摘要:公式树模块的作用是,从训练集X和function_set中进行随机采样,生成一棵公式树,同时提供子树变异、 crossover、hoist变异和点变异的方法。
本文分享自华为云社区《公式树开源库分析》,作者:鲤鱼君 。
1.公式树模块
公式树模块的作用是,从训练集X和function_set中进行随机采样,生成一棵公式树,同时提供子树变异、 crossover、hoist变异和点变异的方法。
1.1基本属性
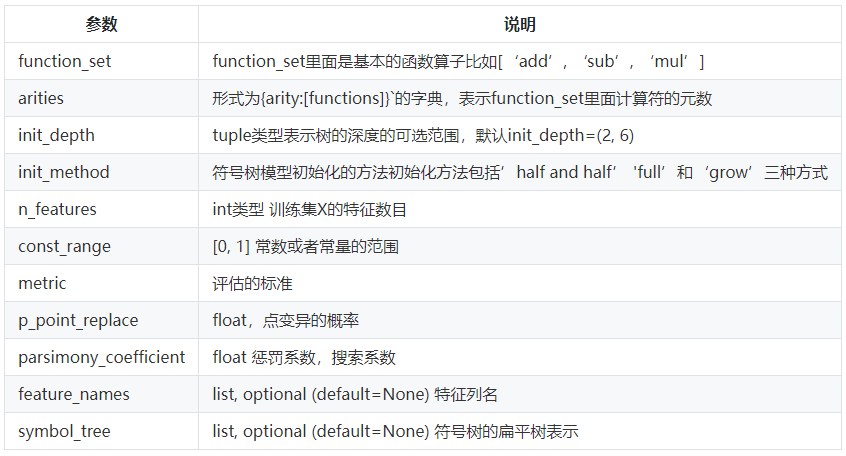
1.2方法
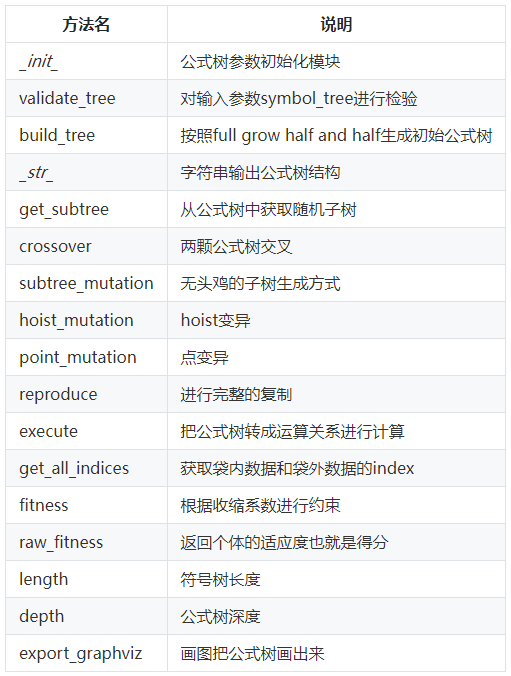
1.3 build_tree算法原理
用到的数据结构:
terminal_stack: 存储是几元运算的一个栈
symbol_tree: lisp_tree 列表树, Lisp列表是基于广义表的结构,所以很容易将一个列表表达成树结构。 S-表达式可能以其在Lisp家族的编程语言中的使用而为人所知,约翰·麦卡锡发明LISP于1958年,首次由史蒂夫·拉塞尔实施在IBM704计算机上,它特别适合用于人工智能方案,因为它有效地处理的符号信息。
在前缀表示法,运算符在自己操作数前写。例如,表达式
a * ( b + c ) / d
被写成
(/ (* a (+ b c) ) d)
例如公式:
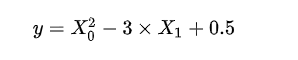
它也可以写作:
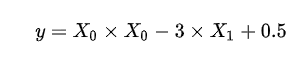
写成S表达式就变成了这个
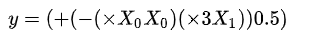
对应的二叉树
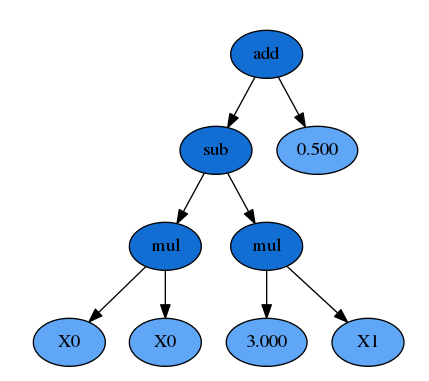
也就是说s表达式对应于符号树的先序遍历
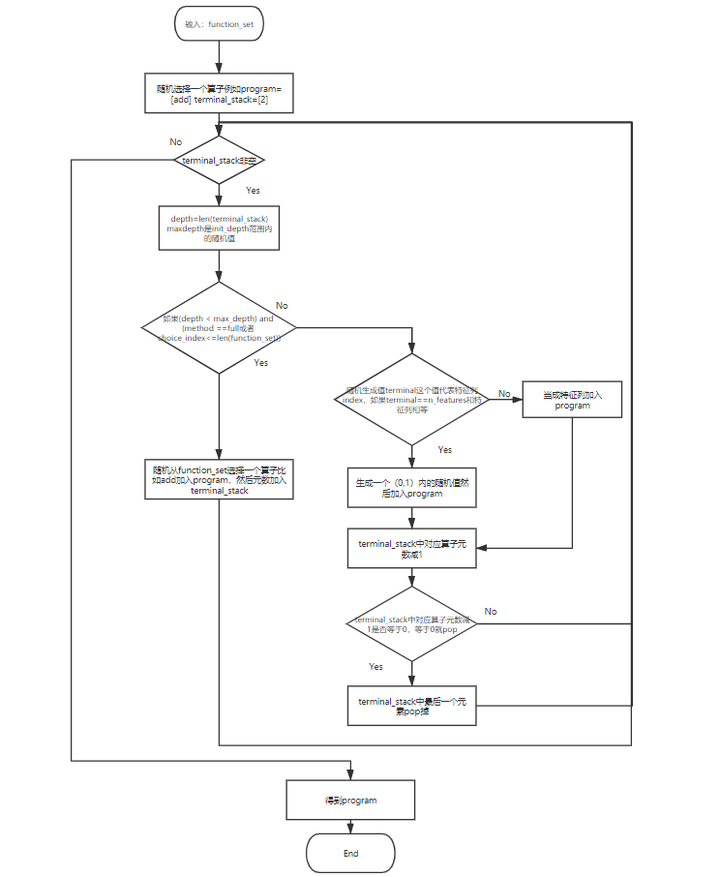
算法输入:function_set[‘add’, ‘sub’, ‘mul’] , arities{2:[‘add’, ‘sub’, ‘mul’]}, method: grow , max_depth:3(2-4内的一个随机数)
method: grow n_features: 10 max_depth:2 function_index:0 function地址:<functions._Function object at 0x000001E538356EB0> function_name:add program:[add] terminal_stack:[2] 循环部分 ############LOOP########################## 第1次 depth: 1 # program的长度也就是符号树的list表长度 等于 len(terminal_stack) choice: 13 choice_index: 1 #depth < max_depth或者choice_index <= len(self.function_set)就会从function_set里面选择一个比如这里选择add function_index: 0 function: add 1_program: [add, add] 1_terminal_stack: [2, 2] 第2次 depth: 2 choice: 13 choice_index: 11 2_terminal: 10 # 这里terminal是10和n_features相等,所以会生成一个随机的float数值 3_terminal: 0.8395650516882855 2_program: [add, add, 0.8395650516882855] 2_terminal_stack: [2, 1]# 加入了常数 第二个值就减去1 第3次 depth: 2 choice: 13 choice_index: 0 2_terminal: 8 # 这里terminal是10和n_features如果不相等的话就加入一个特征列 3_terminal: 8 2_program: [add, ddd, 0.8395650516882855, 8] 2_terminal_stack: [2, 0] 