移动语义
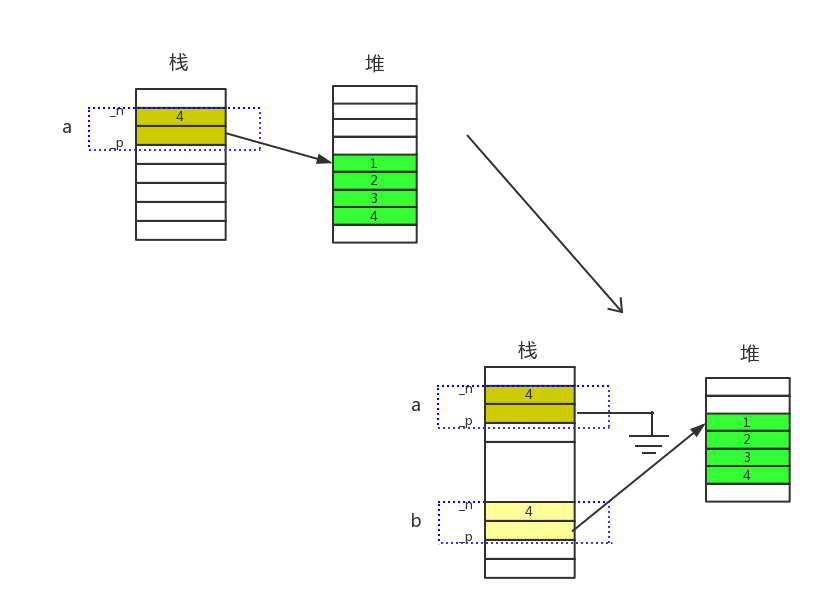
完成所有权的移交,当拷贝构造和赋值构造时,目标对象的所有权必须移交给我们的新的对象,原始对象将丧失所有权,_p指针将不再指向原来的那个数组;
左值与右值
C原始定义
- 左值:可以出现在赋值号的左边或者右边
- 右值:只能出现在赋值号的右边
C++的定义
- 左值:用于标识非临时对象或者非成员函数的表达式
- 右值:用于标识临时对象的表达式或与任何对象无关的值(纯右值),或用于标识即将失效的对象的表达式(失效值)
左值引用与右值引用
左值引用:&
右值引用:&&
- 深拷贝需要频繁分配和释放内存,效率比较低
- 移动语义的目的:所有权移交,不需要重新构造和析构
- 为与构造函数兼容,移动语义必须为引用,而不能是指针或者普通量
- 普通引用传递左值,以允许函数内部修改目标数据对象
- 为区分左值引用,实现移动语义时必须传递右值引用
- 为保证能够修改目标数据对象,在函数内部必须将右值引用作为左值引用对待
class A { public: A() :_n(0), _p(nullptr){} explicit A(int n):_n(n),_p(new int[n]){} A(int n, int *p) :_n(n), _p(p) {} A(A && that); A & operator=(A && that); virtual ~A() { if (_p) { delete[]_p, _p = nullptr; } } public: int & operator[](int i); const int & operator[](int i)const; private: int _n; int *_p; }; A::A(A && that) { //nullptr:C++11预定义的空指针类型nullptr_t的常对象 //可隐式转换为任意指针类型和bool类型,但不能转化为整数类型,以取代NULL _n = that._n, _p = that._p, that._n = 0, that._p = nullptr; //*this = that;//此代码不会调用下面重载的赋值操作符函数 //具名右值引用that在函数内部被当作左值,不是右值 //匿名右值引用才会被当作右值,理论上如此..... //*this = static_cast<A &&>(that);//等价于*this = std::move(that); //上一行代码可以调用下面重载的移动赋值操作符,但是有可能导致程序崩溃 //因为this指向的本对象可能刚刚分配内存,_p字段所指向的目标数据对象无定义 } A & A::operator=(A && that) { if (_p)//删除此行代码可能导致内存泄漏 delete[]_p; //可以测试是否为同一个对象,以避免自身复制操作,但意义不大 _n = that._n, _p = that._p, that._n = 0, that._p = nullptr; return *this; }
移动语义重载
class A { public: A() :_n(0), _p(nullptr) {} explicit A(int n) :_n(n), _p(new int[n]) {} A(int n, int *p) :_n(n), _p(p) {} //可以同时提供拷贝语义与移动语义版本,前者使用常左值引用 //不能修改目标数据对象的值,后者则可以修改 A(const A & that); A(A && that); A & operator =(const A & that);//深拷贝版本 A & operator =(A && that);//移动赋值版本 virtual ~A() { if (_p) { delete[]_p, _p = nullptr; } } public: int & operator[](int i); const int & operator[](int i)const; private: int _n; int *_p; }; int main() { A a(4); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { a[i] = i + 1; } A b(a);//调用拷贝构造函数 b = a; //调用普通赋值版本 //把左值引用转换为右值引用,否则会调用左值版本 A c(static_cast<A &&>(a));//调用移动构造版本 c = static_cast<A &&>(a);//调用移动赋值版本 return 0; }
左值引用同样可以实现移动语义
class A { public: A() :_n(0), _p(nullptr) {} explicit A(int n) :_n(n), _p(new int[n]) {} A(int n, int *p) :_n(n), _p(p) {} A(A & that);//重载非常量版本;移动构造语义 A(const A & that);//重载常量版本;深拷贝构造语义 A & operator=(A &that);//重载非常量版本;移动赋值语义 A & operator=(const A & that);//重载常量版本;深拷贝赋值语义 virtual ~A() { if (_p) { delete[]_p, _p = nullptr; } } public: int & operator[](int i) throw(std::out_of_range); const int & operator[](int i) const throw(std::out_of_range); private: int _n; int *_p; }; A::A(A & that) { _n = that._n, _p = that._p, that._n = 0, that._p = nullptr; } A::A(const A & that) { this->_n = that._n; _p = new int[_n]; for (int i = 0; i < _n; i++) { _p[i] = that._p[i]; } } A & A::operator=(A & that) { _n = that._n, _p = that._p, that._n = 0, that._p = nullptr; return *this; } A & A::operator=(const A & that) { this->_n = that._n; if (_p) { delete[]_p; } _p = new int[_n]; for (int i = 0; i < _n; i++) { _p[i] = that._p[i]; } return *this; } //main.cpp int main() { A a1;//缺省构造 const A a2;//缺省构造 A a3(a1);//调用A::A(A &),移动构造 A a4(a2);//调用A::A(const A &),深拷贝构造 //对于非常量,必须转型为常量才能进行深拷贝 A a5(const_cast<const A &>(a1));//调用A::A(const A &) A a6, a7, a8;//缺省构造 a6 = a1;//调用A::operator=(A &),移动赋值 a7 = a2;//调用A::operator=(const A &),深拷贝赋值 a8 = const_cast<const A &>(a1);//调用A::operator=(const A &) return 0; }
右值引用的意义
右值引用可以使用文字作为函数实际参数
//不接受文字作为实际参数,因无法获取文字的左值 int f(int &x) { return ++x; } //接受文字作为实际参数,传递右值引用 //具名右值引用作为左值,匿名右值引用作为右值 //在函数内部理论如此,但实际上... int f(int && x) { return ++x; } int main() { //错误代码,++操作符的操作数必须为左值 //std::cout << ++10 << std::endl; //可能有问题,传递右值引用,但部分编译器可能将其作为左值 std::cout << f(10) << std::endl;//11? return 0; }
右值引用的意义
避免编写过多的构造与赋值函数
- 不管是左值引用还是右值引用,若同时提供拷贝语义与移动语义,需要2对(4个)构造和赋值函数
- 若通过单独提供成员值的方式构造对象,单成员至少需要4个构造函数和赋值函数,双成员至少需要8个构造和赋值函数
- 使用右值引用,通过函数模板可以缩减代码编写量
实现完美转发