问题:
Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.
You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
分析:
1 计数?
2 HashMap
first try:
import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { Map<Integer, Integer> elementCountMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) { if(elementCountMap.containsKey(nums[i])) { int count = elementCountMap.get(nums[i]); elementCountMap.put(nums[i], count++); } else { elementCountMap.put(nums[i], 1); } }// int majorElement = 0; for(Map.Entry entry : elementCountMap.entrySet()) { if ((nums.length/2)<(Integer)entry.getValue()) { majorElement = (Integer)entry.getKey(); } } return majorElement; } }
result:
Submission Result: Wrong Answer Input: [2,2] Output: 0 Expected: 2
anylysis:
找了很久也找不到错误。甚至还处处println debug,后来发现了犯了低级错误! count++啊啊啊啊
second try:
import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { Map<Integer, Integer> elementCountMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) { if(elementCountMap.containsKey(nums[i])) { int count = elementCountMap.get(nums[i]); elementCountMap.put(nums[i], ++count); } else { elementCountMap.put(nums[i], 1); } }// int majorElement = 0; for(Map.Entry entry : elementCountMap.entrySet()) { if ((nums.length/2)<(Integer)entry.getValue()) { majorElement = (Integer)entry.getKey(); } } return majorElement; } }
result:

third try:
//import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> elementCountMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) { if(elementCountMap.containsKey(nums[i])) { int count = elementCountMap.get(nums[i]); elementCountMap.put(nums[i], ++count); } else { elementCountMap.put(nums[i], 1); } }// int majorElement = 0; for(Map.Entry entry : elementCountMap.entrySet()) { if ((nums.length/2)<(Integer)entry.getValue()) { majorElement = (Integer)entry.getKey(); } } return majorElement; } }
