本文介绍ASP.NET Core默认模板是如何完成初始化的,不多废话,直入主题
首先使用默认模板创建一个ASP.NET Core程序
瞅一眼解决方案结构,包含了EF Core和Identity的默认实现,没啥特别的
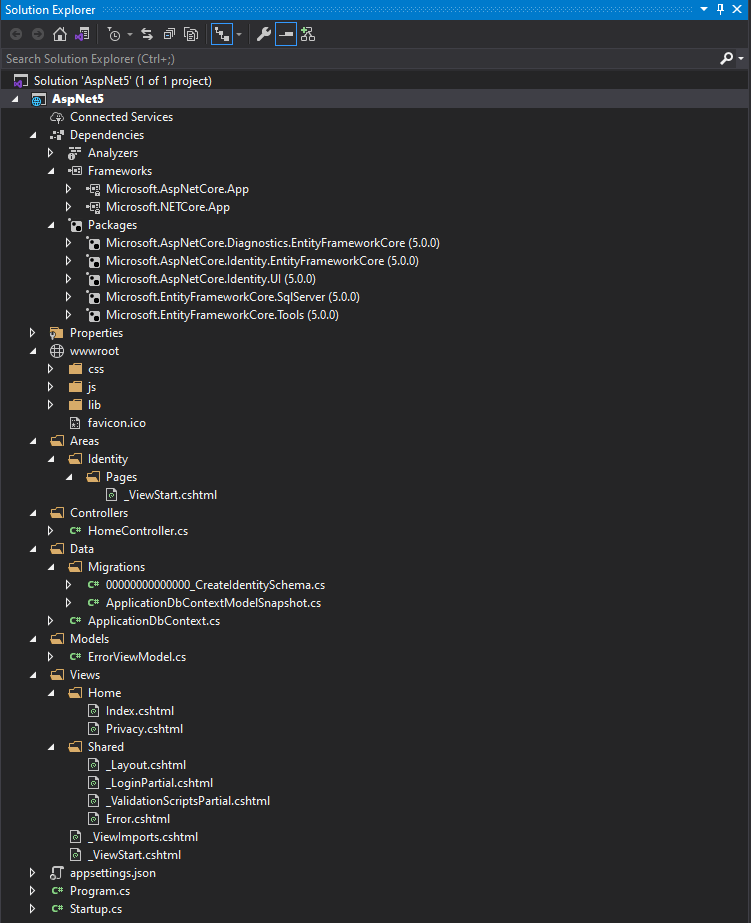
我们知道控制台程序的入口点在Main函数,ASP.NET Core也是一样的。所以我们看Program文件中的Main函数,它长这样
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
namespace AspNet5
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args)
{
return Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder => { webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>(); });
}
}
}
从以上代码我们可以看到,Main函数只调用了CreateHostBuilder一个方法,这个方法利用Host静态类创建了一个IHostBuilder供Main函数Build and Run,从build、builder字样和分析后不难得出这里使用了建造者模式
既然是建造者模式,就涉及到了建造“原料”。在这段代码里,只调用了CreateDefaultBuilder、ConfigureWebHostDefaults和Build三个方法。那么“原料”和建造过程就藏在这几个方法里,我们一个一个来看
首先是CreateDefaultBuilder方法,它完成了以下的事情,提供了“原料”
- 把
IHostEnvironment.ContentRootPath的值设置为Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()(当前工作目录) - 使用前缀为
DOTNET_的环境变量来加载Host - 使用命令行输入的参数
args来加载Host - 使用配置文件
appsettings.json和当前运行环境对应的配置文件,如appsetting.Development.json来加载程序 - 当前运行环境为
Development并且存在和环境变量ApplicationName匹配的入口程序集时,从程序集中加载User Secrets,用其来加载程序 - 使用命令行输入的参数
args来加载程序 - 配置
ILoggerFactory,用来输出日志到命令行窗口、debug窗口、event source - 当前运行环境为
Development时,启用依赖注入容器的范围验证
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="HostBuilder"/> class with pre-configured defaults.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// The following defaults are applied to the returned <see cref="HostBuilder"/>:
/// <list type="bullet">
/// <item><description>set the <see cref="IHostEnvironment.ContentRootPath"/> to the result of <see cref="Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()"/></description></item>
/// <item><description>load host <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from "DOTNET_" prefixed environment variables</description></item>
/// <item><description>load host <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from supplied command line args</description></item>
/// <item><description>load app <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from 'appsettings.json' and 'appsettings.[<see cref="IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName"/>].json'</description></item>
/// <item><description>load app <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from User Secrets when <see cref="IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName"/> is 'Development' using the entry assembly</description></item>
/// <item><description>load app <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from environment variables</description></item>
/// <item><description>load app <see cref="IConfiguration"/> from supplied command line args</description></item>
/// <item><description>configure the <see cref="ILoggerFactory"/> to log to the console, debug, and event source output</description></item>
/// <item><description>enables scope validation on the dependency injection container when <see cref="IHostEnvironment.EnvironmentName"/> is 'Development'</description></item>
/// </list>
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="args">The command line args.</param>
/// <returns>The initialized <see cref="IHostBuilder"/>.</returns>
public static IHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args)
{
var builder = new HostBuilder();
builder.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory());
builder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config =>
{
config.AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix: "DOTNET_");
if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
});
builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) =>
{
IHostEnvironment env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment;
bool reloadOnChange = hostingContext.Configuration.GetValue("hostBuilder:reloadConfigOnChange", defaultValue: true);
config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: reloadOnChange)
.AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: reloadOnChange);
if (env.IsDevelopment() && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(env.ApplicationName))
