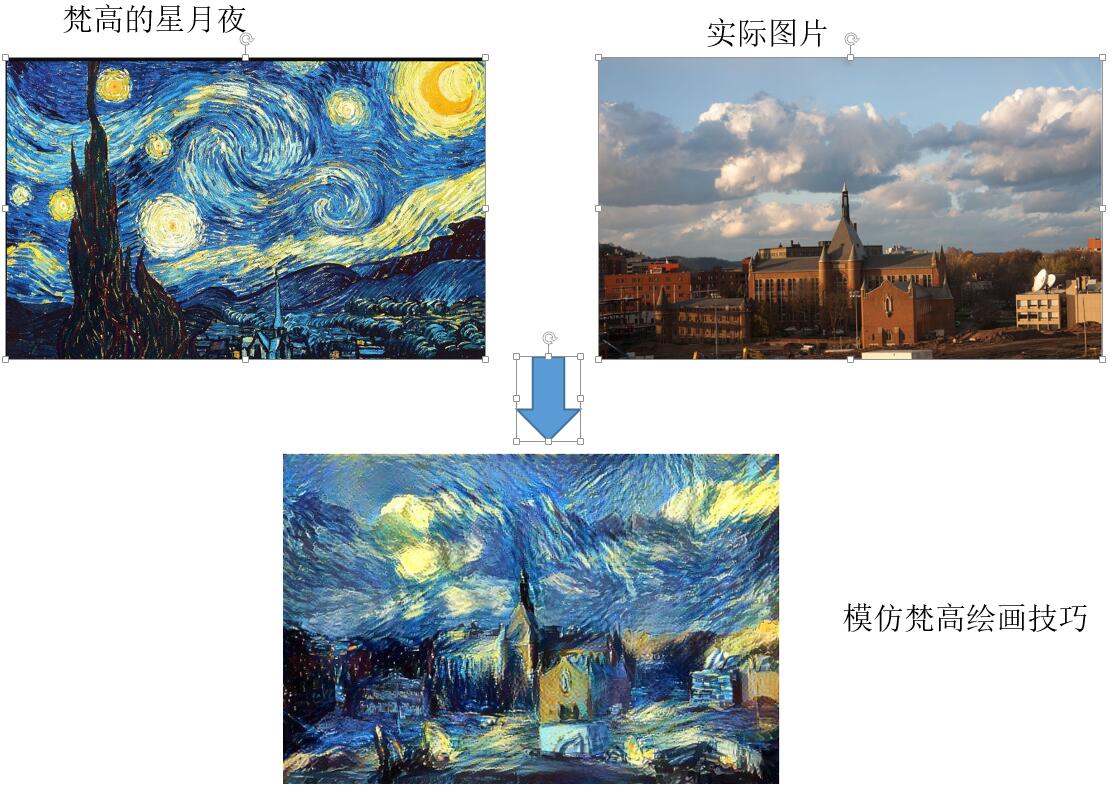
该代码是实现A Neural Algorithm of Artistic Style ,具体可以参考https://github.com/apache/incubator-mxnet/tree/master/example/neural-style
import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.WARN) # disable the verbose INFO messages for cleaner notebook display #这个很重要,不然会出现缺少先关模块的错误 import sys; sys.path.append("/home/hxj/anaconda3/lib/python3.6/site-packages") # some setup %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import os import urllib import numpy as np import mxnet from mxnet import gluon from skimage import io # URL to the style image. Change this to use your own style. style_url = """https://github.com/dmlc/web-data/raw/master/mxnet/neural-style/input/starry_night.jpg""" # URL to the content image. Change this to use your own content content_url = """https://github.com/dmlc/web-data/raw/master/mxnet/neural-style/input/IMG_4343.jpg""" def ensure_dir(path): """Makes sure the path exists so we can save a file to it.""" dirname = os.path.dirname(path) try: os.mkdir(dirname) except OSError: # Probably because the path exists already pass # Download the CNN cnn_url = "https://github.com/dmlc/web-data/raw/master/mxnet/neural-style/model/vgg19.params" cnn_path = 'model/vgg19.params' ensure_dir(cnn_path) #urllib.request.urlretrieve(cnn_url, cnn_path) # Download the images style_path = "input/style.jpg" #content_path = "input/content.jpg" content_path = "input/1.jpg" ensure_dir(style_path) #urllib.request.urlretrieve(style_url, style_path) ensure_dir(content_path) #urllib.request.urlretrieve(content_url, content_path) style_img = io.imread(style_path) content_img = io.imread(content_path) # Show the images plt.subplot(121) plt.axis('off') plt.title('style') plt.imshow(style_img) plt.subplot(122) plt.axis('off') plt.title('content') plt.imshow(content_img) plt.show()
#参数设置 import nstyle # Load code for neural style training args = nstyle.get_args([]) # get the defaults args object # Stopping criterion. A larger value means less time but lower quality. # 0.01 to 0.001 is a decent range. args.stop_eps = 0.005 # Resize the long edge of the input images to this size. # Smaller value is faster but the result will have lower resolution. args.max_size = 600 # content image weight. A larger value means more original content. args.content_weight = 10.0 # Style image weight. A larger value means more style. args.style_weight = 1.0 # Initial learning rate. Change this affacts the result. args.lr = 0.001 # Learning rate schedule. How often to decrease and by how much args.lr_sched_delay = 50 args.lr_sched_factor = 0.6 # How often to update the notebook display args.save_epochs = 50 # How long to run for args.max_num_epochs = 1000 # Remove noise. The amount of noise to remove. args.remove_noise = 0.02 args.content_image = content_path args.style_image = style_path args.output_dir = 'output/' ensure_dir(args.output_dir)
import IPython.display import mxnet.notebook.callback import math eps_chart = mxnet.notebook.callback.LiveTimeSeries(y_axis_label='log_10(eps)', # Setting y-axis to log-scale makes sense, but bokeh has a bug # https://github.com/bokeh/bokeh/issues/5393 # So I'll calculate log by hand below. #y_axis_type='log', ) def show_img(data): eps_chart.update_chart_data(math.log10(data['eps'])) if data.get('filename',None): IPython.display.clear_output() print("Epoch %d eps = %g " % (data['epoch'], data['eps'])) h = IPython.display.HTML("<img src='"+data['filename']+"'>") IPython.display.display(h)
nstyle.train_nstyle(args, callback=show_img)
final_img = io.imread(args.output_dir+'final.jpg') plt.figure(figsize=(3,2)) plt.axis('off') plt.title('final') plt.imshow(final_img) plt.show()
下面是主要函数文件nstyle.py
