi_cache, epi);
return error;
}
kmem_cache_alloc
/**
* slab算法从内存池cachep中分配一个实例返回
* mm/slab.c
* kmem_cache_alloc - Allocate an object
* @cachep: The cache to allocate from.
* @flags: See kmalloc().
*
* Allocate an object from this cache. The flags are only relevant
* if the cache has no available objects.
*
* Return: pointer to the new object or %NULL in case of error
*/
void *kmem_cache_alloc(struct kmem_cache *cachep, gfp_t flags)
{
void *ret = slab_alloc(cachep, flags, _RET_IP_);
trace_kmem_cache_alloc(_RET_IP_, ret,
cachep->object_size, cachep->size, flags);
return ret;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(kmem_cache_alloc);
init_poll_funcptr/ep_ptable_queue_proc/ep_poll_callback/init_waitqueue_func_entry
init_poll_funcptr:设置epq的回调函数为ep_ptable_queue_proc,当调用poll_wait时会调用该回调函数;
ep_ptable_queue_proc:该函数内部所做的主要工作,就是把epitem对应fd的事件到来时的回调函数设置为ep_poll_callback。
ep_poll_callback:主要工作就是把就绪的fd放到就绪链表rdllist上,然后唤醒epoll_wait的调用者,被唤醒的进程再把rdllist上就绪的fd的events拷贝给用户进程,完成一个闭环。
/*
* 设置回调
* include/linux/poll.h
*/
static inline void init_poll_funcptr(poll_table *pt, poll_queue_proc qproc)
{
pt->_qproc = qproc;
pt->_key = ~(__poll_t)0; /* all events enabled */
}
/*
* This is the callback that is used to add our wait queue to the
* target file wakeup lists.
* struct file *file(目标文件)= epi->ffd.file,
* wait_queue_head_t *whead(目标文件的waitlist)= eventpoll->poll_wait,
* poll_table *pt(前面生成的poll_table)
*/
static void ep_ptable_queue_proc(struct file *file, wait_queue_head_t *whead,poll_table *pt)
{
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_epqueue(pt);
// 创建一个struct eppoll_entry,与对应的epitem关联上
struct eppoll_entry *pwq;
// 从pwq_cache内存池中取一个struct eppoll_entry
if (epi->nwait >= 0 && (pwq = kmem_cache_alloc(pwq_cache, GFP_KERNEL))) {
// 把每个epitem对应的回调函数设置为ep_poll_callback,
// 当epitem关注的事件中断到来时会执行回调函数ep_poll_callback
init_waitqueue_func_entry(&pwq->wait, ep_poll_callback);
pwq->whead = whead;
// 关联上epitem
pwq->base = epi;
// 通过add_wait_queue将epoll_entry挂载到目标文件的waitlist。
// 完成这个动作后,epoll_entry已经被挂载到waitlist
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE)
add_wait_queue_exclusive(whead, &pwq->wait);
else
add_wait_queue(whead, &pwq->wait);
// eppoll_entry->llink执行epitem->pwqlist
list_add_tail(&pwq->llink, &epi->pwqlist);
epi->nwait++;
} else {
/* We have to signal that an error occurred */
epi->nwait = -1;
}
}
// include/linux/wait.h
static inline void init_waitqueue_func_entry(struct wait_queue_entry *wq_entry,
wait_queue_func_t func)
{
wq_entry->flags = 0;
wq_entry->private = NULL;
wq_entry->func = func;
}
/*
* fs/eventpoll.c
* This is the callback that is passed to the wait queue wakeup
* mechanism. It is called by the stored file descriptors when they
* have events to report.
*
* This callback takes a read lock in order not to content with concurrent
* events from another file descriptors, thus all modifications to ->rdllist
* or ->ovflist are lockless. Read lock is paired with the write lock from
* ep_scan_ready_list(), which stops all list modifications and guarantees
* that lists state is seen correctly.
*
* Another thing worth to mention is that ep_poll_callback() can be called
* concurrently for the same @epi from different CPUs if poll table was inited
* with several wait queues entries. Plural wakeup from different CPUs of a
* single wait queue is serialized by wq.lock, but the case when multiple wait
* queues are used should be detected accordingly. This is detected using
* cmpxchg() operation.
*/
static int ep_poll_callback(wait_queue_entry_t *wait, unsigned mode, int sync, void *key)
{
int pwake = 0;
struct epitem *epi = ep_item_from_wait(wait);
struct eventpoll *ep = epi->ep;
__poll_t pollflags = key_to_poll(key);
unsigned long flags;
int ewake = 0;
read_lock_irqsave(&ep->lock, flags);
ep_set_busy_poll_napi_id(epi);
/*
* If the event mask does not contain any poll(2) event, we consider the
* descriptor to be disabled. This condition is likely the effect of the
* EPOLLONESHOT bit that disables the descriptor when an event is received,
* until the next EPOLL_CTL_MOD will be issued.
*/
if (!(epi->event.events & ~EP_PRIVATE_BITS))
goto out_unlock;
/*
* Check the events coming with the callback. At this stage, not
* every device reports the events in the "key" parameter of the
* callback. We need to be able to handle both cases here, hence the
* test for "key" != NULL before the event match test.
*/
if (pollflags && !(pollflags & epi->event.events))
goto out_unlock;
/*
* If we are transferring events to userspace, we can hold no locks
* (because we're accessing user memory, and because of linux f_op->poll()
* semantics). All the events that happen during that period of time are
* chained in ep->ovflist and requeued later on.
*/
if (READ_ONCE(ep->ovflist) != EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
// epi->next == EP_UNACTIVE_PTR说明rdllist当前被其他进程持有,
// 因此调用chain_epi_lockless把epitem放入vovflist上
if (epi->next == EP_UNACTIVE_PTR && chain_epi_lockless(epi))
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
goto out_unlock;
}
// rdllist抢占成功,调用list_add_tail_lockless把epitem挂入rdllist上
/* If this file is already in the ready list we exit soon */
if (!ep_is_linked(epi) && list_add_tail_lockless(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist)) {
ep_pm_stay_awake_rcu(epi);
}
/*
* Wake up ( if active ) both the eventpoll wait list and the ->poll()
* wait list.
*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq)) {
if ((epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE) &&
!(pollflags & POLLFREE)) {
switch (pollflags & EPOLLINOUT_BITS) {
case EPOLLIN:
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLIN)
ewake = 1;
break;
case EPOLLOUT:
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLOUT)
ewake = 1;
break;
case 0:
ewake = 1;
break;
}
}
// 同时唤醒eventpoll的wq等待队列,也就是唤醒poll_wait的调用者
wake_up(&ep->wq);
}
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
out_unlock:
read_unlock_irqrestore(&ep->lock, flags);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLEXCLUSIVE))
ewake = 1;
if (pollflags & POLLFREE) {
/*
* If we race with ep_remove_wait_queue() it can miss
* ->whead = NULL and do another remove_wait_queue() after
* us, so we can't use __remove_wait_queue().
*/
list_del_init(&wait->entry);
/*
* ->whead != NULL protects us from the race with ep_free()
* or ep_remove(), ep_remove_wait_queue() takes whead->lock
* held by the caller. Once we nullify it, nothing protects
* ep/epi or even wait.
*/
smp_store_release(&ep_pwq_from_wait(wait)->whead, NULL);
}
return ewake;
}
ep_item_poll/poll_wait/ep_scan_ready_list
/*
* Differs from ep_eventpoll_poll() in that internal callers already have
* the ep->mtx so we need to start from depth=1, such that mutex_lock_nested()
* is correctly annotated.
*/
static __poll_t ep_item_poll(const struct epitem *epi, poll_table *pt,int depth)
{
struct eventpoll *ep;
bool locked;
pt->_key = epi->event.events;
if (!is_file_epoll(epi->ffd.file))
return vfs_poll(epi->ffd.file, pt) & epi->event.events;
// 拿到eventpoll,回头过去看UML数据结构,private_data是指向eventpoll的
ep = epi->ffd.file->private_data;
// 这里面会执行前面设置的ep_ptable_queue_proc回调体
// ep_ptable_queue_proc函数体的工作在前面已经介绍过
poll_wait(epi->ffd.file, &ep->poll_wait, pt);
locked = pt && (pt->_qproc == ep_ptable_queue_proc);
// 把就绪链表rdllist拷贝到用户空间
return ep_scan_ready_list(epi->ffd.file->private_data,
ep_read_events_proc, &depth, depth,
locked) & epi->event.events;
}
// include/linux/poll.h
static inline void poll_wait(struct file * filp, wait_queue_head_t * wait_address,
poll_table *p)
{
if (p && p->_qproc && wait_address)
p->_qproc(filp, wait_address, p);
}
/**
* ep_scan_ready_list - Scans the ready list in a way that makes possible for
* the scan code, to call f_op->poll(). Also allows for
* O(NumReady) performance.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the epoll private data structure.
* @sproc: Pointer to the scan callback.
* @priv: Private opaque data passed to the @sproc callback.
* @depth: The current depth of recursive f_op->poll calls.
* @ep_locked: caller already holds ep->mtx
*
* Returns: The same integer error code returned by the @sproc callback.
*/
static __poll_t ep_scan_ready_list(struct eventpoll *ep,
__poll_t (*sproc)(struct eventpoll *,
struct list_head *, void *),void *priv,
int depth, bool ep_locked)
{
__poll_t res;
int pwake = 0;
struct epitem *epi, *nepi;
LIST_HEAD(txlist);
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
/*
* We need to lock this because we could be hit by
* eventpoll_release_file() and epoll_ctl().
*/
if (!ep_locked)
mutex_lock_nested(&ep->mtx, depth);
/*
* Steal the ready list, and re-init the original one to the
* empty list. Also, set ep->ovflist to NULL so that events
* happening while looping w/out locks, are not lost. We cannot
* have the poll callback to queue directly on ep->rdllist,
* because we want the "sproc" callback to be able to do it
* in a lockless way.
*/
write_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
// 把就绪链表rdllist赋给临时的txlist,执行该操作后rdllist会被清空,
// 因为rdllist需要腾出来给其他进程继续往上放内容,
// 从而把txlist内epitem对应fd的就绪events复制到用户空间
list_splice_init(&ep->rdllist, &txlist);
WRITE_ONCE(ep->ovflist, NULL);
write_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
/*
* sproc就是前面设置好的ep_poll_callback,事件到来了执行该回调体,
* sproc会把就绪的epitem放入rdllist或ovflist上
* Now call the callback function.
*/
res = (*sproc)(ep, &txlist, priv);
write_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
/*
* During the time we spent inside the "sproc" callback, some
* other events might have been queued by the poll callback.
* We re-insert them inside the main ready-list here.
*/
for (nepi = READ_ONCE(ep->ovflist); (epi = nepi) != NULL;
nepi = epi->next, epi->next = EP_UNACTIVE_PTR) {
/*
* We need to check if the item is already in the list.
* During the "sproc" callback execution time, items are
* queued into ->ovflist but the "txlist" might already
* contain them, and the list_splice() below takes care of them.
*/
if (!ep_is_linked(epi)) {
/*
* ->ovflist is LIFO, so we have to reverse it in order
* to keep in FIFO.
*/
list_add(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}
}
/*
* We need to set back ep->ovflist to EP_UNACTIVE_PTR, so that after
* releasing the lock, events will be queued in the normal way inside
* ep->rdllist.
*/
WRITE_ONCE(ep->ovflist, EP_UNACTIVE_PTR);
/*
* 把水平触发EPOLLLT属性的epitem依旧挂回到rdllist,
* 因为我们希望即使没有新的数据到来,只要数据还没被用户空间读完,就继续上报
* Quickly re-inject items left on "txlist".
*/
list_splice(&txlist, &ep->rdllist);
__pm_relax(ep->ws);
if (!list_empty(&ep->rdllist)) {
/*
* Wake up (if active) both the eventpoll wait list and
* the ->poll() wait list (delayed after we release the lock).
* wake_up唤醒epoll_wait的调用者
*/
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->wq))
wake_up(&ep->wq);
if (waitqueue_active(&ep->poll_wait))
pwake++;
}
write_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
if (!ep_locked)
mutex_unlock(&ep->mtx);
/* We have to call this outside the lock */
if (pwake)
ep_poll_safewake(&ep->poll_wait);
return res;
}
到此,epoll_ctl的分析就已经完了,这里只描述的EPOLL_CTL_ADD调用。EPOLL_CTL_MOD/EPOLL_CTL_DEL相对就简单很多,这三个操作差异主要体现在fs/eventpoll.c文件内接口SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_ctl, int, epfd, int, op, int, fd,struct epoll_event __user*, event)的switch语句部分,EPOLL_CTL_MOD和EPOLL_CTL_DEL分别对应ep_modify和ep_remove,这两个函数就是从红黑树中去找到对应的节点进行修改和删除操作,因此这里没有贴代码。
epoll_wait
epoll_wait陷入内核
// fs/eventpoll.c
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(epoll_wait, int, epfd, struct epoll_event __user *,
events,int, maxevents, int, timeout)
{
return do_epoll_wait(epfd, events, maxevents, timeout);
}
do_epoll_wait/ep_poll/ep_send_events/ep_send_events_proc
/*
* Implement the event wait interface for the eventpoll file. It is the kernel
* part of the user space epoll_wait(2).
