上一篇文章主要讨论了字符编码的不同方式,这一篇文章着重谈谈对python的编码解码的理解。
python2
在python2中主要有两种类型的字符类型,一个是str,一个是Unicode。平时我们默认操作的字符串类型是str,在字符串前面加一个u就是Unicode类型。
这两个类型有相应的工厂方法:str()和unicode()
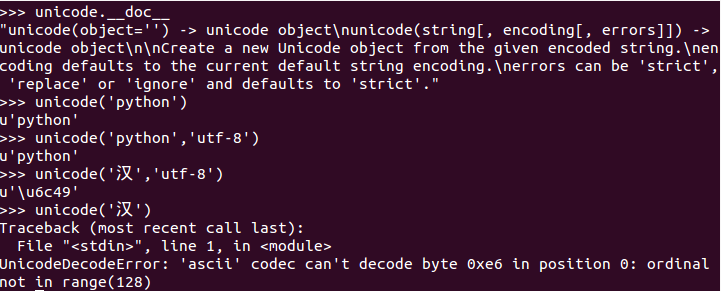
上图的例子中可以看出,unicode方法将传入的string,利用传入的encoding将string转换成unicode对象。注意最后的错误是因为python默认的编码方式是ASCII编码格式。
>>>import sys
>>>sys.getdefaultencoding()
'ascii'
string类型和unicode类型分别拥有str.decode()和unicode.encode()方法。我们实验一下:
>>>a_unicode=u 'Hi u2119' #长度为4
>>>to_string=a_unicode.encode('utf-8')
>>>to_string
'Hi xe2x84x99' #这里长度为6
>>>type(to_string)
'str'
>>>to_new_unicode=to_string.decode('utf-8')
>>>to_noe_unicode==a_unicode
True #这里python2中两者是相等的,但是python3中不相等。
>>>asc_string=a_unicode.encode()
UnicodeEncodeError:'ascii' not in range(128) #上面讲过python默认编码是ascii,而ascii只能表示128的字符,u2119超出了ascii的可编码范围,所以错误
>>>asc_unicode=to_string.decode()
UnicodeEncodeError:'ascii' not in range(128) #这里利用ascii解码utf-8编码过的字符,出现同样的错误。
>>>to_string.encode('utf-8')
UnicodeEncodeError:'ascii' not in range(128)
上述代码,最后一个错误尤其要注意,尝试将一个字符串类型编码成utf-8编码格式,在python内部要经过两个步骤:将字符串转换成unicode,接着将转换后的unicodeencode成'utf-8'格式即:to_string.decode(sys.getdefaultencoding).encode('utf-8')。因为默认为ascii编码,不能转换xe2,所以出现错误。
从上述错误我们要注意两点:
- 在转换的时候,明确转换的字符串的类型,确认是str还是unicode
- 明白python内部包含的隐式转换方法。
参考资料:
http://nedbatchelder.com/text/unipain.html
https://docs.python.org/2/howto/unicode.html
http://blog.csdn.net/trochiluses/article/details/16825269