import find_mxnet import mxnet as mx import numpy as np import importlib #动态导入Python库 import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG) import argparse #Python命令参数传递 from collections import namedtuple #Python集合类 from skimage import io, transform from skimage.restoration import denoise_tv_chambolle #加载该函数,使用TV模型的去噪 CallbackData = namedtuple('CallbackData', field_names=['eps','epoch','img','filename']) def get_args(arglist=None): #加载运行时参数 parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='neural style')#静态方法,定义一个参数对象 parser.add_argument('--model', type=str, default='vgg19',#加载预训练好的模型VGG choices = ['vgg'], help = 'the pretrained model to use') parser.add_argument('--content-image', type=str, default='input/IMG_4343.jpg', help='the content image') #内容图片 parser.add_argument('--style-image', type=str, default='input/starry_night.jpg', help='the style image') #样式图片 parser.add_argument('--stop-eps', type=float, default=.005, help='stop if the relative chanage is less than eps') #迭代次数误差 parser.add_argument('--content-weight', type=float, default=10, help='the weight for the content image') #内容权重 parser.add_argument('--style-weight', type=float, default=1, #样式权重 help='the weight for the style image') parser.add_argument('--tv-weight', type=float, default=1e-2, help='the magtitute on TV loss') #TV模型中相邻两次的误差小于其值,就停止迭代 parser.add_argument('--max-num-epochs', type=int, default=1000, help='the maximal number of training epochs') #最大的训练迭代次数 parser.add_argument('--max-long-edge', type=int, default=600, help='resize the content image') #图像大小 parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=.001, help='the initial learning rate') #learning rate parser.add_argument('--gpu', type=int, default=-1, help='which gpu card to use, -1 means using cpu') #是否GPU parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, default='output/', help='the output image') #输出目录 parser.add_argument('--save-epochs', type=int, default=50, help='save the output every n epochs') #保存每一轮次 parser.add_argument('--remove-noise', type=float, default=.02, help='the magtitute to remove noise') #TV模型去噪的参数,即光滑参数nameda parser.add_argument('--lr-sched-delay', type=int, default=75, help='how many epochs between decreasing learning rate') parser.add_argument('--lr-sched-factor', type=int, default=0.9, help='factor to decrease learning rate on schedule') if arglist is None: return parser.parse_args() else: return parser.parse_args(arglist) #这样写就可以加载默认参数 nstyle.get_args([]) def PreprocessContentImage(path, long_edge): img = io.imread(path) logging.info("load the content image, size = %s", img.shape[:2]) #img.shape=(480,360) 就是height,width factor = float(long_edge) / max(img.shape[:2]) #这里表示最大值是600/480 new_size = (int(img.shape[0] * factor), int(img.shape[1] * factor))# 新图像大小 resized_img = transform.resize(img, new_size) #调整图像大小 sample = np.asarray(resized_img) * 256 #因为调整图像大小后,数字范围在0-1之间 # swap axes to make image from (224, 224, 3) to (3, 224, 224) sample = np.swapaxes(sample, 0, 2) sample = np.swapaxes(sample, 1, 2) # sub mean #图像预处理:减去的均值是数据集所有图片的RGB三个通道的均值构成的向量[Rmean, Gmean, Bmean] #每个通道各一个均值。然后所有图像都减去此向量。 在训练集得到的均值要应用于测试集,保证变换形式相同。 sample[0, :] -= 123.68 sample[1, :] -= 116.779 sample[2, :] -= 103.939 logging.info("resize the content image to %s", new_size) return np.resize(sample, (1, 3, sample.shape[1], sample.shape[2]))#返回shape参数提供给style使用 (1,3,480,360) def PreprocessStyleImage(path, shape): img = io.imread(path) resized_img = transform.resize(img, (shape[2], shape[3])) sample = np.asarray(resized_img) * 256 sample = np.swapaxes(sample, 0, 2) sample = np.swapaxes(sample, 1, 2) sample[0, :] -= 123.68 sample[1, :] -= 116.779 sample[2, :] -= 103.939 return np.resize(sample, (1, 3, sample.shape[1], sample.shape[2])) def PostprocessImage(img): img = np.resize(img, (3, img.shape[2], img.shape[3])) img[0, :] += 123.68 img[1, :] += 116.779 img[2, :] += 103.939 img = np.swapaxes(img, 1, 2) img = np.swapaxes(img, 0, 2) img = np.clip(img, 0, 255) #将图像大小限制在0-255之间 return img.astype('uint8') def SaveImage(img, filename, remove_noise=0.): logging.info('save output to %s', filename) out = PostprocessImage(img) if remove_noise != 0.0: out = denoise_tv_chambolle(out, weight=remove_noise, multichannel=True)#TV模型去噪 io.imsave(filename, out) def style_gram_symbol(input_size, style): #求取样式图像在训练的过程中,在每一次output后加入一个全连接层,求神经元之间的点乘,即格拉姆矩阵 _, output_shapes, _ = style.infer_shape(data=(1, 3, input_size[0], input_size[1]))#mxnet推测输入和输出参数 gram_list = [] grad_scale = [] ''' style的output_shapes如下所示 [(1, 64, 480, 360), (1, 128, 240, 180), (1, 256, 120, 90), (1, 512, 60, 45), (1, 512, 30, 22)] style的list_outputs()如下所示 'relu1_1_output', 'relu2_1_output', 'relu3_1_output', 'relu4_1_output', 'relu5_1_output' ''' for i in range(len(style.list_outputs())): shape = output_shapes[i] x = mx.sym.Reshape(style[i], target_shape=(int(shape[1]), int(np.prod(shape[2:])))) #np.prod(shape[2:])=480*360=172000 # use fully connected to quickly do dot(x, x^T) gram = mx.sym.FullyConnected(x, x, no_bias=True, num_hidden=shape[1])#使用全连接层求X * X^T gram_list.append(gram) grad_scale.append(np.prod(shape[1:]) * shape[1]) return mx.sym.Group(gram_list), grad_scale def get_loss(gram, content): gram_loss = [] for i in range(len(gram.list_outputs())): gvar = mx.sym.Variable("target_gram_%d" % i) gram_loss.append(mx.sym.sum(mx.sym.square(gvar - gram[i]))) cvar = mx.sym.Variable("target_content") content_loss = mx.sym.sum(mx.sym.square(cvar - content)) return mx.sym.Group(gram_loss), content_loss def get_tv_grad_executor(img, ctx, tv_weight): """create TV gradient executor with input binded on img """ if tv_weight <= 0.0: return None nchannel = img.shape[1] simg = mx.sym.Variable("img") skernel = mx.sym.Variable("kernel") channels = mx.sym.SliceChannel(simg, num_outputs=nchannel) out = mx.sym.Concat(*[ mx.sym.Convolution(data=channels[i], weight=skernel, num_filter=1, kernel=(3, 3), pad=(1,1), no_bias=True, stride=(1,1)) for i in range(nchannel)]) kernel = mx.nd.array(np.array([[0, -1, 0], [-1, 4, -1], [0, -1, 0]]) .reshape((1, 1, 3, 3)), ctx) / 8.0 out = out * tv_weight return out.bind(ctx, args={"img": img, "kernel": kernel}) def train_nstyle(args, callback=None): """Train a neural style network. Args are from argparse and control input, output, hyper-parameters. callback allows for display of training progress. """ # input #dev = mx.gpu(args.gpu) if args.gpu >= 0 else mx.cpu() dev = mx.cpu() content_np = PreprocessContentImage(args.content_image, args.max_long_edge) style_np = PreprocessStyleImage(args.style_image, shape=content_np.shape) size = content_np.shape[2:] #shape为(1,3,480,360),所以size为 (480,360) # model Executor = namedtuple('Executor', ['executor', 'data', 'data_grad'])#将这些字符串加入集合Executor里面 model_module = importlib.import_module('model_' + args.model) #加载模型 model_vgg19, 即model_vgg19.py style, content = model_module.get_symbol() #调用model_vgg19.py文件里面的get_symbol方法 gram, gscale = style_gram_symbol(size, style)#求出style的格拉姆矩阵 model_executor = model_module.get_executor(gram, content, size, dev) #调用model_vgg19.py文件里面的get_executor方法 model_executor.data[:] = style_np model_executor.executor.forward()#样式前馈 style_array = [] for i in range(len(model_executor.style)): style_array.append(model_executor.style[i].copyto(mx.cpu())) model_executor.data[:] = content_np model_executor.executor.forward() #内容前馈 content_array = model_executor.content.copyto(mx.cpu()) # delete the executor del model_executor style_loss, content_loss = get_loss(gram, content) #获得损失值 model_executor = model_module.get_executor( #再次调用get_executor方法,不过传入的是损失值 