IDEA导入阿里规约插件,当你这样写代码时,插件就会自动监测出来,并给你红线提醒。
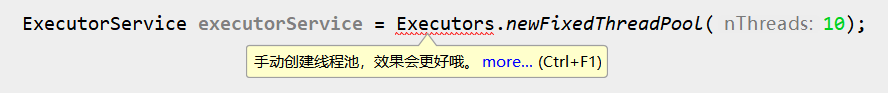
告诉你手动创建线程池,效果会更好。
在探秘原因之前我们要先了解一下线程池 ThreadPoolExecutor 都有哪些参数及其意义。
ThreadPoolExecutor 构造方法:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
//code...
}
参数的意义:
1.corePoolSize 指定了线程池里的线程数量,核心线程池大小
2.maximumPoolSize 指定了线程池里的最大线程数量
3.keepAliveTime 当线程池线程数量大于corePoolSize时候,多出来的空闲线程,多长时间会被销毁。
4.unit 时间单位。TimeUnit
5.workQueue 任务队列,用于存放提交但是尚未被执行的任务。
我们可以选择如下几种:
- ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组结构的有界阻塞队列,FIFO。
- LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表结构的有界阻塞队列,FIFO。
- SynchronousQueue:不存储元素的阻塞队列,每个插入操作都必须等待一个移出操作,反之亦然。
- PriorityBlockingQueue:具有优先级别的阻塞队列。
6.threadFactory 线程工厂,用于创建线程,一般可以用默认的
7.handler 拒绝策略,所谓拒绝策略,是指将任务添加到线程池中时,线程池拒绝该任务所采取的相应策略。
什么时候拒绝?当向线程池中提交任务时,如果此时线程池中的线程已经饱和了,而且阻塞队列也已经满了,则线程池会选择一种拒绝策略来处理该任务,该任务会交给RejectedExecutionHandler 处理。
线程池提供了四种拒绝策略:
- AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常,默认策略;
- CallerRunsPolicy:用调用者所在的线程来执行任务;
- DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃阻塞队列中靠最前的任务,并执行当前任务;
- DiscardPolicy:直接丢弃任务;
-------
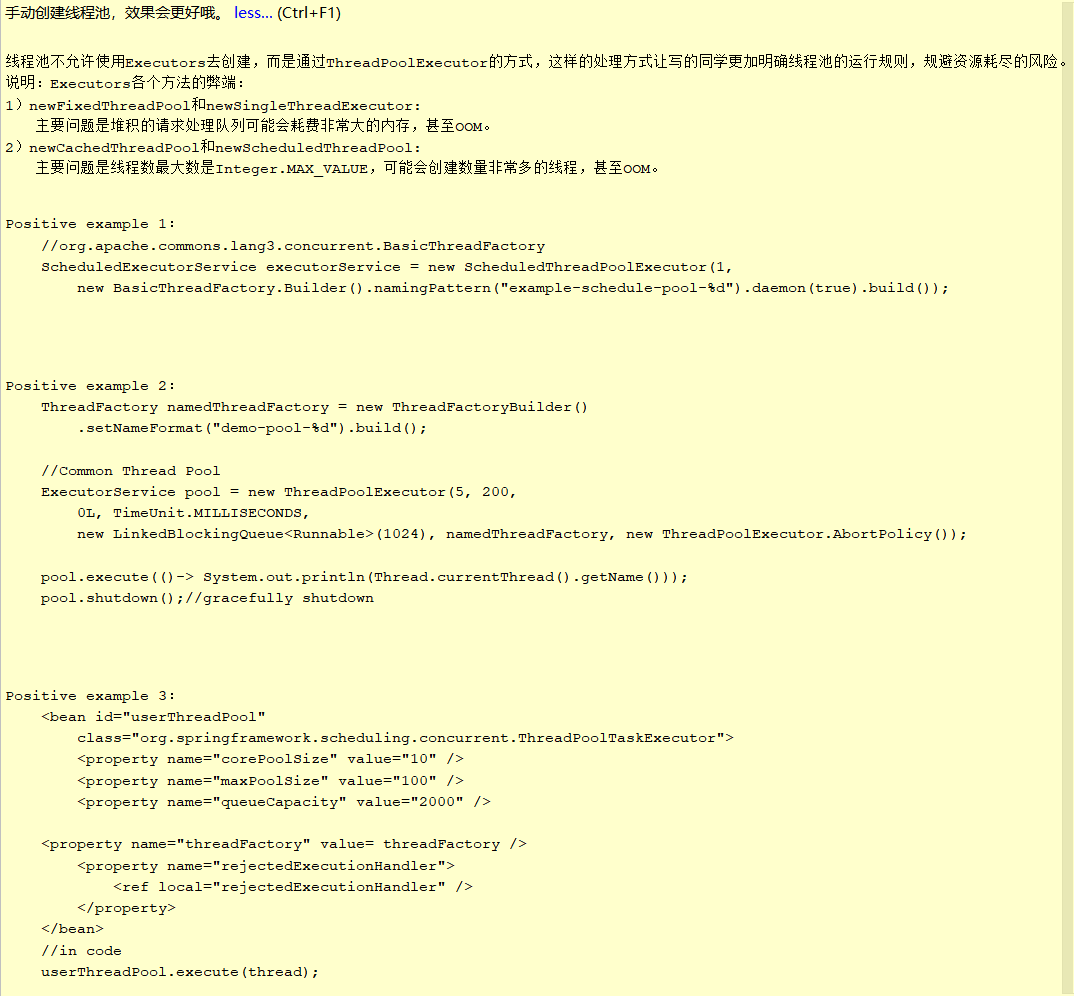
阿里规约之所以强制要求手动创建线程池,也是和这些参数有关。具体为什么不允许,规约是这么说的:
线程池不允许使用Executors去创建,而是通过ThreadPoolExecutor的方式,这样的处理方式让写的同学更加明确线程池的运行规则,规避资源耗尽的风险。
Executor提供的四个静态方法创建线程池,但是阿里规约却并不建议使用它。
Executors各个方法的弊端:
1)newFixedThreadPool和newSingleThreadExecutor:
主要问题是堆积的请求处理队列可能会耗费非常大的内存,甚至OOM。
2)newCachedThreadPool和newScheduledThreadPool:
主要问题是线程数最大数是Integer.MAX_VALUE,可能会创建数量非常多的线程,甚至OOM。
看一下这两种弊端怎么导致的。
第一种,newFixedThreadPool和newSingleThreadExecutor分别获得 FixedThreadPool 类型的线程池 和 SingleThreadExecutor 类型的线程池。
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()); }
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() { return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService (new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())); }
因为,创建了一个无界队列LinkedBlockingQueuesize,是一个最大值为Integer.MAX_VALUE的线程阻塞队列,当添加任务的速度大于线程池处理任务的速度,可能会在队列堆积大量的请求,消耗很大的内存,甚至导致OOM。
第二种,newCachedThreadPool 和 newScheduledThreadPool创建的分别是CachedThreadPool 类型和 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutorScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类型的线程池。
CachedThreadPool是一个会根据需要创建新线程的线程池 ,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor可以用来在给定延时后执行异步任务或者周期性执行任务。
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() { return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS, new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>()); }
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) { return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize); } public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) { super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, new DelayedWorkQueue()); }
创建的线程池允许的最大线程数是Integer.MAX_VALUE,空闲线程存活时间为0,当添加任务的速度大于线程池处理任务的速度,可能会创建大量的线程,消耗资源,甚至导致OOM。
这两种都是有点极端的,稍微点进去看一下源码就能看出来。
阿里规约提倡手动创建线程池,而非Java内置的线程池,给出的正例如下:
正例1:
//org.apache.commons.lang3.concurrent.BasicThreadFactory ScheduledExecutorService executorService = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, new BasicThreadFactory.Builder().namingPattern("example-schedule-pool-%d").daemon(true).build());
正例2:
ThreadFactory namedThreadFactory = new ThreadFactoryBuilder().setNameFormat("demo-pool-%d").build(); //Common Thread Pool ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 200, 0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1024), namedThreadFactory, new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()); pool.execute(()-> System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName())); pool.shutdown();//gracefully shutdown
正例3:
<bean id="userThreadPool" class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor"> <property name="corePoolSize" value="10" /> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="100" /> <property name="queueCapacity" value="2000" /> <property name="threadFactory" value= threadFactory /> <property name="rejectedExecutionHandler"> <ref local="rejectedExecutionHandler" /> </property> </bean> //in code userThreadPool.execute(thread);
IDEA安装阿里规约插件,就能提示你不要这么使用。

鼠标放上去,就会给你提示信息。
---
