摘要:本文将通过一句口诀,教你如何辨别索引失效。
本文分享自华为云社区《虚竹哥教你一句口诀辨别索引失效七大场景》,作者:小虚竹 。
一、口诀
教你一句功法口诀:模 型 数 或 运 最 快
二、初始化数据
创建存储引擎为InnoDB的学生表
drop table if exists student; CREATE TABLE `student` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '自增ID', `order_num` bigint NOT NULL COMMENT '序号', `student_name` varchar(20) NOT NULL COMMENT '姓名', `age` int COMMENT '年龄', `create_time` TIMESTAMP COMMENT '创建时间', `gender` int COMMENT '性别 0:男; 1:女; 2:其他', PRIMARY KEY (`id`) )ENGINE=InnoDB CHARACTER SET utf8 COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
插入100万条数据,这里使用了存储过程,进行批量提交数据,先关闭自动提交,插入一定条数再进行提交。
--创建存储过程 drop procedure if exists add_student; CREATE PROCEDURE `add_student`(in n int,in batchNum int) BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 1; DECLARE age1 INT DEFAULT 1; DECLARE gender1 INT DEFAULT 1; WHILE (i < n+1 ) DO set age1=floor(18+( rand() * 5)); set gender1 = floor(rand() * 3); set autocommit = 0; INSERT into student (order_num,student_name,age,create_time,gender) VALUES (i,concat('student_name',i),age1,now(),gender1); set i=i+1; if i mod batchNum = 0 then commit; end if; END WHILE; commit; END
-- 调用 CALL add_student(1000000,100000)
三、口诀详解
模
like 模糊全匹配(like ‘%内容%’),会导致全表扫描;like模糊左匹配(like ‘%内容’),会导致全表扫描。
实战验证
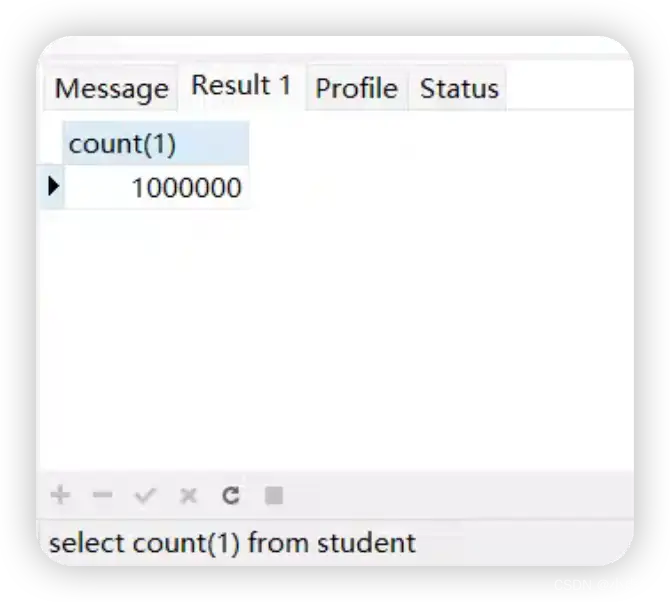
查看student表的索引
show index from student;
对student_name 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_student_name ON student(student_name(20));
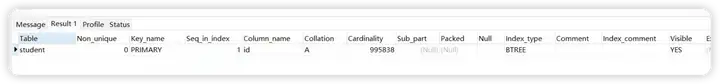
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;

测试:
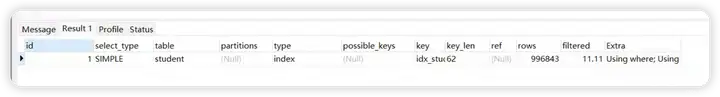
like 右匹配是可以命中索引的
explain select count(1) from student where student_name like 'student_name1%'

解析出来的type级别是range
当查询条件使用索引检索某个范围的数据,典型的场景为使用=、<>、>、>=、<、<=、IS [NOT] NULL、<=>、BETWEEN AND或者IN操作符时,类型为range
like 左匹配:
explain select count(1) from student where student_name like '%student_name1'
解析出来的type级别是index
查询条件中的字段包含索引中的字段(含有非索引字段,就会是ALL了),此时只需要扫描索引树。也是全表扫描的。
like 完全匹配:
explain select count(1) from student where student_name like '%student_name1%'
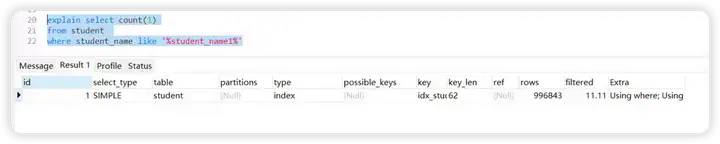
解析出来的type级别是index
查询条件中的字段包含索引中的字段(含有非索引字段,就会是ALL了),此时只需要扫描索引树。也是全表扫描的。
测试结论
模 字决索引失效成立。
型
代表数据类型。例如对字符串name字段加的索引,where条件写name=1,索引会失效。
实战验证
查看student表的索引
show index from student;

对student_name 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_student_name ON student(student_name(20));
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;

测试:
explain select count(1) from student where student_name=1
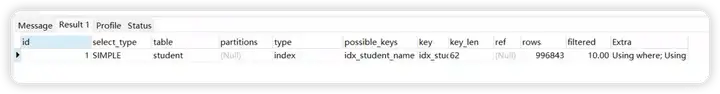
解析出来的type级别是index
查询条件中的字段包含索引中的字段(含有非索引字段,就会是ALL了),此时只需要扫描索引树。也是全表扫描的。
测试结论
型 字决索引失效成立。
数
是函数的意思。对索引的字段使用内部函数,索引也会失效。这种情况下应该建立基于函数的索引。
SELECT * FROM user WHERE DATE(create_time) = ‘2020-09-03’;
这里使用DATE函数
实战验证
查看student表的索引
show index from student;

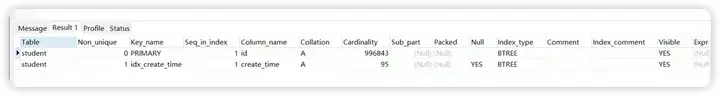
对create_time 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_create_time ON student(create_time);
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;
测试:
explain SELECT count(1) FROM student WHERE DATE(create_time) = '2020-09-03';
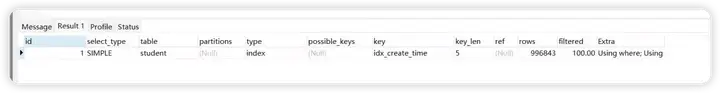
解析出来的type级别是index
查询条件中的字段包含索引中的字段(含有非索引字段,就会是ALL了),此时只需要扫描索引树。也是全表扫描的。
直接查create_time 字段是可以的:
explain SELECT count(1) FROM student WHERE create_time = '2020-09-03';
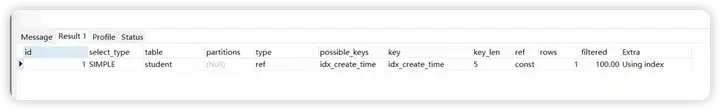
解析出来的type级别是ref
当查询语句中的连接条件或者查询条件使用的索引不是主键和非空唯一索引,或者只是一个索引的一部分,则type的取值为ref
测试结论
数 字决索引失效成立。
或
在 where 子句中使用 or 来连接条件,如果一个字段有索引,一个字段没有索引,将导致引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描;
实战验证
查看student表的索引
show index from student;

对order_num 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_order_num ON student(order_num);
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;

测试:
explain select count(1) from student where order_num = 20 or student_name='student_name10'
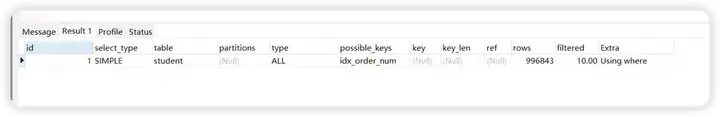
测试结论
或 字决索引失效成立。
运
对索引的列进行运算,索引失效,例如:WHERE age+1=8;
实战验证
查看student表的索引
show index from student;

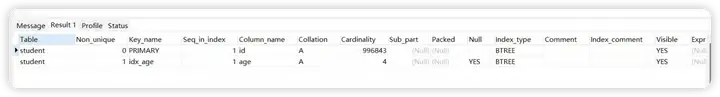
对age 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_age ON student(age);
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;
测试:
explain select count(1) from student where age+1 = 20
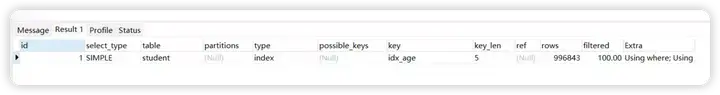
解析出来的type级别是index
查询条件中的字段包含索引中的字段(含有非索引字段,就会是ALL了),此时只需要扫描索引树。也是全表扫描的。
测试结论
运 字决索引失效成立。
最
组合索引,查询时的条件列不是联合索引中的第一个列,索引失效(索引的最左原则)。
实战验证
查看student表的索引
show index from student;

对student_name,age,gender 字段添加组合索引
CREATE INDEX idx_student_name_age_gender ON student(student_name,age,gender);
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;
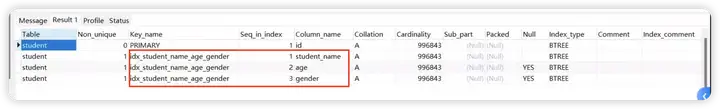
测试:
查询条件中包含索引的第一列,索引生效:
explain select count(1) from student where student_name ='student_name9527' and gender =1
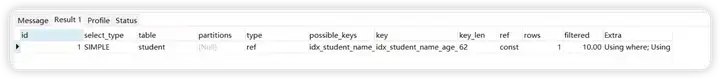
解析出来的type级别是ref
当查询语句中的连接条件或者查询条件使用的索引不是主键和非空唯一索引,或者只是一个索引的一部分,则type的取值为ref
索引生效,查询条件中包含索引的第一列,其他排列组合,大家可自行体验下。
查询条件中不包含索引的第一列,索引不生效:
explain select count(1) from student where age=20 and gender =1
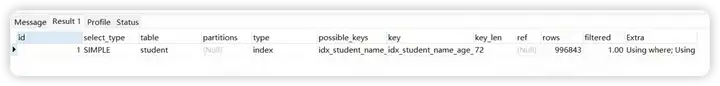
测试结论
最 字决索引失效成立。
快
查询数量是超过表的一部分,mysql30%,oracle 20%(这个数据可能不准确,不是官方说明,仅供参考),导致索引失效;
实战验证
show index from student;

对create_time 字段添加索引
CREATE INDEX idx_create_time ON student(create_time);
再查看student表的索引
show index from student;

测试:
查出来的数据量少,可命中索引:
explain select * from student where create_time >='2022-10-03 22:48:12' and create_time <='2022-10-03 22:48:13'

解析出来的type级别是range
当查询条件使用索引检索某个范围的数据,典型的场景为使用=、<>、>、>=、<、<=、IS [NOT] NULL、<=>、BETWEEN AND或者IN操作符时,类型为range。
查询出来的数据量多,会直接走全表:
explain select * from student where create_time >='2022-10-03 22:48:12'
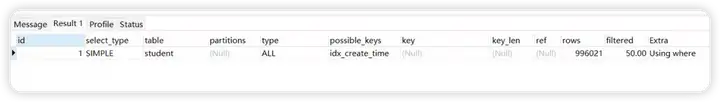
测试结论
快 字决索引失效成立。