1.pickle模块简介
The pickle module implements binary protocols for serializing and de-serializing a Python object structure。
大意是说:pickle模块是用来实现二进制存储对于python对象结构的的序列化和反序列化。
2.使用前导入模块
import pickle
3.创造要序列化的数据结构
如列表:my_list = [123,3.14,'小甲鱼',['another list',20]]
4.创建一个二进制文件
pick_file = open('D:\test\my_list.pkl','wb')
5.使用pickle的函数dump装入文件
pickle.dump(my_list,pick_file)
6.关闭打开的文件完成写入
pick_file.close()
7.运行结果,由于写入的是二进制文件,那么用文本打开肯定是乱码的

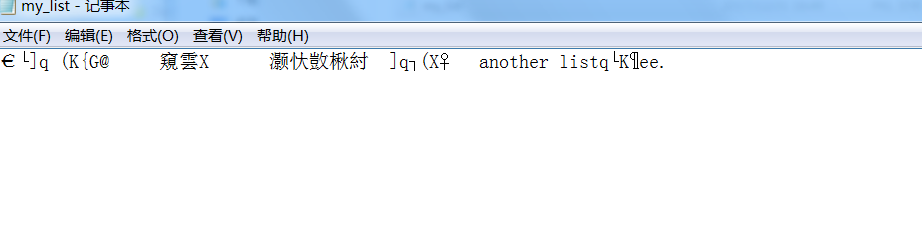
8.以指读方式打开刚才存储的二进制文件
pickfile = open('D:\test\my_list.pkl','rb')
9.读取文件内容到列表,怎么写入的怎么读取
listfile = pickle.load(pickfile)
10.查看读取结果,我们写入的内容又被我们读取出来了
>>> print(listfile)
[123, 3.14, '小甲鱼', ['another list', 20]]
11.介绍文档
NAME
pickle - Create portable serialized representations of Python objects.
DESCRIPTION
See module copyreg for a mechanism for registering custom picklers.
See module pickletools source for extensive comments.
Classes:
Pickler
Unpickler
Functions:
dump(object, file)
dumps(object) -> string
load(file) -> object
loads(string) -> object
Misc variables:
__version__
format_version
compatible_formats
FUNCTIONS
dump(obj, file, protocol=None, *, fix_imports=True)
Write a pickled representation of obj to the open file object file.
This is equivalent to ``Pickler(file, protocol).dump(obj)``, but may
be more efficient.
The optional *protocol* argument tells the pickler to use the given
protocol supported protocols are 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. The default
protocol is 3; a backward-incompatible protocol designed for Python 3.
Specifying a negative protocol version selects the highest protocol
version supported. The higher the protocol used, the more recent the
version of Python needed to read the pickle produced.
The *file* argument must have a write() method that accepts a single
bytes argument. It can thus be a file object opened for binary
writing, an io.BytesIO instance, or any other custom object that meets
this interface.
If *fix_imports* is True and protocol is less than 3, pickle will try
to map the new Python 3 names to the old module names used in Python
2, so that the pickle data stream is readable with Python 2.
dumps(obj, protocol=None, *, fix_imports=True)
Return the pickled representation of the object as a bytes object.
The optional *protocol* argument tells the pickler to use the given
protocol; supported protocols are 0, 1, 2, 3 and 4. The default
protocol is 3; a backward-incompatible protocol designed for Python 3.
Specifying a negative protocol version selects the highest protocol
version supported. The higher the protocol used, the more recent the
version of Python needed to read the pickle produced.
If *fix_imports* is True and *protocol* is less than 3, pickle will
try to map the new Python 3 names to the old module names used in
Python 2, so that the pickle data stream is readable with Python 2.
load(file, *, fix_imports=True, encoding='ASCII', errors='strict')
Read and return an object from the pickle data stored in a file.
This is equivalent to ``Unpickler(file).load()``, but may be more
efficient.
The protocol version of the pickle is detected automatically, so no
protocol argument is needed. Bytes past the pickled object's
representation are ignored.
The argument *file* must have two methods, a read() method that takes
an integer argument, and a readline() method that requires no
arguments. Both methods should return bytes. Thus *file* can be a
binary file object opened for reading, an io.BytesIO object, or any
other custom object that meets this interface.
Optional keyword arguments are *fix_imports*, *encoding* and *errors*,
which are used to control compatibility support for pickle stream
generated by Python 2. If *fix_imports* is True, pickle will try to
map the old Python 2 names to the new names used in Python 3. The
*encoding* and *errors* tell pickle how to decode 8-bit string
instances pickled by Python 2; these default to 'ASCII' and 'strict',
respectively. The *encoding* can be 'bytes' to read these 8-bit
string instances as bytes objects.
loads(data, *, fix_imports=True, encoding='ASCII', errors='strict')
Read and return an object from the given pickle data.
The protocol version of the pickle is detected automatically, so no
protocol argument is needed. Bytes past the pickled object's
representation are ignored.
Optional keyword arguments are *fix_imports*, *encoding* and *errors*,
which are used to control compatibility support for pickle stream
generated by Python 2. If *fix_imports* is True, pickle will try to
map the old Python 2 names to the new names used in Python 3. The
*encoding* and *errors* tell pickle how to decode 8-bit string
instances pickled by Python 2; these default to 'ASCII' and 'strict',
respectively. The *encoding* can be 'bytes' to read these 8-bit
string instances as bytes objects.