2_terminal_stack.pop(): 0 # 等于0的时候就被pop掉了 然后stack减去1 第4次 depth: 1 choice: 13 choice_index: 5 2_terminal: 0 3_terminal: 0 2_program: [add, add, 0.8395650516882855, 8, 0] 2_terminal_stack: [0] 2_terminal_stack.pop(): 0 最后树的形状变成这个 tree1: add(add(0.840, X8), X0) 生成第2颗树的过程 method: grow max_depth:4 function_index:0 function的地址:<functions._Function object at 0x000001E538356EB0> function_name:add program:[add] terminal_stack:[2] #############LOOP######################### 第1次 depth: 1 choice: 13 choice_index: 4 2_terminal: 3 3_terminal: 3 2_program: [add, 3] 2_terminal_stack: [1] 第2次 depth: 1 choice: 13 choice_index: 4 2_terminal: 6 3_terminal: 6 2_program: [add, 3, 6] 2_terminal_stack: [0] 2_terminal_stack.pop(): 0 最后树的形状变成这个 tree2: [add, 3, 6]
画成流程图就是
1.4 get_subtree 获取随机子树
给symbol_tree里面的元素赋予权重如果是算子就是0.9 不是算子就是0.1
比如tree是
tree1: mul(X6, sub(X3, X1))
那么久赋予权重
probs: [0.9 0.1 0.9 0.1 0.1]
然后进行归一化就是除以sum
_probs: [0.42857143 0.47619048 0.9047619 0.95238095 1. ]
这里是采用轮盘赌法来选择切割点的
步骤
1)随机生成一个(0,1)内的随机值比如生成
s_index:0.8299421213898753
2)找到随机值在probs中应该在的位置这里这个位置就是start的位置
start: 2
3)初始化 end = start=2
stack = 1
如果end - start < stack那么
node = program[end]
如果node是算子的话那么stack要加上元数
stack += node.arity
end 自身一直加一直到program最后
画成流程图就是
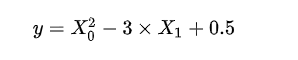
1.5 crossover算法模块原理
crossover的目的是进行子树交叉
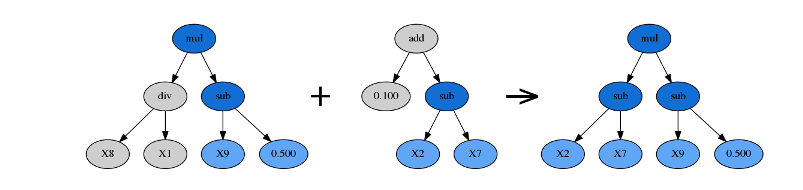
第一步从符号树模块获得随机子树
start, end = self.get_subtree(random_state)
第二步从其他符号树个体中获得随机子树
donor_start, donor_end = self.get_subtree(random_state, donor)
第三步获得交叉后的符号树
self.symbol_tree[: start] + donor[donor_start : donor_end] + self.symbol_tree[end : ] tree1: add(mul(X9, X4), X6) start, end: 1, 4 removed:range(1, 4) donor: [mul, 6, 0.6656811846792283] donor_start, donor_end:(0, 3) donor_removed:[] 结合生成的子树 new_tree[add, mul, 6, 0.6656811846792283, 6] 最后得到的结果 add mul x6 0.6656811846792283 x6 self.symbol_tree[: start] + donor[donor_start : donor_end] + self.symbol_tree[end : ]
