通常我们就会看到一个配置文件,比如:jdbc.properties,它是以“.properties”格式结尾的。在java中,这种文件的内容以键值对<key,value>存储,通常以“=”分隔key和value,当然也可以用":"来分隔,但通常不这么干。
- 读取配置文件
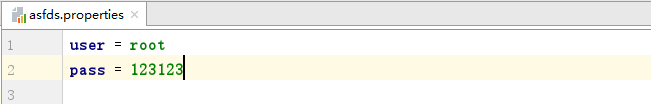
这里有一个文件叫asfds.properties,里面简单的存了两个键值对,如下图所示:
读取配置文件的基本步骤是:
- 实例化一个Properties对象;
- 将要读取的文件放入数据流中;
- 调用Properties对象的load方法,将属性文件的键值对加载到Properties类对象中;
- 调用Properties对象的getProperty(String key)读入对应key的value值。
注:如果想要读取key值,可以调用Properties对象的stringPropertyNames()方法获取一个set集合,然后遍历set集合即可。
读取配置文件的方法:
1 /** 2 * read properties file 3 * @param paramFile file path 4 * @throws Exception 5 */ 6 public static void inputFile(String paramFile) throws Exception 7 { 8 Properties props=new Properties();//使用Properties类来加载属性文件 9 FileInputStream iFile = new FileInputStream(paramFile); 10 props.load(iFile); 11 12 /**begin*******直接遍历文件key值获取*******begin*/ 13 Iterator<String> iterator = props.stringPropertyNames().iterator(); 14 while (iterator.hasNext()){ 15 String key = iterator.next(); 16 System.out.println(key+":"+props.getProperty(key)); 17 } 18 /**end*******直接遍历文件key值获取*******end*/ 19 20 /**begin*******在知道Key值的情况下,直接getProperty即可获取*******begin*/ 21 String user=props.getProperty("user"); 22 String pass=props.getProperty("pass"); 23 System.out.println(" "+user+" "+pass); 24 /**end*******在知道Key值的情况下,直接getProperty即可获取*******end*/ 25 iFile.close(); 26 27 }
- 写入配置文件
写入配置文件的基本步骤是:
- 实例化一个Properties对象;
- 获取一个文件输出流对象(FileOutputStream);
- 调用Properties对象的setProperty(String key,String value)方法设置要存入的键值对放入文件输出流中;
- 调用Properties对象的store(OutputStream out,String comments)方法保存,comments参数是注释;
写入配置文件的方法:
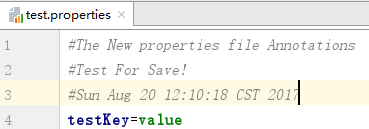
1 /** 2 *write properties file 3 * @param paramFile file path 4 * @throws IOException 5 */ 6 private static void outputFile(String paramFile) throws IOException { 7 ///保存属性到b.properties文件 8 Properties props=new Properties(); 9 FileOutputStream oFile = new FileOutputStream(paramFile, true);//true表示追加打开 10 props.setProperty("testKey", "value"); 11 //store(OutputStream,comments):store(输出流,注释) 注释可以通过“ ”来换行 12 props.store(oFile, "The New properties file Annotations"+" "+"Test For Save!"); 13 oFile.close(); 14 }
- 测试输出
文件读取:
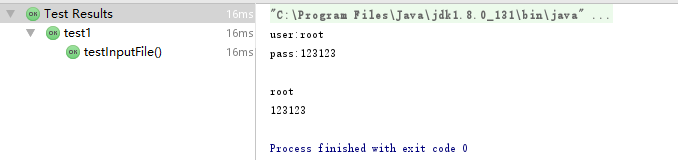
@Test public void testInputFile(){//read properties file try { inputFile("resources/asfds.properties"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
输出:
文件写入:
@Test public void testOutputFile(){//write properties file try { outputFile("resources/test.properties"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
写入的文件: