摘要:java.util.LinkedList 是 Java 集合框架中的成员之一,底层是基于双向链表实现,集合容量可动态变化的。
本文分享自华为云社区《LinkedList 源码分析》,作者: 陈皮的JavaLib。
LinkedList 简介
java.util.Linked List 是 Java 集合框架中的成员之一,底层是基于双向链表实现,集合容量可动态变化的。它继承自 Abstract Sequential List 抽象类,实现了 List 接口。同时还实现了 Cloneable 和 Serializable 三个标记接口,说明 Array List 是可克隆复制的,可序列化的。
Array List 数组列表底层是基于动态数组实现的,所以优点是能支持快速随机访问,但是增删操作可能会比较慢(因为可能需要进行数组扩容,数据拷贝)。而且数组需要先申请一定的内存空间,可能会造成浪费。而链表列表 LinkedList 的优点是增删操作速度比较快,而且列表存储多少元素就动态申请多少节点来存储,比较节省内存空间。
为何要使用双向链表呢,主要在于遍历效率比单向链表高。例如当我们需要查找指定下标的节点,在指定下标进行增删改操作时,先判断这个位置是靠近头部还是尾部,从而决定从头部还是从尾部开始查找,提高效率。
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { }
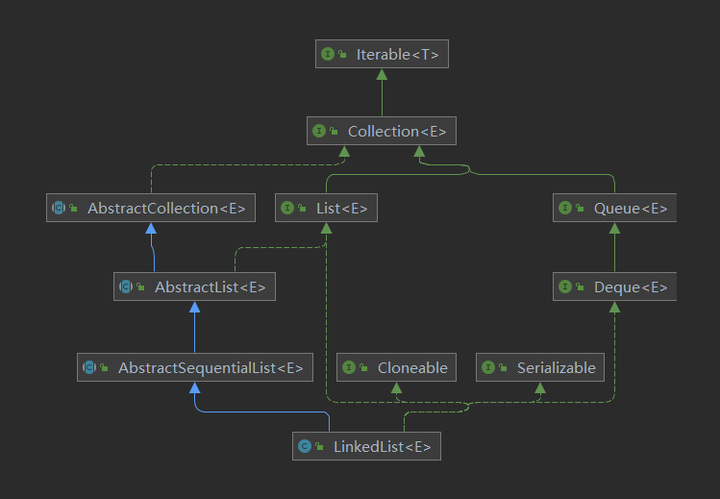
2 LinkedList 源码分析
2.1 内部变量
LinkedList 的元素是存储在节点对象中的,节点类是 LinkedList 类的一个内部私有静态类,源码如下所示:
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
LinkedList 中定义了3个变量,一个代表当前列表的元素个数,另外两个变量指向链表的头部和尾部。以及它的父类 AbstractList 中的 modCount 变量,每次对链表的增删改操作都会使它加1。
transient int size = 0; transient Node<E> first; transient Node<E> last; protected transient int modCount = 0;
2.2 构造函数
ArrayList 有2个构造函数,一个无参构造函数,另一个使用指定 Collection 集合来构造集合的构造函数。
无参构造函数,什么都没有操作。
public LinkedList() {}
使用指定 Collection 集合来构造链表,如果 Collection 不能为 null ,否则会抛出 npe 。
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c); } public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true; }
2.3 常用方法
- public E getFirst()
获取链表的第一个元素,如果不存在第一个节点,抛出异常。
public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; }
- public E getLast()
获取链表的最后一个元素,如果链表为空,则抛出异常。
public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; }
- public E removeFirst()
删除第一个元素,如果链表为空,则抛出异常。
public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); }
- public E removeLast()
删除最后一个元素,如果链表为空,则抛出异常。
public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); }
- public void clear()
情况链表,遍历每一个节点,将每一个节点的内部引用都置为 null ,便于进行垃圾回收。
public void clear() { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; }
- public boolean add(E e)
在链表尾部添加一个元素。
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
- public Iterator iterator()