{
var appAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(env.ApplicationName));
if (appAssembly != null)
{
config.AddUserSecrets(appAssembly, optional: true);
}
}
config.AddEnvironmentVariables();
if (args != null)
{
config.AddCommandLine(args);
}
})
.ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) =>
{
bool isWindows = RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows);
// IMPORTANT: This needs to be added *before* configuration is loaded, this lets
// the defaults be overridden by the configuration.
if (isWindows)
{
// Default the EventLogLoggerProvider to warning or above
logging.AddFilter<EventLogLoggerProvider>(level => level >= LogLevel.Warning);
}
logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging"));
logging.AddConsole();
logging.AddDebug();
logging.AddEventSourceLogger();
if (isWindows)
{
// Add the EventLogLoggerProvider on windows machines
logging.AddEventLog();
}
logging.Configure(options =>
{
options.ActivityTrackingOptions = ActivityTrackingOptions.SpanId
| ActivityTrackingOptions.TraceId
| ActivityTrackingOptions.ParentId;
});
})
.UseDefaultServiceProvider((context, options) =>
{
bool isDevelopment = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment();
options.ValidateScopes = isDevelopment;
options.ValidateOnBuild = isDevelopment;
});
return builder;
}
然后是ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法,它完成了以下事情,也提供了“原料”
- 使用默认值配置IHostBuilder来托管Web应用程序
- 使用Kestrel作为Web服务器,并使用应用程序的配置提供程序对其进行配置
- 配置
IWebHostEnvironment.WebRootFileProvider以包含开发过程中入口程序集引用的项目中的Web静态文件 - 加入
HostFiltering中间件 - 当
ASPNETCORE_FORWARDEDHEADERS_ENABLED=true时,加入ForwardedHeaders中间件 - 启用IIS集成
- 通过类型为
Action<IWebHostBuilder>的configure委托来进一步配置依赖注入服务和中间件(也是就是Startup文件)
/// <summary>
/// Configures a <see cref="IHostBuilder" /> with defaults for hosting a web app.
/// </summary>
/// <remarks>
/// The following defaults are applied to the <see cref="IHostBuilder"/>:
/// <list type="bullet">
/// <item><description>use Kestrel as the web server and configure it using the application's configuration providers</description></item>
/// <item><description>configure <see cref="IWebHostEnvironment.WebRootFileProvider"/> to include static web assets from projects referenced by the entry assembly during development</description></item>
/// <item><description>adds the HostFiltering middleware</description></item>
/// <item><description>adds the ForwardedHeaders middleware if ASPNETCORE_FORWARDEDHEADERS_ENABLED=true,</description></item>
/// <item><description>enable IIS integration</description></item>
/// </list>
/// </remarks>
/// <param name="builder">The <see cref="IHostBuilder" /> instance to configure.</param>
/// <param name="configure">The configure callback</param>
/// <returns>A reference to the <paramref name="builder"/> after the operation has completed.</returns>
public static IHostBuilder ConfigureWebHostDefaults(this IHostBuilder builder, Action<IWebHostBuilder> configure)
{
if (configure is null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(configure));
}
return builder.ConfigureWebHost(webHostBuilder =>
{
WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults(webHostBuilder);
configure(webHostBuilder);
});
}
internal static void ConfigureWebDefaults(IWebHostBuilder builder)
{
builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((ctx, cb) =>
{
if (ctx.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment())
{
StaticWebAssetsLoader.UseStaticWebAssets(ctx.HostingEnvironment, ctx.Configuration);
}
});
builder.UseKestrel((builderContext, options) =>
{
options.Configure(builderContext.Configuration.GetSection("Kestrel"), reloadOnChange: true);
})
.ConfigureServices((hostingContext, services) =>
{
// Fallback
services.PostConfigure<HostFilteringOptions>(options =>
{
if (options.AllowedHosts == null || options.AllowedHosts.Count == 0)
{
// "AllowedHosts": "localhost;127.0.0.1;[::1]"
var hosts = hostingContext.Configuration["AllowedHosts"]?.Split(new[] { ';' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
// Fall back to "*" to disable.
