相信作为一个Java程序员都会或多或少的了解过Java8中的lambda表达式、函数式编程等,本人也是用过lambda表达式,使用的都是比较简单
的实现
通过一个例子去都感受lambda:
Comparator<Student> comparator = new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getStudentAge() - o2.getStudentAge();
}
};
Comparator<Student> comparator1 = (Student o1, Student o2) -> o1.getStudentAge() - o2.getStudentAge();
一、什么是lambda表达式?
可以理解为简洁地表示可传递的匿名函数的一种方式:它没有名称,但它有参数列表、函数主体、返回类型,可能还有一个可以抛出的异常列表。
1、匿名:
我们说匿名,是因为它不像普通的方法那样有一个明确的名称:写得少而想得多!
2、函数:
我们说它是函数,是因为Lambda函数不像方法那样属于某个特定的类。但和方法一样,Lambda有参数列表、函数主体、返回类型,还可能有可以
抛出的异常列表。
3、传递:
Lambda表达式可以作为参数传递给方法或存储在变量中。
4、简洁:
无需像匿名类那样写很多模板代码。
上面的定义有点长,我们主要是去理解lambda的特点。lambda这个词自于学术界开发出来的一套用来描述计算的λ演算法
二、lambda表达式结构

1、参数:采用了Comparator中compare方法的参数,两个Student。
2、箭头:箭头 -> 把参数列表与Lambda主体分隔开。
3、主体:比较两个Student的年龄。表达式就是Lambda的返回值了。
基本语法
1、(parameters) -> expression
2、(parameters) -> { statements; } //请注意语句的花括号
举个栗子
(String s) -> s.length()
(int x, int y) -> {
System.out.println("Result:");
System.out.println(x+y);
}
第一个例子:参数为String类型并返回一个 int 。Lambda没有 return 语句,因为已经隐含了 return,对应第一种语法
第二个例子:具有两个 int 类型的参数而没有返回值( void返回)。注意Lambda表达式可以包含多行语句,对应第二种语法
错误示例:
() -> {return "Mario";} //这也是正确的lambda,显式返回String
(Integer i) -> return "Alan" + i; // 错误的lambda,需要使用花括号
(String s) -> {"IronMan";} //这是一个表达式,不是一个语句,可以改成
(String s) -> "Iron Man"或者 (String s)->{return "IronMan";}
三、在哪里使用、怎么使用lambda
函数式接口
就是有且只有一个抽象方法的接口,例如Runnable,Callable
Lambda表达式允许以内联的形式为为函数式接口的抽象方法提供实现,并把整个表达式作为函数式接口的实例
举个栗子
Runnable r1 = () -> System.out.println("Hello World 1"); //使用lambda表达式
Runnable r2 = new Runnable(){ //使用匿名内部类
public void run(){
System.out.println("Hello World 2");
}
};
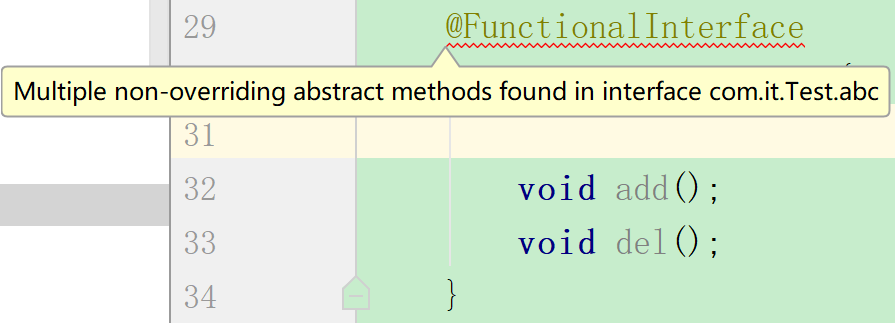
PS:default、static方法是不算的,照样还是函数式接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface abc{
void add();
static void del() {
System.out.println("aaa");
};
default void update(){
System.out.println("bbb");
};
}
函数描述符
函数式接口的抽象方法的签名基本上就是Lambda表达式的签名。我们将这种抽象方法叫作函数描述符。
例如:
1、Runnable接口只有一个run(),而且返回值是void,所以签名就是() -> void,代表参数为空,返回值为void
2、Callable接口只有一个call(),而且返回值是T(你可以通过String或者其他数据类型去代替),签名是 () -> String
来个反面教材
execute(() -> "abc"); //返回值定义为String,签名() -> String,就和Runnable中的抽象方法run的签名不相匹配了
public void execute(Runnable r){
r.run();
}
Lambda表达式可以被赋给一个变量,或传递给一个接受函数式接口作为参数的方法,当然这个Lambda表达式的签名要和函数式接口的抽象方法一样
举个栗子
public void process(Runnable r){
r.run();
}
process(() -> System.out.println("This is awesome!!"));
结果:
This is awesome!!
相当于
test.process(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("This is awesome!!");
}
});
@FunctionalInterface
表示该接口会设计成一个函数式接口,如果不是函数式接口,注解就会报错,表示存在多个抽象方法,这个注解不是必须的,就像
@Override一样
很多接口在Java8中都添加了这个注解
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Comparator<T> {}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {)
简单使用总结:
1、对于函数式接口的使用
Runnable runnable = () -> {
System.out.println("abc");
};
2、作为函数式接口方法的参数
public void process(Runnable r){
r.run();
}
process(() -> System.out.println("This is awesome!!"));
3、赋值给一个变量
4、对集合的循环遍历
List<Student> list = Arrays.asList(new Student(1001, "sam", 20),
new Student(1002, "jesen", 28));
list.forEach(student -> {
System.out.println(student);
});
以上只是lambda的简单使用,可以当做入门,更进一步,结合FunctionalInterface Lib, forEach, stream(),method reference等新特性可以使代码变的更加简洁!
下面的例子来自:zhihu.com/question/20125256/answer/324121308
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Excutor {
void excutor(Student student);
}
@FunctionalInterface
public interface NameChecker {
boolean check(Student student);
}
public static void checkAndExcutor(List<Student> studentList, NameChecker nameChecker, Excutor excutor) {
for (Student student : studentList) {
if (nameChecker.check(student)) {
excutor.excutor(student);
}
}
}
我们调用这个静态函数并赋值lambda表达式
我们一般能想到的方式
checkAndExcutor(studentList, student -> student.getStudentName().startsWith("s"),
student -> System.out.println(student.getStudentName()));
下面应该是最简洁的版本
studentList.stream()
.filter(student -> student.getStudentName().startsWith("s"))
.forEach(System.out::println);
想要理解这些,需要了解函数式编程等各种Java8知识