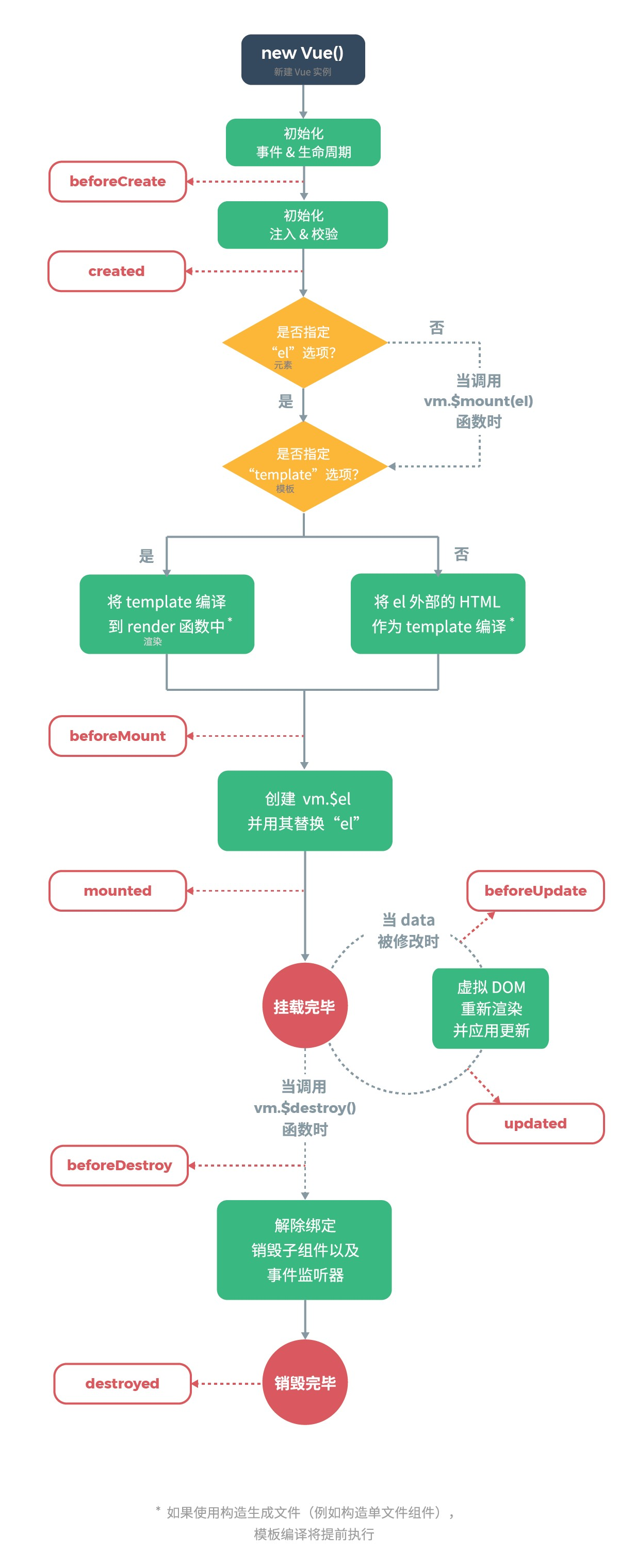
使用方法 --- 4个before,4个ed,创造,装载,更新,销毁
初始化阶段
beforeCreate(){} // 准备怀孕
created(){} // 怀上了 *******************************************
beforeMount(){} // 准备生
mounted(){} // 生下来了 *************************************************
运行时阶段
beforeUpdate(){} // 每天都在长大
updated(){} ************************
销毁阶段
beforeDestroy(){} // 马上 game over
destroyed(){} // game over gg ************
综上所述,会在 created 或者 mounted 中请求数据
如果必须使用dom操作,那么可以在 mounted 和 updated 中
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <button @click="des">销毁</button> <button @click="add">修改状态</button>{{ count }} </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { count: 0 }, methods: { add () { this.count += 1 }, des () { this.$destroy() // 触发销毁 } }, beforeCreate () { console.log('创建实例之前', this.$el) // undefined console.log('创建实例之前', this.$data) // undefined console.log('创建实例之前', this.count) // undefined }, created () { console.log('创建实例成功', this.$el) // undefined console.log('创建实例成功', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('创建实例成功', this.count) // 0 }, beforeMount () { console.log('装载之前', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('装载之前', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('装载之前', this.count) // 0 }, mounted () { console.log('装载之后', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('装载之后', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('装载之后', this.count) // 0 }, beforeUpdate () { console.log('更新之前', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('更新之前', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('更新之前', this.count) // 1 }, updated () { console.log('更新之后', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('更新之后', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('更新之后', this.count) // 1 }, beforeDestroy () { console.log('销毁之前', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('销毁之前', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('销毁之前', this.count) // 1 }, destroyed () { console.log('销毁之后', this.$el) // <div id="app"></div> console.log('销毁之后', this.$data) // {count: 0} console.log('销毁之后', this.count) // 1 } }) </script> </html>
AJAX请求数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> ul li{ list-style: none; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="item of list" :key="item.userid"> {{item.username}}--{{item.age}}--{{item.sex}} </li> </ul> </div> </body> <script src="../jquery.min.js"></script> <script src="../vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el:"#app", data:{ list:[] }, created(){ $.ajax({ url:"http://localhost:3000/users", success:(data)=>{ console.log(data.data) this.list=data.data } }) } }) </script> </html>
fetch请求数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="item of list" :key="item.userid">{{ item.username }}</li> </ul> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { list: [] }, created () { fetch('http://localhost:3000/users').then(res => res.json()).then(data => { console.log(data) this.list = data.data }) } }) </script> </html>
axios请求数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <ul> <li v-for="item of list" :key="item.userid">{{ item.username }}</li> </ul> </div> </body> <script src="vue.js"></script> <script src="axios.js"></script> <script> new Vue({ el: '#app', data: { list: [] }, created () { // $.get axios.get('http://localhost:3000/users').then(res => { console.log(res.data.data) this.list = res.data.data }) } }) </script> </html>
如果使用post请求:
fetch(url).then(
// 得到的是 promise 对象,前端需要的json数据,需要将其转换为json数据
// res => res.json()
function (res) { return res.json() }
).then(
// 得到的就是json对象,可以供前端直接使用
data => console.log(data)
)
```
**默认的是get的请求方式,如果为post请求呢**
```
fetch('http://****/login', {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
},
body: JSON.stringify({username: '', password: ''})
}).then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
});
axios.get(url).then(res => {})
axios.post(url, {username: ''}).then(res => {})
axios({
url: '',
method: 'post',
data: {
username: ''
}
}).then(res => {})