*/
static int do_epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, int timeout)
{
int error;
// struct fd结构在数据结构部分代码已经列出
struct fd f;
struct eventpoll *ep;
/* The maximum number of event must be greater than zero */
if (maxevents <= 0 || maxevents > EP_MAX_EVENTS)
return -EINVAL;
/* Verify that the area passed by the user is writeable */
if (!access_ok(events, maxevents * sizeof(struct epoll_event)))
return -EFAULT;
/* Get the "struct file *" for the eventpoll file */
f = fdget(epfd);
if (!f.file)
return -EBADF;
/*
* We have to check that the file structure underneath the fd
* the user passed to us _is_ an eventpoll file.
*/
error = -EINVAL;
if (!is_file_epoll(f.file))
goto error_fput;
/*
* At this point it is safe to assume that the "private_data" contains
* our own data structure.
* 直接拿到eventpoll对象
*/
ep = f.file->private_data;
// ep_poll时主循环体,当rdllist为空时调用者根据设置的超时参数,
// 决定是等待还是返回
/* Time to fish for events ... */
error = ep_poll(ep, events, maxevents, timeout);
error_fput:
fdput(f);
return error;
}
/**
* ep_poll - Retrieves ready events, and delivers them to the caller supplied
* event buffer.
*
* @ep: Pointer to the eventpoll context.
* @events: Pointer to the userspace buffer where the ready events should be
* stored.
* @maxevents: Size (in terms of number of events) of the caller event buffer.
* @timeout: Maximum timeout for the ready events fetch operation, in
* milliseconds. If the @timeout is zero, the function will not block,
* while if the @timeout is less than zero, the function will block
* until at least one event has been retrieved (or an error
* occurred).
*
* Returns: Returns the number of ready events which have been fetched, or an
* error code, in case of error.
*/
static int ep_poll(struct eventpoll *ep, struct epoll_event __user *events,
int maxevents, long timeout)
{
int res = 0, eavail, timed_out = 0;
u64 slack = 0;
bool waiter = false;
wait_queue_entry_t wait;
ktime_t expires, *to = NULL;
lockdep_assert_irqs_enabled();
// 超时设置
if (timeout > 0) {
struct timespec64 end_time = ep_set_mstimeout(timeout);
slack = select_estimate_accuracy(&end_time);
to = &expires;
*to = timespec64_to_ktime(end_time);
} else if (timeout == 0) { // 立即返回
/*
* Avoid the unnecessary trip to the wait queue loop, if the
* caller specified a non blocking operation. We still need
* lock because we could race and not see an epi being added
* to the ready list while in irq callback. Thus incorrectly
* returning 0 back to userspace.
*/
timed_out = 1;
write_lock_irq(&ep->lock);
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
write_unlock_irq(&ep->lock);
goto send_events;
}// 否则是永久等待,直到有新的事件到来
fetch_events:
if (!ep_events_available(ep))
ep_busy_loop(ep, timed_out);
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
goto send_events;
/*
* Busy poll timed out. Drop NAPI ID for now, we can add
* it back in when we have moved a socket with a valid NAPI
* ID onto the ready list.
*/
ep_reset_busy_poll_napi_id(ep);
/*
* We don't have any available event to return to the caller. We need
* to sleep here, and we will be woken by ep_poll_callback() when events
* become available.
*/
if (!waiter) {
waiter = true;
// ep->rdllist存放的是已就绪(read)的fd,为空时说明当前没有就绪的fd,
// 创建一个等待队列,并使用当前进程(current)初始化
init_waitqueue_entry(&wait, current);
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
// 将当前进程添加到等待队列
__add_wait_queue_exclusive(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
for (;;) {
/*
* We don't want to sleep if the ep_poll_callback() sends us
* a wakeup in between. That's why we set the task state
* to TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE before doing the checks.