style_loss, content_loss, size, dev) grad_array = [] for i in range(len(style_array)): style_array[i].copyto(model_executor.arg_dict["target_gram_%d" % i]) grad_array.append(mx.nd.ones((1,), dev) * (float(args.style_weight) / gscale[i])) grad_array.append(mx.nd.ones((1,), dev) * (float(args.content_weight))) print([x.asscalar() for x in grad_array]) content_array.copyto(model_executor.arg_dict["target_content"]) # train # initialize img with random noise img = mx.nd.zeros(content_np.shape, ctx=dev) img[:] = mx.rnd.uniform(-0.1, 0.1, img.shape)#生成一个空白图像 lr = mx.lr_scheduler.FactorScheduler(step=args.lr_sched_delay, factor=args.lr_sched_factor) optimizer = mx.optimizer.NAG( learning_rate = args.lr, wd = 0.0001, momentum=0.95, lr_scheduler = lr) optim_state = optimizer.create_state(0, img) logging.info('start training arguments %s', args) old_img = img.copyto(dev) clip_norm = 1 * np.prod(img.shape) tv_grad_executor = get_tv_grad_executor(img, dev, args.tv_weight) #图像锐化 for e in range(args.max_num_epochs): img.copyto(model_executor.data) model_executor.executor.forward() model_executor.executor.backward(grad_array) gnorm = mx.nd.norm(model_executor.data_grad).asscalar() if gnorm > clip_norm: model_executor.data_grad[:] *= clip_norm / gnorm if tv_grad_executor is not None: tv_grad_executor.forward() optimizer.update(0, img, model_executor.data_grad + tv_grad_executor.outputs[0], optim_state) else: optimizer.update(0, img, model_executor.data_grad, optim_state) new_img = img eps = (mx.nd.norm(old_img - new_img) / mx.nd.norm(new_img)).asscalar() old_img = new_img.copyto(dev) logging.info('epoch %d, relative change %f', e, eps) if eps < args.stop_eps: logging.info('eps < args.stop_eps, training finished') break if callback: cbdata = { 'eps': eps, 'epoch': e+1, } if (e+1) % args.save_epochs == 0: outfn = args.output_dir + 'e_'+str(e+1)+'.jpg' npimg = new_img.asnumpy() SaveImage(npimg, outfn, args.remove_noise) if callback: cbdata['filename'] = outfn cbdata['img'] = npimg if callback: callback(cbdata) final_fn = args.output_dir + '/final.jpg' SaveImage(new_img.asnumpy(), final_fn) if __name__ == "__main__": args = get_args() train_nstyle(args)
model_vgg19.py
import find_mxnet import mxnet as mx import os, sys from collections import namedtuple ConvExecutor = namedtuple('ConvExecutor', ['executor', 'data', 'data_grad', 'style', 'content', 'arg_dict']) def get_symbol(): # declare symbol data = mx.sym.Variable("data") conv1_1 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv1_1', data=data , num_filter=64, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu1_1 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu1_1', data=conv1_1 , act_type='relu') conv1_2 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv1_2', data=relu1_1 , num_filter=64, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu1_2 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu1_2', data=conv1_2 , act_type='relu') pool1 = mx.symbol.Pooling(name='pool1', data=relu1_2 , pad=(0,0), kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2), pool_type='avg') conv2_1 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv2_1', data=pool1 , num_filter=128, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu2_1 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu2_1', data=conv2_1 , act_type='relu') conv2_2 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv2_2', data=relu2_1 , num_filter=128, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu2_2 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu2_2', data=conv2_2 , act_type='relu') pool2 = mx.symbol.Pooling(name='pool2', data=relu2_2 , pad=(0,0), kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2), pool_type='avg') conv3_1 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv3_1', data=pool2 , num_filter=256, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu3_1 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu3_1', data=conv3_1 , act_type='relu') conv3_2 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv3_2', data=relu3_1 , num_filter=256, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu3_2 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu3_2', data=conv3_2 , act_type='relu') conv3_3 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv3_3', data=relu3_2 , num_filter=256, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu3_3 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu3_3', data=conv3_3 , act_type='relu') conv3_4 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv3_4', data=relu3_3 , num_filter=256, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu3_4 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu3_4', data=conv3_4 , act_type='relu') pool3 = mx.symbol.Pooling(name='pool3', data=relu3_4 , pad=(0,0), kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2), pool_type='avg') conv4_1 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv4_1', data=pool3 , num_filter=512, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu4_1 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu4_1', data=conv4_1 , act_type='relu') conv4_2 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv4_2', data=relu4_1 , num_filter=512, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu4_2 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu4_2', data=conv4_2 , act_type='relu') conv4_3 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv4_3', data=relu4_2 , num_filter=512, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu4_3 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu4_3', data=conv4_3 , act_type='relu') conv4_4 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv4_4', data=relu4_3 , num_filter=512, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu4_4 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu4_4', data=conv4_4 , act_type='relu') pool4 = mx.symbol.Pooling(name='pool4', data=relu4_4 , pad=(0,0), kernel=(2,2), stride=(2,2), pool_type='avg') conv5_1 = mx.symbol.Convolution(name='conv5_1', data=pool4 , num_filter=512, pad=(1,1), kernel=(3,3), stride=(1,1), no_bias=False, workspace=1024) relu5_1 = mx.symbol.Activation(name='relu5_1', data=conv5_1 , act_type='relu') # style and content layers style = mx.sym.Group([relu1_1, relu2_1, relu3_1, relu4_1, relu5_1]) content = mx.sym.Group([relu4_2]) return style, content def get_executor(style, content, input_size, ctx): out = mx.sym.Group([style, content]) # make executor arg_shapes, output_shapes, aux_shapes = out.infer_shape(data=(1, 3, input_size[0], input_size[1])) arg_names = out.list_arguments() arg_dict = dict(zip(arg_names, [mx.nd.zeros(shape, ctx=ctx) for shape in arg_shapes])) grad_dict = {"data": arg_dict["data"].copyto(ctx)} # init with pretrained weight pretrained = mx.nd.load("./model/vgg19.params") for name in arg_names: if name == "data": continue key = "arg:" + name if key in pretrained: pretrained[key].copyto(arg_dict[name]) else: print("Skip argument %s" % name) executor = out.bind(ctx=ctx, args=arg_dict, args_grad=grad_dict, grad_req="write") return ConvExecutor(executor=executor, data=arg_dict["data"], data_grad=grad_dict["data"], style=executor.outputs[:-1], content=executor.outputs[-1], arg_dict=arg_dict) def get_model(input_size, ctx): style, content = get_symbol() return get_executor(style, content, input_size, ctx)
加入mxnet的Python的环境
try: import mxnet as mx except ImportError: import os, sys curr_path = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)) sys.path.append(os.path.join(curr_path, "../../python")) import mxnet as mx
实验结果如下: