直接进入正题:
1.TestNG的运行方式如下:
1 With a testng.xml file 直接run as test suite 2 With ant 使用ant 3 From the command line 从命令行 4 IDE 直接在IDE中执行
在IDEA中直接运行的时候,需要说明的是:可以运行一个测试类,也可以单独运行一个测试的方法。
在IDEA里执行,只需要右键,点击 Run xxx 即可。 如果是在某一个方法的代码块里右键,出现的是 Run methodName ,即只运行当前的方法; 如果是在类的代码块里右键,出现的是 Run className ,即运行当前类中的所有Test方法; 也可以创建testng.xml,右键出现的 Run path/testng.xml ,即运行该配置文件中需要运行的方法。
2.TestNG常见的注解:
| 注解 | 描述 |
| @DataProvider | 为测试方法提供数据 |
| @BeforeMethod | 在每个测试方法 前 执行 |
| @AfterMethod | 在每个测试方法 后 执行 |
| @BeforeClass | 被注释的方法将在当前类的第一个测试方法调用前运行 |
| @AfterClass | 被注释的方法将在当前类的所有测试方法调用后运行 |
| @BeforeGroups | 被配置的方法将在列表中的gourp前运行。这个方法保证在第一个属于这些组的测试方法调用前立即执行 |
| @BeforeTest | 被注释的方法将在测试运行前运行 |
| @AfterTest | 被注释的方法将在测试运行后运行 |
| @BeforeSuite | 被注释的方法将在所有测试运行前运行 |
| @AfterSuite | 被注释的方法将在所有测试运行后运行 |
另外还有一些属性,
alwaysRun:对于每个bufore方法(beforeSuite, beforeTest, beforeTestClass 和 beforeTestMethod, 但是不包括 beforeGroups):
如果设置为true,被配置的方法将总是运行而不管它属于哪个组。
对于after方法(afterSuite, afterClass, ...): 如果设置为true,被配置的方法甚至在一个或多个先调用的方法失败或被忽略时也将运行。
dependsOnGroups:这个方法依赖的组列表
dependsOnMethod:这个方法依赖的方法列表
enabled:这个类的方法是否激活
groups:这个类或方法所属的分组列表
inheritGroups:如果设置为true,这个方法被属于在类级别被@Test annotation指定的组例如:
例如: 1 @Test(enabled = false) //表示该测试用例不被执行 2 public Object runTest() { 3 xxxxxx 4 }
3.testNG.xml配置详解:
testng.xml的基本格式可以在官网上查看,基本格式如下:

以下详细XML结构规则
suite
--tests
----parameters
----groups
------definitions
------runs
----classes
--parameters
比较详细的结构如下:
1 <test name="xxxx"> 2 <!-- 参数定义的方法 --> 3 <parameter name="first-name" value="Cedric"/> 4 5 <!-- groups的用法,前提是需要存在classes的组,否则所有方法不被运行 --> 6 <groups> 7 <!-- 定义组中组的方法 --> 8 <define name="groups_name"> 9 <include name="group1"/> 10 <include name="group2"/> 11 </define> 12 13 <run> 14 <!-- 此处用组名来区别 --> 15 <inclue name="groups_name" /> 16 <exclue name="groups_name" /> 17 </run> 18 </groups> 19 20 <!-- classes的用法,classes中包含类名,类名底下可以包含方法名或排除方法名 --> 21 <classes> 22 <class name="class1"> 23 <methods> 24 <!-- 此处用方法名来区别 --> 25 <inclue name="method_name" /> 26 <exclue name="method_name" /> 27 </methods> 28 </class> 29 </classes> 30 </test>
具体的元素说明:
| 参数 | 说明 | 使用方法 | 参数值 |
| name | 必选项,<suite>的名字,将出现在reports里 | name="XXX" | suite名字 |
| junit | 是否执行Junit模式(识别setup()等) | junit="true" | true和false,默认false |
| verbose | 控制台输出的详细内容等级,0-10级(0无,10最详细) | verbose="5" | 0到10 |
| parallel | 是否在不同的线程并行进行测试,要与thread-count配套使用 | parallel="mehods" | 详见表格下内容,默认false |
| parent-module | 和Guice框架有关,只运行一次,创建一个parent injector给所有guice injectors | ||
| guice-stage | 和Guice框架有关 | guice-stage="DEVELOPMENT" | DEVELOPMENT,PRODUCTION,TOOL,默认"DEVELOPMENT" |
| configfailurepolicy | 测试失败后是再次执行还是跳过,值skip和continue | configfailurepolicy="skip" | skip、continue,默认skip |
| thread-count | 与parallel配套使用,线程池的大小,决定并行线程数量 | thread-count="10" | 整数,默认5 |
| annotations | 获取注解,值为javadoc时,使用JavaDoc的注释;否则用JDK5注释 | annotations="javadoc" | javadoc |
| time-out | 设置parallel时,终止执行单元之前的等待时间(毫秒) | time-out="10000" | 整数,单位毫秒 |
| skipfailedinvocationcounts | 是否跳过失败的调用 | skipfailedinvocationcounts="true" | true和false,默认false |
| data-provider-thread-count | 并发时data-provider的线程池数量 | data-provider-thread-count="5" | 整数 |
| object-factory | 一个实现IObjectFactory接口的类,实例化测试对象 | object-factory="classname" | 类名 |
| allow-return-values | 是否允许返回函数值 | all-return-values="true" | true和false |
| preserve-order | 是否按照排序执行 | preserve-order="true" | true和false,默认true |
| group-by-instances | 按照实例分组 | group-by-instances="true" | true和false,默认false |
1 <suite-files> 2 <suite-file path="/path/suitefile1"></suite-file> 3 </suite-files>
| 参数 | 说明 | 使用方法 | 参数值 |
| name | test的名字,将出现在报告里 | name="testname" | test的名字 |
| junit | 是否按照Junit模式运行 | junit="true" | true和false,默认false |
| verbose | 控制台输出的详细内容等级,0-10级(0无,10最详细),不在报告显示 | verbose="5" | 0到10 |
| parallel | 是否在不同的线程并行进行测试,要与thread-count配套使用 | parallel="mehods" | 与suite的parallel一致,默认false |
| thread-count | 与parallel配套使用,线程池的大小,决定并行线程数量 | thread-count="10" | 整数,默认5 |
| annotations | 获取注解,值为javadoc时,使用JavaDoc的注释;否则用JDK5注释 | annotations="javadoc" | javadoc |
| time-out | 设置parallel时,终止执行单元之前的等待时间(毫秒) | time-out="10000" | 整数,单位毫秒 |
| enabled | 标记是否执行这个test | enabled="true" | true和false,默认true |
| skipfailedinvocationcounts | 是否跳过失败的调用 | skipfailedinvocationcounts="true" | true和false,默认false |
| preserve-order | 是否按照排序执行,如果是true,将按照xml文件中的顺序去执行 | preserve-order="true" | true和false,默认true |
| allow-return-values | 是否允许返回函数值 | all-return-values="true" | true和false,默认false |
1 <method-selectors> 2 <method-selector> 3 <selector-class name="classname" priority="1"></selector-class> 4 <script language="java"></script> (language还可以用beanshell等) 5 </method-selector> 6 </method-selectors>
1 <groups> 2 <define name ="all"> 3 <include name ="testgroup1"/> 4 <exclude name ="testgroup2'/> 5 </define> 6 <run> 7 <include name ="all"/> 8 <include name ="testmethod1"/> 9 <exclude name="testmethod2"/> 10 </run> 11 <dependencies> 12 <group name ="group1" depends-on="goup2 group3"/> 13 </dependencies> 14 </groups>
1 <classes> 2 <class name="要执行的class名"> 3 <methods> 4 <include name ="要执行的方法名"></include> 5 </methods> 6 </class> 7 </classes>
1 <packages> 2 <package name="packagename"/> 3 <package name="packagename"> 4 <include name="methodname"/> 5 <exclude name="methodname"/> 6 </package> 7 </packages>
1 <listeners> 2 <listener class-name="com.example.MyListener"/> 3 <listener class-name="com.example.MyMehodIntercepor"/> 4 </listeners>
(3)一个简单的testng.xml文档
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <!DOCTYPE suite SYSTEM "http://testng.org/testng-1.0.dtd"> 3 4 <suite name="Suite" parallel="classes" thread-count="3"> 5 <test verbose="2" preserve-order="true" name="TestDebug"> 6 7 <classes> 8 <class name="com.hera.util.MathTest" /> 9 10 </classes> 11 </test> <!-- Test --> 12 </suite> <!-- Suite -->
说明: suite定义一个测试套件,可以设置是否使用多线程,可包含多个测试用例或者测试group
parallel = classes 每个测试用例class级别多线程
thread-count =3 线程数为5,可同时执行3个case
preserve-order = true classes和methods按照配置中的顺序执行,false为乱序执行。(If you want the classes and methods listed in this file to be run in an unpredictible order, set the preserve-order attribute to false)
parameter 标签传递参数
4.TestNG参数化测试
软件测试中,经常需要测试大量的数据集。 测试代码的逻辑完全一样,只是测试的参数不一样。 这样我们就需要一种 “传递测试参数的机制”。 避免写重复的测试代码
TestNG提供了2种传递参数的方式。
第一种: testng.xml 方式使代码和测试数据分离,方便维护
第二种:@DataProvider能够提供比较复杂的参数。 (也叫data-driven testing)
方法一:通过testng.xml传递参数给测试代码,在testng.xml文件中定义的简单参数,然后在源文件中引用这些参数。
下面是支持的类型:
String
int/Integer
boolean/Boolean
byte/Byte
char/Character
double/Double
float/Float
long/Long
short/Short
例子:
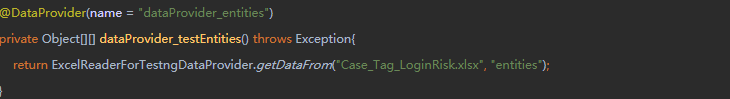
方法二:通过DataProvider传递参数,当你需要通过复杂的参数或参数需要创建从Java(复杂的对象,对象读取属性文件或数据库等..),在这种情况下,可以将参数传递使用数据提供者。数据提供者@DataProvider的批注的方法。
(可以通过excel来管理case数据)