options.AllowedHosts = (hosts?.Length > 0 ? hosts : new[] { "*" });
}
});
// Change notification
services.AddSingleton<IOptionsChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>>(
new ConfigurationChangeTokenSource<HostFilteringOptions>(hostingContext.Configuration));
services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, HostFilteringStartupFilter>();
if (string.Equals("true", hostingContext.Configuration["ForwardedHeaders_Enabled"], StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
services.Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
// Only loopback proxies are allowed by default. Clear that restriction because forwarders are
// being enabled by explicit configuration.
options.KnownNetworks.Clear();
options.KnownProxies.Clear();
});
services.AddTransient<IStartupFilter, ForwardedHeadersStartupFilter>();
}
services.AddRouting();
})
.UseIIS()
.UseIISIntegration();
}
最后来看Build方法,它完成了以下事情,负责使用以上提供的原料来“建造”Host
- 保证
Build方法只能被调用一次 - 使用以上提供的各种
IConfigurationBuilder构建Host配置 - 创建托管环境
- 创建
Host Builder上下文 - 使用以上提供的各种
IConfigurationBuilder构建应用程序配置 - 创建
Service Provider(服务提供者),也就是我们常说的依赖注入容器 - 从容器中获取
IHost服务并返回
/// <summary>
/// Run the given actions to initialize the host. This can only be called once.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>An initialized <see cref="IHost"/></returns>
public IHost Build()
{
if (_hostBuilt)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException("Build can only be called once.");
}
_hostBuilt = true;
BuildHostConfiguration();
CreateHostingEnvironment();
CreateHostBuilderContext();
BuildAppConfiguration();
CreateServiceProvider();
return _appServices.GetRequiredService<IHost>();
}
这里的CreateServiceProvider比较有意思,我把代码贴下面供大家阅读
private void CreateServiceProvider()
{
var services = new ServiceCollection();
#pragma warning disable CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete
services.AddSingleton<IHostingEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment);
#pragma warning restore CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete
services.AddSingleton<IHostEnvironment>(_hostingEnvironment);
services.AddSingleton(_hostBuilderContext);
// register configuration as factory to make it dispose with the service provider
services.AddSingleton(_ => _appConfiguration);
#pragma warning disable CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete
services.AddSingleton<IApplicationLifetime>(s => (IApplicationLifetime)s.GetService<IHostApplicationLifetime>());
#pragma warning restore CS0618 // Type or member is obsolete
services.AddSingleton<IHostApplicationLifetime, ApplicationLifetime>();
services.AddSingleton<IHostLifetime, ConsoleLifetime>();
services.AddSingleton<IHost, Internal.Host>();
services.AddOptions();
services.AddLogging();
foreach (Action<HostBuilderContext, IServiceCollection> configureServicesAction in _configureServicesActions)
{
configureServicesAction(_hostBuilderContext, services);
}
object containerBuilder = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateBuilder(services);
foreach (IConfigureContainerAdapter containerAction in _configureContainerActions)
{
containerAction.ConfigureContainer(_hostBuilderContext, containerBuilder);
}
_appServices = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateServiceProvider(containerBuilder);
if (_appServices == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException($"The IServiceProviderFactory returned a null IServiceProvider.");
}
// resolve configuration explicitly once to mark it as resolved within the
// service provider, ensuring it will be properly disposed with the provider
_ = _appServices.GetService<IConfiguration>();
}
最后的最后,在Main调用了IHost的Run方法,使用“建造”好的Host来跑应用程序
总结
以上内容,源码才是精华,我只是一个无情的翻译机器,顺便把大体流程梳理了一下。个人认为,读懂源码需要掌握但不限于以下知识(只列举在ASP.NET Core中大量使用的)
- 委托
- 函数式编程
- DI、IOC概念,services生命周期
- 建造者模式
- 工厂模式
- Provider概念
- 扩展方法
- 反射
除了默认的实现,我们还可以通过一系列IHostBuilder的方法、扩展方法来自定义我们应用程序的初始化过程
了解了应用程序的启动过程,下一篇介绍依赖注入容器相关的内容