result:
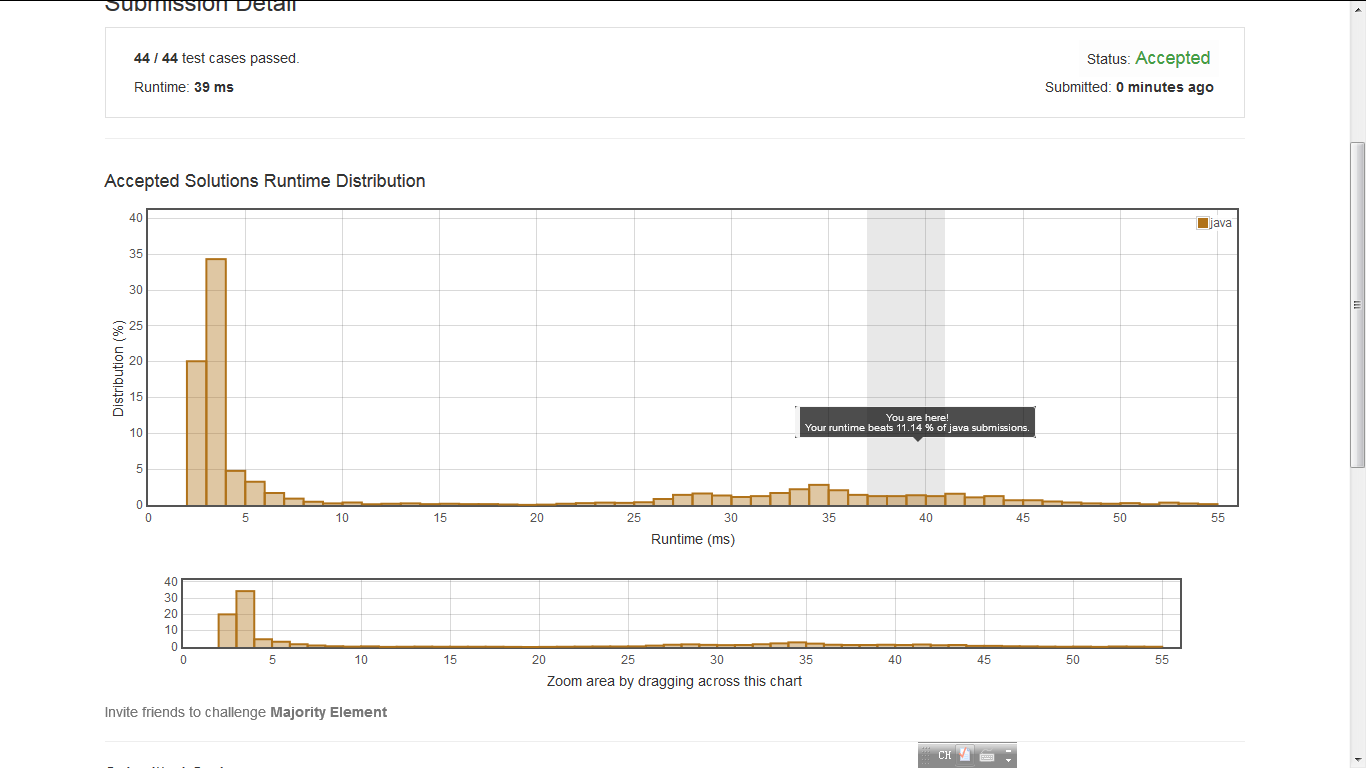
分析:
怎么效率还变差了。。。
try again:
//import java.util.Map; import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> elementCountMap = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) { if(elementCountMap.containsKey(nums[i])) { int count = elementCountMap.get(nums[i]); elementCountMap.put(nums[i], ++count); } else { elementCountMap.put(nums[i], 1); } }// int majorElement = 0; for(Map.Entry entry : elementCountMap.entrySet()) { if ((nums.length/2)<(Integer)entry.getValue()) { majorElement = (Integer)entry.getKey(); return majorElement; } } return majorElement; } }
result:
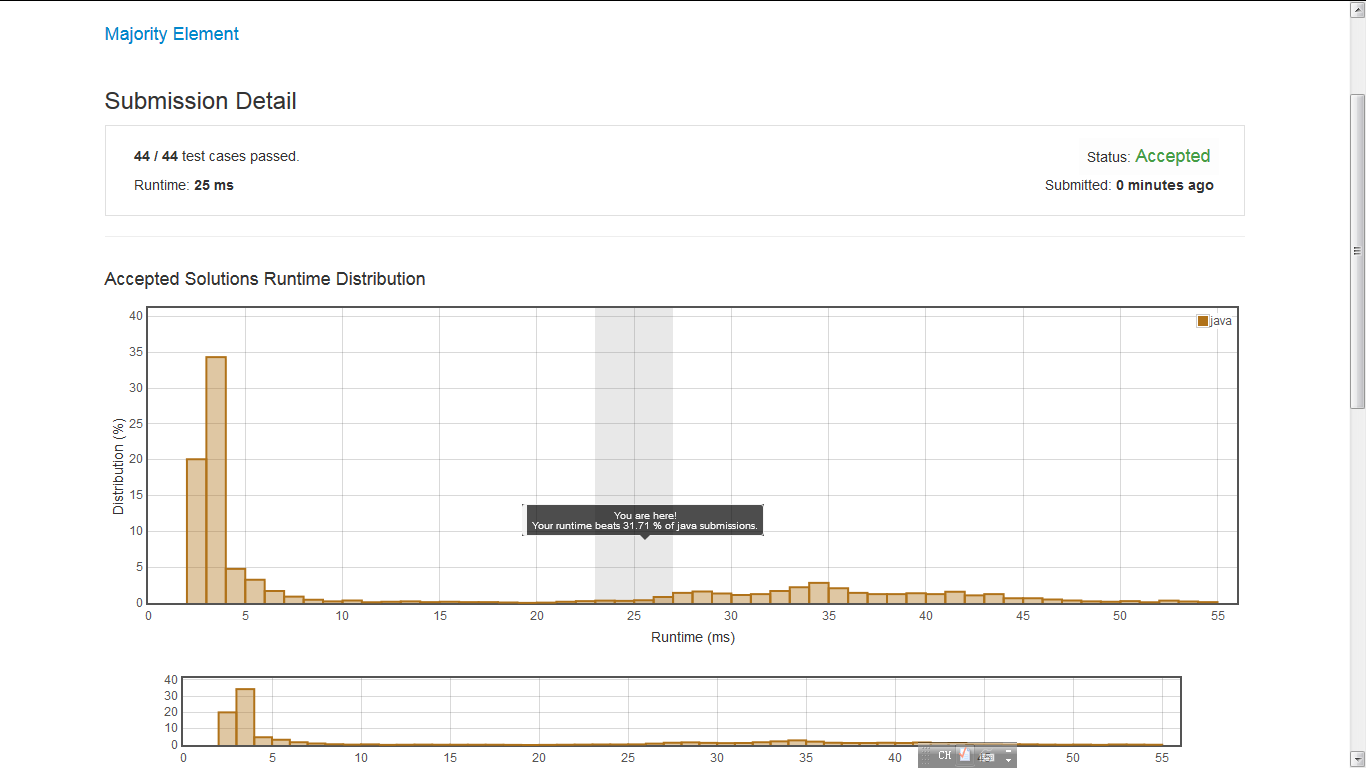
精妙算法BM投票算法:
分析:
是流算法的一个prototypical example:
In computer science, streaming algorithms are algorithms for processing data streams in which the input is presented as a sequence of items and can be examined in only a few passes (typically just one). In most models, these algorithms have access to limited memory (generally logarithmic in the size of and/or the maximum value in the stream). They may also have limited processing time per item.
try:
class Solution { public int majorityElement(int[] nums) { int count=0; int currentMajor=nums[0]; for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){ if(nums[i]==currentMajor){ count++; }else{ count--; } if(count==0 && i+1<nums.length){ currentMajor=nums[i+1]; } } return currentMajor; } }
result:

conclusion: