快捷键:
1.ctrl+q 打开查询窗口
3.ctrl+shift +/ 解除注释
4.ctrl+r 运行查询窗口的sql语句
5.ctrl+shift+r 只运行选中的sql语句
6.F6 打开一个mysql命令行窗口
7.ctrl+l 删除一行
8.ctrl+n 打开一个新的查询窗口
9.ctrl+w 关闭一个查询窗口
一、数据库(DB):是按照数据库结构来组织。存储和管理数据的,且是建立在计算机存储设备上的仓库。
二、数据库是由3个主要部分组成:
1、数据库(Database System):用于存储数据的地方。
2、数据库管理系统(Database Management System,DBMS):用户管理数据库的软件。
3、数据库应用程序(Database Application):为了提高数据库系统的处理能力所使用的管理数据库的软件补充。
三、数据库的优势:
1、存储数据量大
2、方便管理
3、多用户共享
4、独立的数据集合
四、数据库分类:
关系型数据库:mysql、oracle、sql server、sybase
特点:1、数据以表格的形式出现
2、每行为各种记录名称
3、每列为记录名称所对应的数据域
4、许多的行和列组成一张表单
5、若干的表单组成database
非关系型数据库:redis、MongoDB
mysql的简单命令:
use mysql -- 进入mysql数据库
show databases -- 显示当前mysql中所有的数据库
show tables -- 显示mysql数据库中所有的表
select user,host from user -- 查询mysql中user表的数据
数据库的操作:在cmd打开的小黑框中最后必须要加英文的分号,中mysql中最后的分号可加可不加
1、显示数据库:
show databases;
show create database 表名;
select database();
2、进入指定数据库:
use 数据库名称
3、创建数据库:
create databese 数据库名;
也可以在创建数据库的时候同时设置编码方式:
create databese 数据库名 default character set=utf8;
数据库的命名规则:
可以由字母、数字、下划线、@、#、¥组成 区分大小写 唯一性 不能使用关键字 如:create select 不能单独使用数字 最长128位
4、删除数据库:
drop database 数据库名;
5、修改数据库
alter database 表名 charset utf8;
5、也可通过命令行将当前的编码集设置成utf8
set character_set_client=utf8
set character_set_server=utf8
set character_set_ connection=utf8
set character_set_database=utf8
set character_set_results=utf8
set collation_connection=utf8_general_ci
set collation_database=utf8_general_ci
set collation_server=utf8_general_ci
在数据库中创建表及对表的操作:
与表相关的语法:
#语法:
create table 表名(
字段名1 类型 宽度 约束条件,
字段名2 类型 宽度 约束条件,
字段名3 类型 宽度 约束条件
);
show tables; #查看某库下所有表名
describe 表名; #查看表结构,可简写成 desc 表名
show create table t1G #查看表的详细结构,可加G
#注意:
1、在同一张表中,字段名是不能相同的
2、宽度和约束条件可写可不写
3、字段名和类型是必须的
1、修改表名
alter table 表名 rename 新表名;
2、增加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...];
add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...] first;
add 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...] after 字段名;
3、删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;
4、修改字段
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 数据类型 [完整性约束条件...];
change 旧字段名 新字段名 旧数据类型 [完整性约束条件...];
change 旧字段名 新字段名 新数据类型 [完整性约束条件...];
1、修改存储引擎
alter table service engine=innodb;
2、添加字段
alter table student add name varchar(20) not null,
add age int(3) not null default 22;
alter table student add stu_num varchar(10) not null after name; # 添加name字段之后
alter table student add sex enum('male','female') default 'male' first; # 天加到最前面
3、删除字段
alter table student drop sex;
alter table service drop mac;
4、修改字段类型modify
alter table student modify age int(3);
alter table student modify id int(11) not null primary key auto_increment; #修改为主键
5、增加约束(针对已有的主键增加auto_increment)
alter table student modify id int(11) not null auto_increment;
6、对已经存在的表增加复合主键
alter table service add primary key(字段名1,字段名2);
7、增加主键
alter table student modify name varchar(10) not null primary key;
8、增加主键和自增长
alter table student modify id int not null primary key auto_increment;
9、删除主键
a、删除自增约束
alter table student modify id int(11) not null;
b、删除主键
alter table student drop primary key;
复制表
复制表结构+记录(key 不会复制:主键、外键和索引)
create table new_service select * from service;
只复制表结构:
select * from service where 1=2; # 条件为假,查不到任何记录
create table new1_service select * from service where 1=2;
create table t like employees;
删除表
drop table 表名;
示例:
1、创建表:
create table people(
p_id varchar(7) not null,
p_name varchar(10),
p_age int(5) not null,
p_menpai varchar(20) not null,
p_leader varchar(7) not null,
p_sal int(10) not null
)
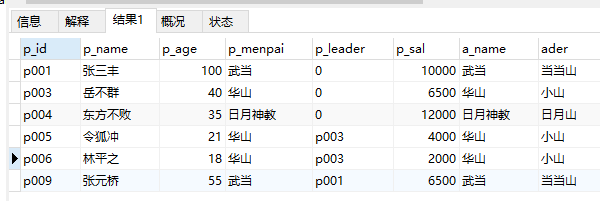
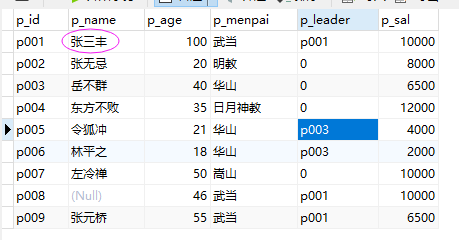
最后得到下表
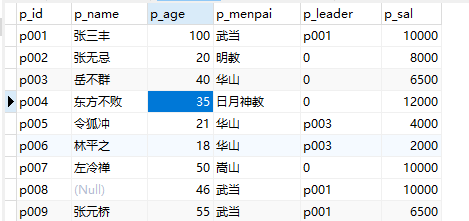
2、向表中添加一行数据:
insert into people(p_id,p_name,p_age,p_menpai,p_leader,p_sal) values('p010','天门道长','47','泰山派','0','12000')
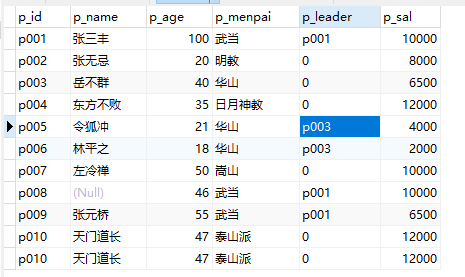
3、删除表中的天门道长:
delete from people where p_name='天门道长'
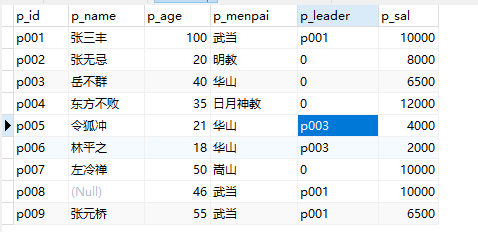
4、修改表中的数据:使用updata:
updata people set p_name='张三丰' where p_name='张三'
5、查询:
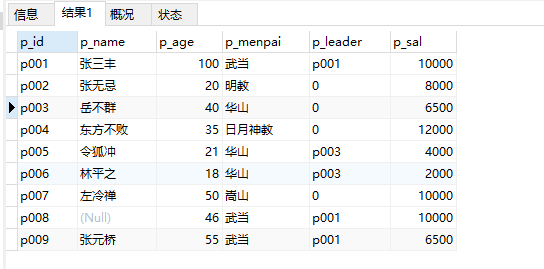
1、查询表中的所有信息:
select * from people
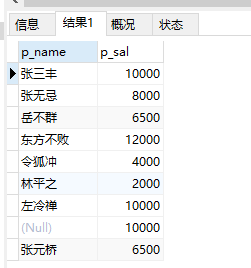
2、查询表中的具体某一个具体项(即key):
select p_name,p_sal from people
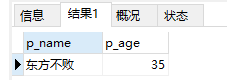
3、查询表中某个具体key对应的value:
select p_name,p_age from people where p_age='35'
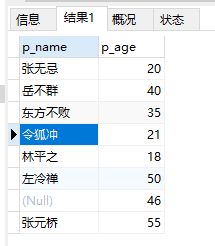
4、查询60岁以下的人员:
select p_name,p_age from people where p_age<'60'
或者:
select * from people where p_age<'60'
常见的逻辑运算符:<:小于 >:大于 <=:小于等于 >=:大于等于 <>、!=:不等于
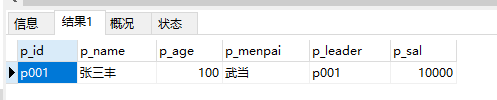
5、查询50岁以上并且工资大于8000的人员:
select * from people where p_age>50 and p_sal>8000
注意:and 用于连接两个条件,表示并且的意思;
or 用于连接两个条件,表示或者意思
6、查询姓张的人员:
select * from people where p_name like '张%'
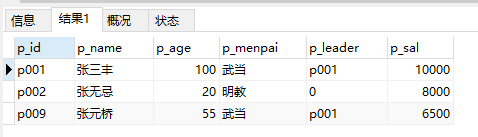
select * from people where p_name like '%张%' -- 可以查找姓名中有张的人员信息
7、查询哪些人员属于 武当/华山/嵩山:
select * from people where p_menpai='武当' or p_menpai='华山' or p_menpai='嵩山'
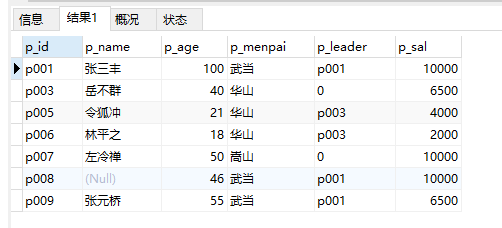
select * from peopel where p_menpai not in ('武当','华山','嵩山') -- 查找除了武当、华山、嵩山以外的人
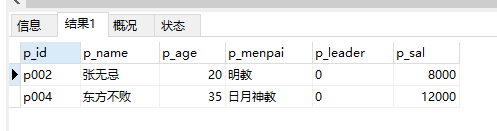
8、查询工资质5000-9000之间的人员:
select * from people where p_sal between 5000 and 9000
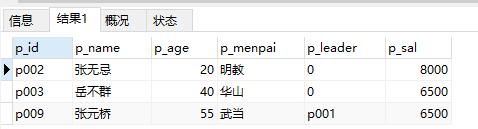
9、查询所有人员,要求按工资升序排列:(最后的asc可以不写,默认为升序排列)
select * from people where p_sal order by p_sal asc
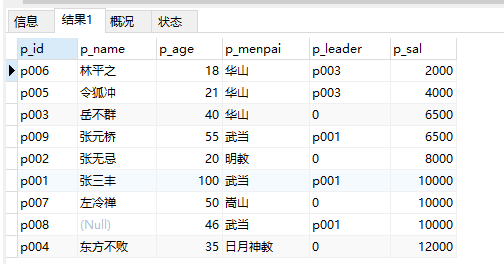
10、倒序排列:
select * from people where p_sal order p_sal desc
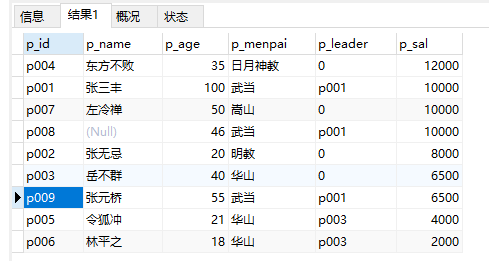
11、查询年龄为21岁人员的领导人是谁:
select * from people where p_id=(select p_leader from people where p_age='21')
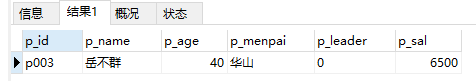
12、 查询当前人员中谁的工资最高
select * from ren where p_sal=(select max(p_sal) from ren )
注意:max()表示最大值
as 表示别名
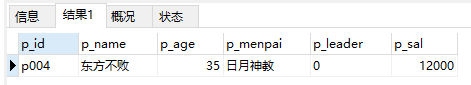
13、查询当前人员中谁的工资最低
select * from ren where p_sal=(select min(p_sal) from ren)
注意:min()表示最小值
14、查询当前人员的平均工资
select avg(p_sal) from ren
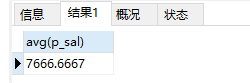
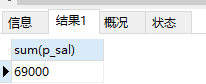
15、查询所有人工资的总和
select sum(p_sal) from ren
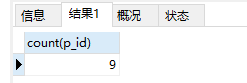
16、查询当前有多少个人员
select count(p_id) from ren
注意:count(主键):表示计算机中的记录的总个数,一般写主键(使用主键的效率是最高的)
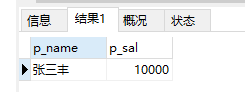
17、查询武当最高工资是谁
select p_name,p_sal from ren where p_sal =( select max(p_sal) from ren where p_menpai='武当') and p_menpai='武当'
18、查询各门派的平均工资
select avg(p_sal),p_menpai from ren group by p_menpai order by avg(p_sal) DESC
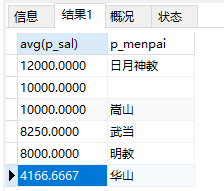
19、查询当前有哪些门派
select * from ren group by p_menpai
或者:
select distinct p_menpai from ren
注意:distinct表示去重复查询,要求查询的所有字段必须一样才行
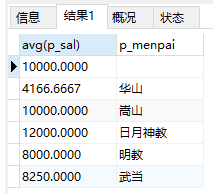
20、查询当前有哪些门派和门派的平均工资
select avg(p_sal),p_menpai from ren group by p_menpai
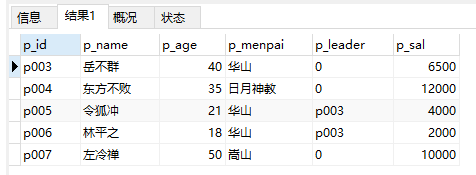
21、查询当前人员中第3条到第7条数据
select * from ren limit 2,5
注意:limit表示分页,其中:参数1:表示从第几条开始查询(下标从0开始);参数2:表示每次查询几条。
22、查询当前没有门派的人
select * from ren where p_menpai='' -- 其中=''表示查询字段为空的数据
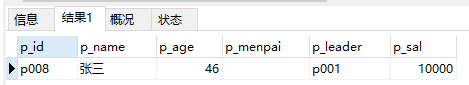
select * from ren where p_menpai is null --注意:is null表示查询字段为null 的数据
23、查询武当门派下的小弟
select * from ren where p_menai='武当' and p_leader='0'
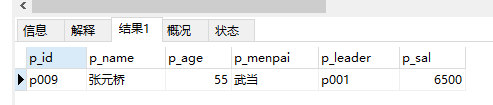
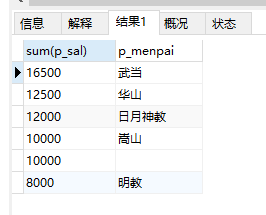
24、查询各门派的工资总和,按正序/倒序排列
select sum(p_sal),p_menpai from ren group by p_menpai order by sum(p_sal) DESC
25、查询人员并显示门派所在的位置(多表联合查询)
select * from ren ,wei --表,表 之后不加条件得到的是两张表的乘积(又叫笛卡尔乘积)
select * from ren , wei where p_menpai = a_name --在使用多表联合查询时,一定要加条件;如果是多个表的话,则需要表两两之间有关联。
结果:符合两个表条件的结果
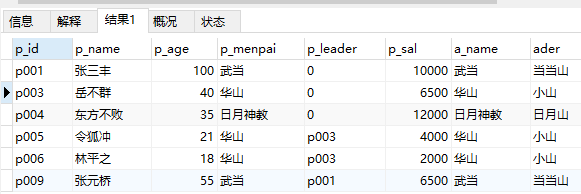
26、查询人员表,如果人员门派存在位置则显示位置信息,不存在则不显示位置
select * from ren left join wei on ren.p_menpai=wei.a_name
表示左连接查询
注意:on 表示条件 专门配置 left join 来使用
特点:左表数据全要,右表的数据与左表数据相匹配则显示,不匹配则以null显示
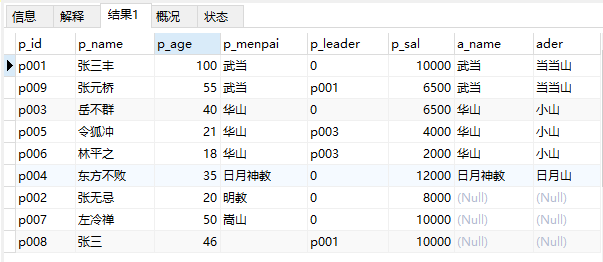
27、查询位置表,如果人员的门派有位置信息,则显示人员,没有则不显示
select * from wei left join ren on wei.a_name=ren.p_menpai
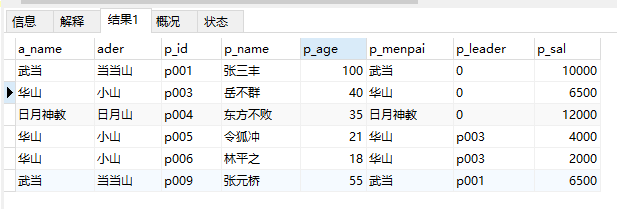
28、查询登记了地理位置的门派人员信息
select * from ren inner JOIN wei on ren.p_menpai = wei.a_name