多线程三大特性:
可见性、原子性、有序性
synchronize的特性:
1、同一时刻只有一个线程访问临界资源
2、其它未获取到锁执行权的线程必须排队等待
3、保证共享资源的原子性、可见性和有序性
4、进入synchronized范围内自动加锁,synchronized作用域外锁自动消除,即使异常也会释放锁
synchronize加锁的方式:
-
对于普通同步方法,锁是当前实例对象。
-
对于静态同步方法,锁是当前类的Class对象。
-
对于同步方法块,锁是Synchonized括号里配置的对象。
通过具体的例子来看一下
首先是普通方法:
class NoSyncTest { public void method1() { Log.i("sync", "method 1 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 1 execute"); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 1 end"); } public void method2() { Log.i("sync", "method 2 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 2 execute"); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 2 end"); } } private void noSyncTest() { final NoSyncTest test = new NoSyncTest(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test.method1(); } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test.method2(); } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); }
这是一个没有任何同步的方法,NoSyncTest这个类有两个方法method1和method2,分别执行睡3s和0.5s的动作,然后再两个线程中分别调用这个类的实例test的两个方法,看一下结果:
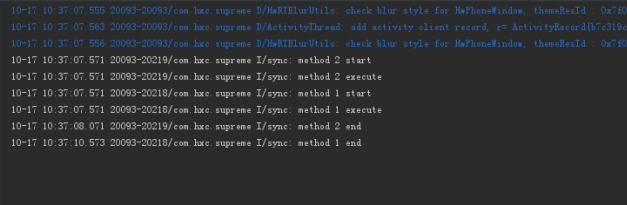
可以看到method2和method1同时执行,method2因为sleep的时间短所以先结束。
再看一下普通方法同步:
class MethodSyncTest { public synchronized void method1() { Log.i("sync", "method 1 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 1 execute"); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 1 end"); } public synchronized void method2() { Log.i("sync", "method 2 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 2 execute"); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 2 end"); } } private void MethodSyncTest() { final MethodSyncTest test = new MethodSyncTest(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test.method1(); } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test.method2(); } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start();
synchronize修饰的method1和method2,其他不变,看一下结果:
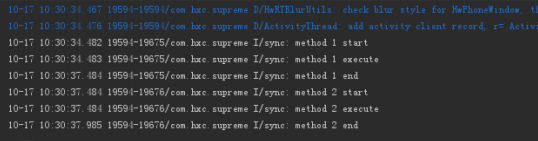
method1先执行然后3s之后结束了method2才开始执行。(注意这个地方不能new 不同的对象来调用方法,因为修饰普通方法本质是对对象的同步加锁。)
看一下第三种静态同步方法:
static class StaticMethodSyncTest { public static synchronized void method1() { Log.i("sync", "method 1 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 1 execute"); Thread.sleep(3000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 1 end"); } public static synchronized void method2() { Log.i("sync", "method 2 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 2 execute"); Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 2 end"); } public static synchronized void method3() { Log.i("sync", "method 3 start"); try { Log.i("sync", "method 3 execute"); Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } Log.i("sync", "method 3 end"); } } private void StaticMethodSyncTest() { final StaticMethodSyncTest test1 = new StaticMethodSyncTest(); final StaticMethodSyncTest test2 = new StaticMethodSyncTest(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test1.method1(); } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { test2.method2(); } }); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { StaticMethodSyncTest.method3(); } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread3.start(); }
static修饰方法相当于这个方法是类方法,可以直接通过类名.方法名调用。我们在这new出了test1和test2两个对象分别调用method1和method2,以及通过类名.方法名调用method3,看一下结果
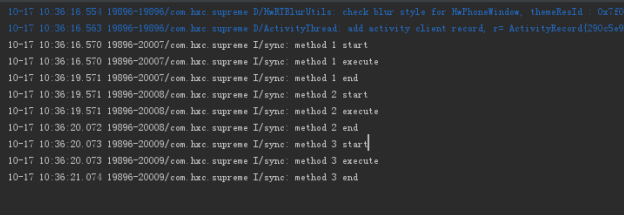
method1、method2、method3顺序执行。(同步静态方法的本质是锁的当前类)