1.6 subtree_mutation子树变异
由p_subtree_mutation参数控制。这是一种更激进的变异策略:优胜者的一棵子树将被另一棵完全随机的全新子树代替。
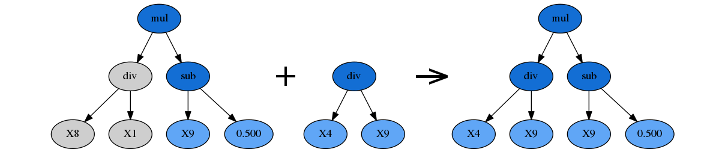
chicken = self.build_tree(random_state) 直接生产一棵新的子树
self.crossover(chicken, random_state) # 然后用crossover算法直接进行交叉生成子树
1.7 hoist_mutation hoist变异
hoist变异是一种对抗公式树膨胀(bloating,即过于复杂)的方法:从优胜者公式树内随机选择一个子树A,再从A里随机选择一个子树B,然后把B提升到A原来的位置,用B替代A。hoist的含义即「升高、提起」。
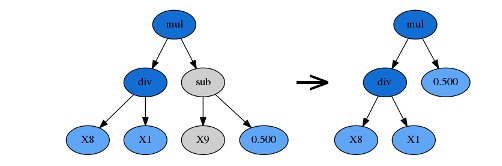
第一步获取一个随机子树A
start, end = self.get_subtree(random_state)
subtree = self.symbol_tree[start:end]
第二步从子树A中获取一个子树B
# 获取随机子树B sub_start, sub_end = self.get_subtree(random_state, subtree) hoist = subtree[sub_start:sub_end]
第三步 把B提升到A原来的位置,用B替代A
self.symbol_tree[:start] + hoist + self.symbol_tree[end:] tree1: add(X6, sub(add(X0, X2), X6)) start, end: 0, 7 subtree : [add, x6, sub, add, x0, x2, x6] mutation: sub_start, sub_end: 3, 6 mutation_hoist : [add, x0, x2] removed: [0, 1, 2, 6] new_tree: [add, x0, x2] 第二次 tree1: mul(X8, X0) mutation_start, end: 0, 3 mutation_subtree : [mul, x8, x0] mutation: sub_start, sub_end: 1, 2 mutation_hoist : [x8] removed: [0, 2] new_tree: [8]
1.8 point_mutation 点变异
由p_point_replace参数控制。一个随机的节点将会被改变,比如加法可以被替换成除法,变量X0可以被替换成常数-2.5。点变异可以重新加入一些先前被淘汰的函数和变量,从而促进公式的多样性。
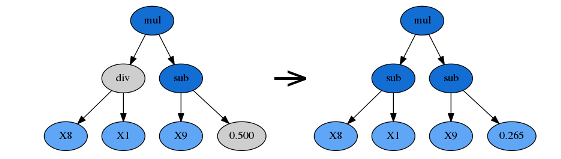
第一步复制符号树,并获取一个随机的点
program = copy(self.symbol_tree) # 自己复制一份 # 随机生成符号树长度个点,然后找到其中小于点变异概率的点组成一个list mutate = np.where(random_state.uniform(size = len(program)) < self.p_point_replace)[0] # 获取一个随机的点
第二步遍历mutate的node节点,如果node是一个Function就替换,不是的话就加入常量或者feature
if isinstance(program[node], _Function): arity = program[node].arity # 算子元数 replacement_len = len(self.arities[arity]) # 找到和arity元数一样的算子有多少个 replacement_index = random_state.randint(replacement_len) # 从里面随机选择一个 replacement = self.arities[arity][replacement_index] # 找到index对应的算子 program[node] = replacement # 进行替换
