DRAM的一些知识点,先记录下来再进行整理
1.何为Memory rank?
A memory rank is a set of DRAM chips connected to the same chip select, which are therefore accessed simultaneously. In practice they also share all of the other command and control signals, and only the data pins for each DRAM are separate (but the data pins are shared across ranks).
The term “rank” was created and defined by JEDEC, the memory industry standards group. On a DDR, DDR2, or DDR3 memory module, each rank has a 64 bit wide data bus (72 bit wide on DIMMs that support ECC). The number of physical DRAMs depends on their individual widths. For example, a rank of x8 (8 bit wide) DRAMs would consist of eight physical chips (nine if ECC is supported), but a rank of x4 (4 bit wide) DRAMs would consist of 16 physical chips (18 if ECC is supported). Multiple ranks can coexist on a single DIMM, and modern DIMMs can consist of one rank (single rank), two ranks (dual rank), four ranks (quad rank), or eight ranks (octal rank).
There is little difference between a dual rank UDIMM and two single rank UDIMMs in the same memory channel, other than that the DRAMs reside on different PCBs. The electrical connections between the memory controller and the DRAMs are almost identical (with the possible exception of which chip selects go to which ranks). Increasing the number of ranks per DIMM is mainly intended to increase the memory density per channel. Too many ranks in the channel can cause excessive loading and decrease the speed of the channel. DRAM load on the CA (Command/Address) bus can be reduced by using registered memory.【1】
2.如何识别SODIMM的Memory Rank数?

“模组型号”(红圈内)中的“R”是“RANK”的意思,也即是这个模组中只有一个RANK。“×8”是颗粒的位宽(bit width)。
下图为该内存对应框图,可以看出所有的cs片选信号均是连接在一起的。
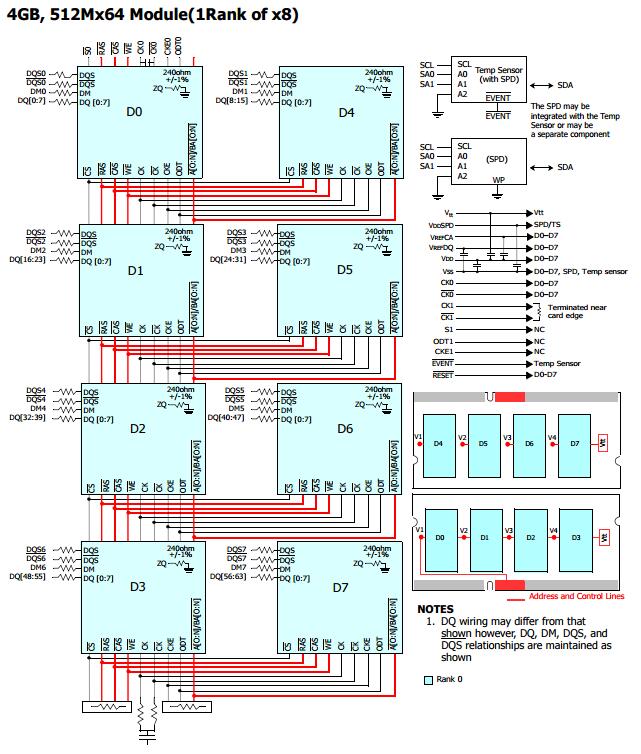
内存框图【2】
3.关于Rank的一些讨论(引自【3】):
1.如何根据模组的编号计算模组的RANK数?
答:根据模组组成原理可以知道:如果模组的深度等于颗粒的深度,就是一个RANK;如果模组的深度等于两倍颗粒深度,就是两个RANK。例如,编号为M378B5673DZ1的三星模组的模组深度是256M。又因为这种模组采用的是K4T1G084QD颗粒。这种颗粒的密度是1024Mb;位宽是8b,因此,颗粒深度是1024Mb÷8b=128M。即模组深度是颗粒深度的两倍,因此,是两个RANK。
此外,从模组编号或颗粒编号给出的颗粒位宽和实际颗理粒数也可以计算出RANK数。例如,当颗粒位宽是8b时,模组用了8个颗粒,8×8b=64b,就是一个RANK;如果用了16颗颗粒,16×8b=128b,就是两个RANK。
2.模组的RANK数跟模组的面数有什么关系?
答:模组的面(side)数跟RANK数是两个不同的概念。而且在内存的编号中也都没有反映面数。但是,模组的面,不是一个,就是两个;而目前的RANK数也是这样。因此,用符号表示它们时,很容易混淆。但是,可以很明确地说:内存标签中的“R”是表示RANK,不是表示面数,内存“面”的英文字是Side,如果表示两个面的话面,应该是“2S”才是呀!
3.内存标签上的2R×8就表明内存是双面8个颗粒吗?
答:不是的。“R”表示RANK,这在上面已经解释过了。“×8”就是颗粒位宽是8bit的意思。因为1个RANK是64bit,两个RANK就是128bit,因此,符号“2R×8”就表示这个模组有2个RANK,颗粒的位宽是8b。因此,这个模组用的颗粒是128b÷8b/颗=16颗,而不是8颗。同理,当内存条上的标签标明是“1R×16”时,就表明这个模组是1个RANK;颗粒位宽是16bit。其颗粒数是64b÷16b/颗=4颗。绝不是16颗。
参考文献:
【1】https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Memory_rank
【2】computing_ds_4Gb_DDR3L(B-ver)based_SODIMMs(Rev.1.0).pdf 源自“https://www.skhynix.com/products.view.do?vseq=963&cseq=75”
【3】http://blog.csdn.net/force_eagle/article/details/7961317