实验任务详情:
完成火车站售票程序的模拟。
要求:
(1)总票数1000张;
(2)10个窗口同时开始卖票;
(3)卖票过程延时1秒钟;
(4)不能出现一票多卖或卖出负数号票的情况。
实验代码
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
private int ticket=1000;
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<1001;i++) {
synchronized(this) {
if(ticket>0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+"正在售出第"+ticket--+"张票");
System.out.println("当前剩余"+ticket+"张");
}
}
}
}
}
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread mt=new MyThread();
Thread t1=new Thread(mt,"窗口一");
Thread t2=new Thread(mt,"窗口二");
Thread t3=new Thread(mt,"窗口三");
Thread t4=new Thread(mt,"窗口四");
Thread t5=new Thread(mt,"窗口五");
Thread t6=new Thread(mt,"窗口六");
Thread t7=new Thread(mt,"窗口七");
Thread t8=new Thread(mt,"窗口八");
Thread t9=new Thread(mt,"窗口九");
Thread t10=new Thread(mt,"窗口十");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
t6.start();
t7.start();
t8.start();
t9.start();
t10.start();
}
}
这里不知道为什么一直是窗口一运行,但后面就有别的窗口运行了
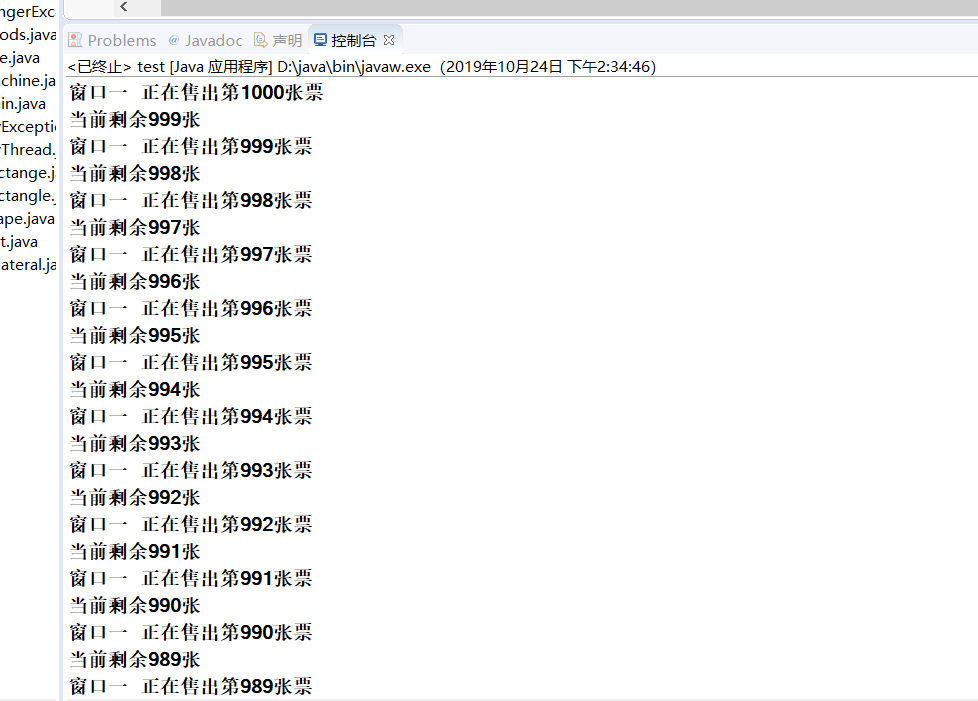
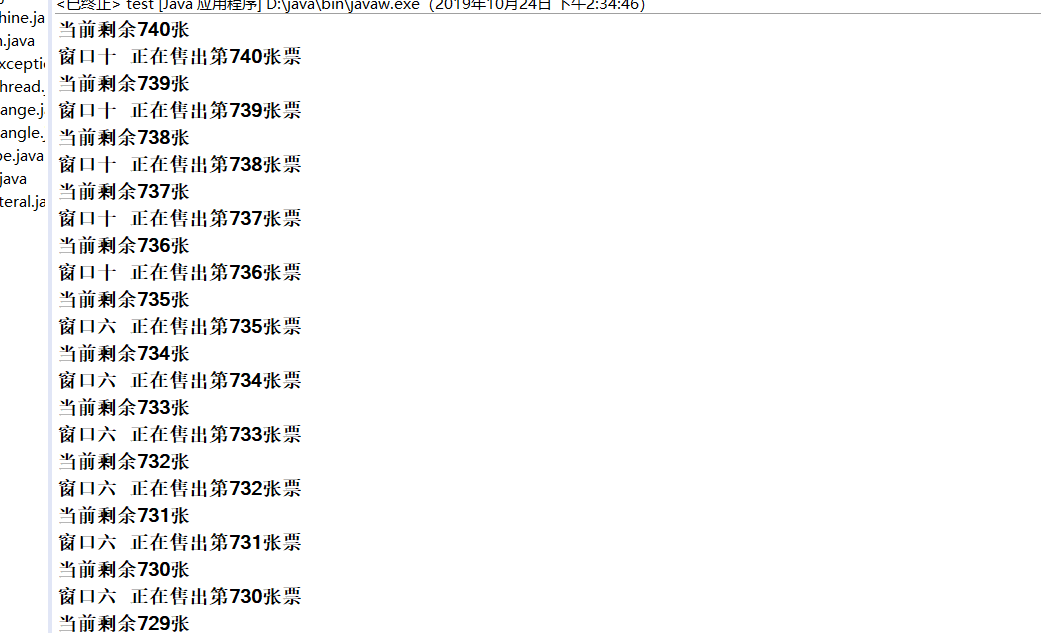
总结
对线程
实现多线程有两种方式,一种是继承Thread类,一种是实现Runnable接口,但都要覆写run方法。
启动线程不是直接调用run方法,而是start方法。
线程的操作方法
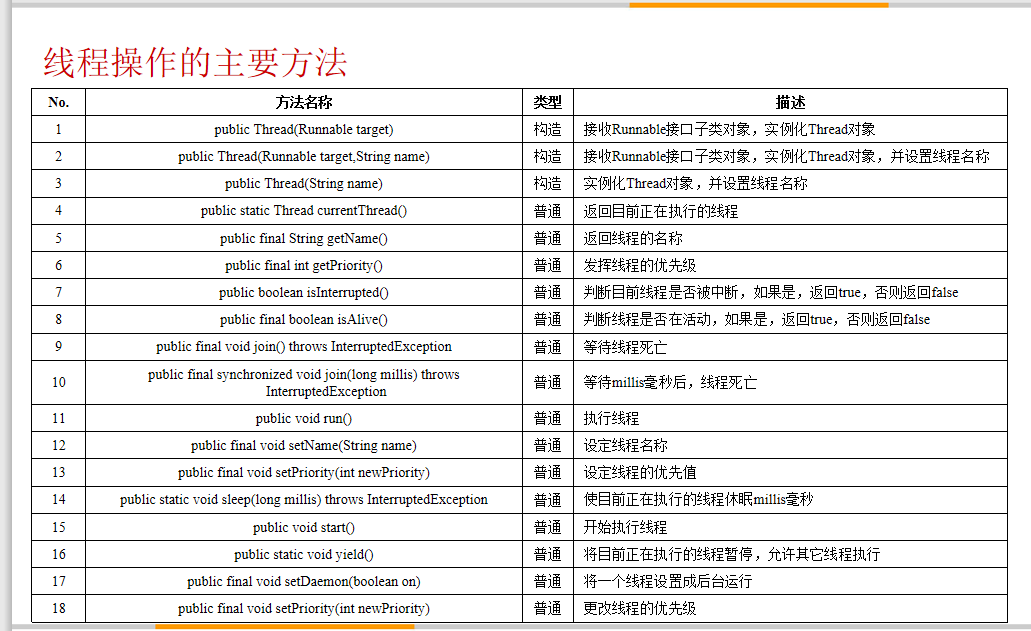
哪个线程优先级高,是可能先执行,并不是一定先执行。
同步synchronized的用法
synchronized(同步对象){
代码
}