如果不是function
第一种情况
# 不是算子的话就是常量或者端点 加入一个常量 if self.const_range is not None: terminal = random_state.randint(self.n_features + 1) else: terminal = random_state.randint(self.n_features) # 随机生成一个(0,n_features)内的一个数字terminal if terminal == self.n_features: # 如果terminal和n_features相等的话就替换为一个(0,1)内float的数字 terminal = random_state.uniform(*self.const_range) if self.const_range is None: raise ValueError('A constant was produced with const_range=None.') program[node] = terminal
2. fitness 模块获得符号树的适应性
2.1 get_all_indices 接口获得所有数据的index
第一步:进行参数校验
if self._indices_state is None and random_state is None: # 如果_indices_state和random_state都是None raise ValueError('The program has not been evaluated for fitness\n yet, indices not available.') if n_samples is not None and self._n_samples is None: #如果n_samples不为None self._n_samples = n_samples if max_samples is not None and self._max_samples is None: # n_samples代表数据集的行数 self._max_samples = max_samples # max_samples最大采样树 if random_state is not None and self._indices_state is None: self._indices_state = random_state.get_state()
第二步 获得随机种子,然后获得袋外数据和袋内数据的index
indices_state = check_random_state(None) indices_state.set_state(self._indices_state) # 得到random_state not_indices = sample_without_replacement( self._n_samples, self._n_samples - self._max_samples, random_state=indices_state) # 袋外数据 这里是从[0,self._n_samples]中选出self._n_samples - self._max_samples个数据 sample_counts = np.bincount(not_indices, minlength=self._n_samples) # 找到每个index出现的次数了 indices = np.where(sample_counts == 0)[0] # 出现次数是零的index就是被留下的数据,在袋内的数据了
其他函数
sample_without_replacement(n_population, n_samples, random_state,method): 采样函数,随机获取袋外数据,从集合[0,n_population]中选择n_samples个数据,有放回的抽样
参数介绍

2.2 raw_fitness
接口
raw_fitness(self, X, y, sample_weight)
