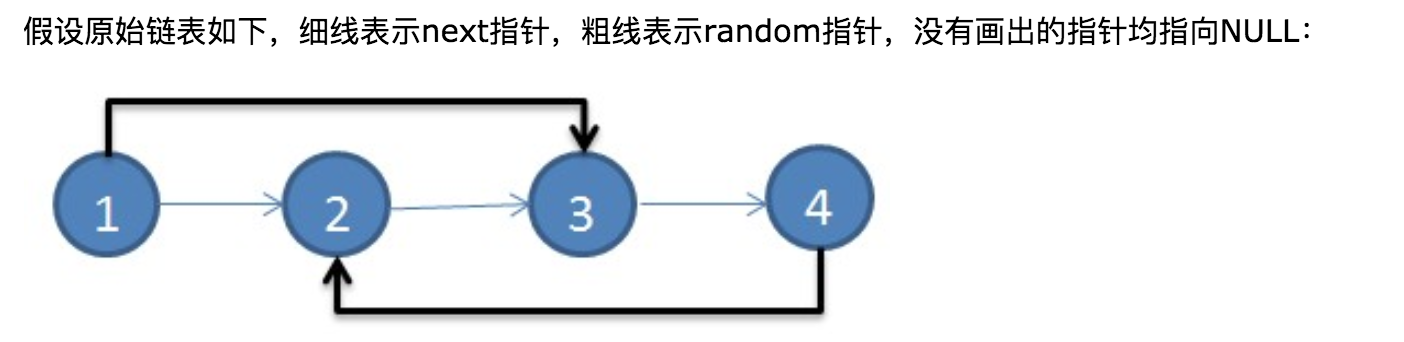
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
算法1:我们在构建新链表的节点时,保存原始链表的next指针映射关系,并把指针做如下变化(蓝色为原始链表节点,紫红色为新链表节点):

然后在上图的基础上进行如下两步
1、构建新链表的random指针:比如new1->random = new1->random->random->next, new2->random = NULL, new3-random = NULL, new4->random = new4->random->random->next
2、恢复原始链表:根据最开始保存的原始链表next指针映射关系恢复原始链表
该算法时间空间复杂度均为O(N)
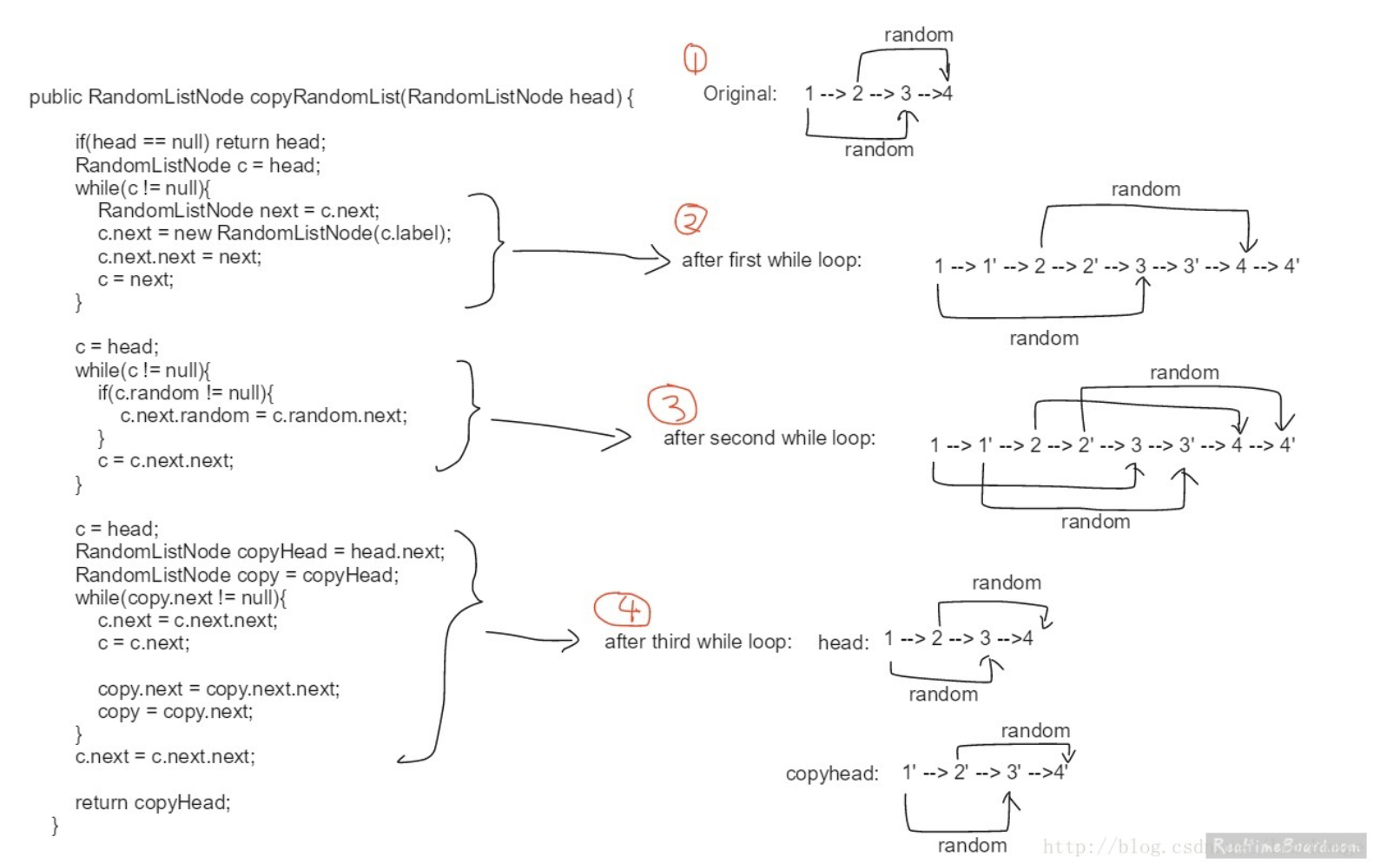
算法2:该算法更为巧妙,不用保存原始链表的映射关系,构建新节点时,指针做如下变化,即把新节点插入到相应的旧节点后面:

同理分两步
1、构建新节点random指针:new1->random = old1->random->next, new2-random = NULL, new3-random = NULL, new4->random = old4->random->next
2、恢复原始链表以及构建新链表:例如old1->next = old1->next->next, new1->next = new1->next->next
该算法时间复杂度O(N),空间复杂度O(1)
算法2的代码:
public RandomListNode copyRandomList(RandomListNode head) { if(head == null) return head; RandomListNode cur = head; while(cur != null){ RandomListNode sec = new RandomListNode(cur.label); sec.next = cur.next; cur.next = sec; cur = cur.next.next; } cur = head; while(cur != null){ if(cur.random != null) cur.next.random = cur.random.next; cur = cur.next.next; } cur = head; RandomListNode res = head.next; RandomListNode sec = res; while(sec.next != null){ cur.next = cur.next.next; cur = cur.next; sec.next = sec.next.next; sec = sec.next; } cur.next = cur.next.next; return res; } --------------------- 作者:liuchongee 来源:CSDN 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchonge/article/details/74858192 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
图示
reference:
https://blog.csdn.net/liuchonge/article/details/74858192
http://www.cnblogs.com/TenosDoIt/p/3387000.html