题目:
Design and implement a data structure for Least Recently Used (LRU) cache. It should support the following operations: get and set.
get(key) - Get the value (will always be positive) of the key if the key exists in the cache, otherwise return -1.set(key, value) - Set or insert the value if the key is not already present. When the cache reached its capacity, it should invalidate the least recently used item before inserting a new item.
题解:
这道题是一个数据结构设计题,在leetcode里面就这么一道,还是挺经典的一道题,可以好好看看。
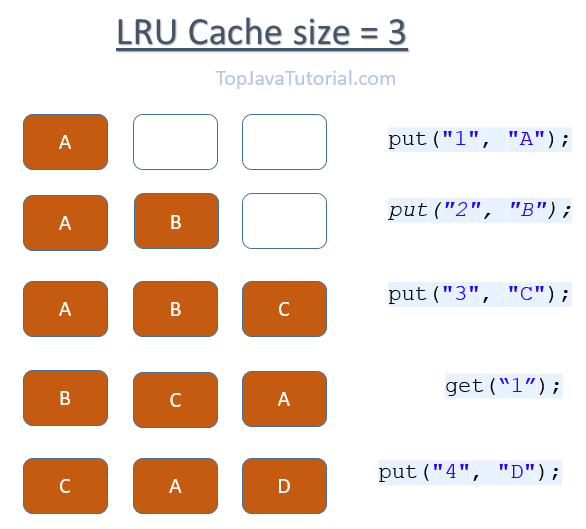
这道题要求设计实现LRU cache的数据结构,实现set和get功能。学习过操作系统的都应该知道,cache作为缓存可以帮助快速存取数据,但是确定是容量较小。这道题要求实现的cache类型是LRU,LRU的基本思想就是“最近用到的数据被重用的概率比较早用到的大的多”,是一种更加高效的cache类型。
解决这道题的方法是:双向链表+HashMap。
“为了能够快速删除最久没有访问的数据项和插入最新的数据项,我们将双向链表连接Cache中的数据项,并且保证链表维持数据项从最近访问到最旧访问的顺序。 每次数据项被查询到时,都将此数据项移动到链表头部(O(1)的时间复杂度)。这样,在进行过多次查找操作后,最近被使用过的内容就向链表的头移动,而没 有被使用的内容就向链表的后面移动。当需要替换时,链表最后的位置就是最近最少被使用的数据项,我们只需要将最新的数据项放在链表头部,当Cache满 时,淘汰链表最后的位置就是了。 ”
“注: 对于双向链表的使用,基于两个考虑。
首先是Cache中块的命中可能是随机的,和Load进来的顺序无关。
其次,双向链表插入、删除很快,可以灵活的调整相互间的次序,时间复杂度为O(1)。”
解决了LRU的特性,现在考虑下算法的时间复杂度。为了能减少整个数据结构的时间复杂度,就要减少查找的时间复杂度,所以这里利用HashMap来做,这样时间苏咋读就是O(1)。
所以对于本题来说:
get(key): 如果cache中不存在要get的值,返回-1;如果cache中存在要找的值,返回其值并将其在原链表中删除,然后将其作为头结点。
set(key,value):当要set的key值已经存在,就更新其value, 将其在原链表中删除,然后将其作为头结点;当药set的key值不存在,就新建一个node,如果当前len<capacity,就将其加入hashmap中,并将其作为头结点,更新len长度,否则,删除链表最后一个node,再将其放入hashmap并作为头结点,但len不更新。
原则就是:对链表有访问,就要更新链表顺序。
class DoubleLinkedListNode { public int val; public int key; public DoubleLinkedListNode pre; public DoubleLinkedListNode next; public DoubleLinkedListNode(int key, int value) { val = value; this.key = key; } } public class LRUCache { private HashMap<Integer, DoubleLinkedListNode> map = new HashMap<Integer, DoubleLinkedListNode>(); private DoubleLinkedListNode head; private DoubleLinkedListNode end; private int capacity; private int len; public LRUCache(int capacity) { this.capacity = capacity; len = 0; } public int get(int key) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { DoubleLinkedListNode latest = map.get(key); removeNode(latest); setHead(latest); return latest.val; } else return -1; } public void set(int key, int value) { if(map.containsKey(key)) { DoubleLinkedListNode oldNode = map.get(key); oldNode.val = value; removeNode(oldNode); setHead(oldNode); } else { DoubleLinkedListNode newNode = new DoubleLinkedListNode(key, value); if(len<capacity) { setHead(newNode); map.put(key,newNode); len++; } else { map.remove(end.key); end = end.pre; if (end != null) { end.next = null; } setHead(newNode); map.put(key,newNode); } } } public void removeNode(DoubleLinkedListNode node) { DoubleLinkedListNode cur = node; DoubleLinkedListNode pre = node.pre; DoubleLinkedListNode next = node.next; if(pre!=null) { pre.next = next; // next.pre = pre; next may be NULL! } else { head = next; } if(next!=null) { next.pre = pre; // pre.next = next; ? } else { end = pre; } } public void setHead(DoubleLinkedListNode node) { node.next = head; node.pre = null; // head.pre = node; if (head != null) { head.pre = node; //Head may be NULL!empty linkedlist } head = node; if(end==null){ end = node; } } }
http://www.topjavatutorial.com/java/java-programs/lru-cache-java/