获取 list 的迭代器,用于遍历集合中的元素。
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return new Itr(); }
- public int size():返回集合元素个数。
- public boolean contains(Object o):是否包含某个元素。
- public boolean remove(Object o):删除某个元素。
- public E get(int index):获取指定下标的元素。
- public E set(int index, E element):在指定下标修改元素值。
- public void add(int index, E element):在指定下标添加元素。
3 常见面试题分析
3.1 LinkedList 是线程安全的吗?
我们通过分析源码可知,对它的任何操作都是没有加锁的,所以在多线程场景下,它是线程不安全的。它适合在非多线程使用场景下,并且增删操作比较多的情况。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); } }, "Thread01"); thread1.start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); } }, "Thread02"); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(list.size()); // 输出不一定是2000,例如1850 }
如果增删操作比较多的话,可以使用 LinkedList ,LinkedList 增删操作速度比较快。
如果需要线程安全的话,可以使用 JDK 集合中的工具类 Collections 提供一个方法 synchronizedList 可以将线程不安全的 List 集合变成线程安全的集合对象,如下所示。
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); // 封装成线程安全的集合 List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(list); Thread thread1 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { synchronizedList.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); } }, "Thread01"); thread1.start(); Thread thread2 = new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { synchronizedList.add(Thread.currentThread().getName() + i); } }, "Thread02"); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println(synchronizedList.size()); }
3.2 LinkedList 优缺点
- 优点:增删操作速度快,不仅有头部和尾部双指针,可以根据要操作的下标靠近哪边,从而决定从哪一边开始遍历找到指定的下标。找到位置后,删除和插入操作的时间复杂度为 O(1) 。
- 缺点:不支持快速随机访问,相对 ArrayList 比较慢,但也不是决定的,取决于列表的长度,以及访问的下标位置。
3.3 使用迭代器 Iterator 过程中,可以增删元素吗?
通过源码分析,在获取集合的迭代器方法中,返回的是 AbstractList 抽象类中定义的 ListItr 迭代器对象,在他的父类 Itr 中持有变量 expectedModCount ,在初始化迭代器对象时这个变量的值被赋予此时链表中的操作次数 modCount 。在迭代获取元素时,会检查这两变量是否相等,不相等则抛出并发修改异常。所以不支持在使用迭代器的过程中,对原链表进行增删改操作。但是可以调用迭代器的增删操作。
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { ListItr(int index) { cursor = index; } public boolean hasPrevious() { return cursor != 0; } public E previous() { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor - 1; E previous = get(i); lastRet = cursor = i; return previous; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } public int nextIndex() { return cursor; } public int previousIndex() { return cursor-1; } public void set(E e) { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e); expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } public void add(E e) { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; AbstractList.this.add(i, e); lastRet = -1; cursor = i + 1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } } private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { /** * Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next. */ int cursor = 0; /** * Index of element returned by most recent call to next or * previous. Reset to -1 if this element is deleted by a call * to remove. */ int lastRet = -1; /** * The modCount value that the iterator believes that the backing * List should have. If this expectation is violated, the iterator * has detected concurrent modification. */ int expectedModCount = modCount; public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size(); } public E next() { checkForComodification(); try { int i = cursor; E next = get(i); lastRet = i; cursor = i + 1; return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } public void remove() { if (lastRet < 0) throw new IllegalStateException(); checkForComodification(); try { AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet); if (lastRet < cursor) cursor--; lastRet = -1; expectedModCount = modCount; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount) throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }
3.4 LinkedList 可以存储 null 值吗?元素可以重复吗?
LinkedList 底层是由双向链表实现的,并且在添加元素的时候,没有对元素进行值校验,所以可以存储 null 值,并且存储的元素是可以重复的。
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
3.5 如何边遍历 ArrayList 元素,边删除指定元素?
不支持在遍历的同时对原链表进行操作,会抛出 ConcurrentModificationException 并发修改异常,前面我们提到使用迭代器 Iterator 遍历集合时,不能对集合进行增删操作(会导致 modCount 值变化)。应该使用 Iterator 类的 remove 方法。
package com.chenpi; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; /** * @author 陈皮 * @version 1.0 * @description * @date 2022/3/1 */ public class ChenPi { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add("Java"); list.add("C++"); list.add("Python"); list.add("Lua"); Iterator<String> iterator = list.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { String next = iterator.next(); if ("C++".equals(next)) { iterator.remove(); continue; } System.out.println(next); } } } // 输出结果如下 Java Python Lua