*/
set_current_state(TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
/*
* Always short-circuit for fatal signals to allow
* threads to make a timely exit without the chance of
* finding more events available and fetching
* repeatedly.
*/
if (fatal_signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
// ep_events_available内部会判断rdllist是否为空
eavail = ep_events_available(ep);
if (eavail)
break; // 循环体,如果rdllist不为空,则跳出循环体,进入send_events
if (signal_pending(current)) {
res = -EINTR;
break;
}
if (!schedule_hrtimeout_range(to, slack, HRTIMER_MODE_ABS)) {
timed_out = 1;
break;
}
}
__set_current_state(TASK_RUNNING);
send_events:
/*
* Try to transfer events to user space. In case we get 0 events and
* there's still timeout left over, we go trying again in search of
* more luck.
* ep_send_events接口复制txlist内epitem对应fd的就绪events到用户空间
*/
if (!res && eavail && !(res = ep_send_events(ep, events, maxevents))
&& !timed_out)
goto fetch_events;
if (waiter) {
spin_lock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
// 将当前进程移出等待队列
__remove_wait_queue(&ep->wq, &wait);
spin_unlock_irq(&ep->wq.lock);
}
return res;
}
fs/eventpoll.c
static int ep_send_events(struct eventpoll *ep,
struct epoll_event __user *events, int maxevents)
{
struct ep_send_events_data esed;
esed.maxevents = maxevents;
esed.events = events;
// 传入ep_send_events_proc
ep_scan_ready_list(ep, ep_send_events_proc, &esed, 0, false);
return esed.res;
}
// 实际执行复制到用户空间的工作是由该函数体负责
static __poll_t ep_send_events_proc(struct eventpoll *ep, struct list_head *head,void *priv)
{
struct ep_send_events_data *esed = priv;
__poll_t revents;
struct epitem *epi, *tmp;
struct epoll_event __user *uevent = esed->events;
struct wakeup_source *ws;
poll_table pt;
init_poll_funcptr(&pt, NULL);
esed->res = 0;
/*
* We can loop without lock because we are passed a task private list.
* Items cannot vanish during the loop because ep_scan_ready_list() is
* holding "mtx" during this call.
*/
lockdep_assert_held(&ep->mtx);
// lambda表达式
list_for_each_entry_safe(epi, tmp, head, rdllink) {
if (esed->res >= esed->maxevents)
break;
/*
* Activate ep->ws before deactivating epi->ws to prevent
* triggering auto-suspend here (in case we reactive epi->ws
* below).
*
* This could be rearranged to delay the deactivation of epi->ws
* instead, but then epi->ws would temporarily be out of sync
* with ep_is_linked().
*/
ws = ep_wakeup_source(epi);
if (ws) {
if (ws->active)
__pm_stay_awake(ep->ws);
__pm_relax(ws);
}
list_del_init(&epi->rdllink);
/*
* If the event mask intersect the caller-requested one,
* deliver the event to userspace. Again, ep_scan_ready_list()
* is holding ep->mtx, so no operations coming from userspace
* can change the item.
*/
revents = ep_item_poll(epi, &pt, 1);
if (!revents)
continue;
// 复制到用户空间
if (__put_user(revents, &uevent->events) ||
__put_user(epi->event.data, &uevent->data)) {
list_add(&epi->rdllink, head);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
if (!esed->res)
esed->res = -EFAULT;
return 0;
}
esed->res++;
uevent++;
if (epi->event.events & EPOLLONESHOT)
epi->event.events &= EP_PRIVATE_BITS;
else if (!(epi->event.events & EPOLLET)) {
/*
* If this file has been added with Level
* Trigger mode, we need to insert back inside
* the ready list, so that the next call to
* epoll_wait() will check again the events
* availability. At this point, no one can insert
* into ep->rdllist besides us. The epoll_ctl()
* callers are locked out by
* ep_scan_ready_list() holding "mtx" and the
* poll callback will queue them in ep->ovflist.
*/
list_add_tail(&epi->rdllink, &ep->rdllist);
ep_pm_stay_awake(epi);
}
}
return 0;
}
参考文献
[1] epoll react
[2] linux epoll源码分析
[3] IO复用select/poll/epoll
[4] IO复用epoll
[5] linux epoll源码
[6] linux poll/epoll实现
[7] linux源码github仓库