先执行X的算法得到y_pred,然后根据y,y_pred以及权重计算误差
# 根据x,y 评估符号树的适用性 返回fitness y_pred = self.execute(X) raw_fitness = self.metric(y, y_pred, sample_weight)
2.3 fitness模块
接口
fitness(self, parsimony_coefficient=None)
先执行X的算法得到y_pred,然后根据y,y_pred以及权重计算误差
if parsimony_coefficient is None: parsimony_coefficient = self.parsimony_coefficient penalty = parsimony_coefficient * len(self.symbol_tree) * self.metric.sign # 这里是节约系数乘以公式树的长度如果越大越好sign是1否则是-1 return self.raw_fitness_ - penalty # fitness进行了约减,这里惩罚了树过于膨胀的公式
3.并行模块
3.1并行parallel_evolve
接口
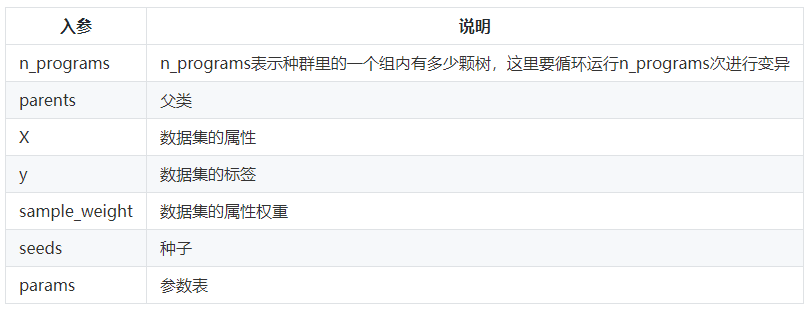
_parallel_evolve(n_programs, parents, X, y, sample_weight, seeds, params)
入参
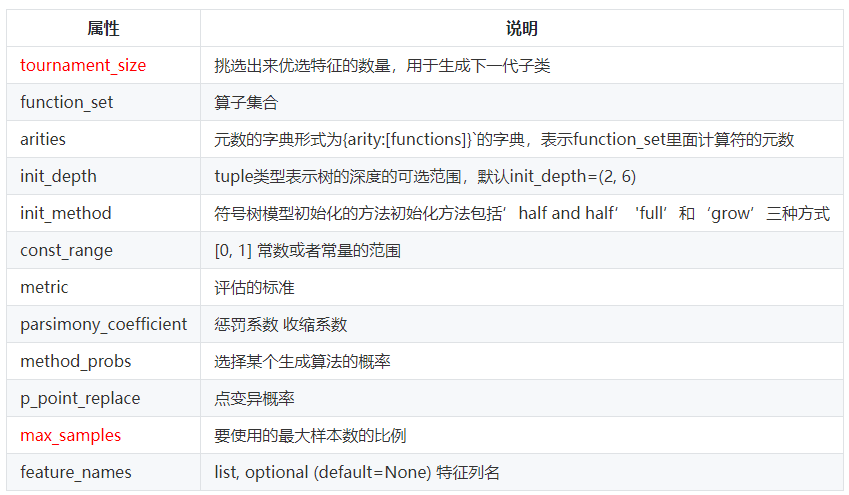
属性:
3.2内置接口_tournament
目的:找到表现最好的符号树
contenders = random_state.randint(0, len(parents), tournament_size) # 生成tournament_size个(0,len(parents))的数字相当于从父类中随机选多少个 fitness = [parents[p].fitness_ for p in contenders] # 得到这些被选中的符公式树的评分 if metric.greater_is_better: # 判断指标是不是越大越好还是越小越好 parent_index = contenders[np.argmax(fitness)] # np.argmax找到最大的那个值的index else: parent_index = contenders[np.argmin(fitness)] # 越小越好 return parents[parent_index], parent_index # 返回最大的对象和他的index
3.3运行流程:
第一步:n_programs表示种群里的一个组内有多少颗树,这里要循环n_programs次
初始化
method = random_state.uniform() # method从crossover subtree hoist point变异里选中的概率
parent, parent_index = _tournament() # 找到了表现好的公式树
第二步根据method的概率选择突变的类型
method_probs定义 self._method_probs = np.array([self.p_crossover, self.p_subtree_mutation, self.p_hoist_mutation, self.p_point_mutation]) self._method_probs = np.cumsum(self._method_probs) if method < method_probs[0]: # 如果method小于crossover概率的话 # 走crossover方法 donor, donor_index = _tournament() # 次好的公式树作为子树 program, removed, remains = parent.crossover(donor.symbol_tree, random_state) # 两者交叉 genome = {'method':'Crossover', 'parent_idx': parent_index, 'parent_nodes':removed, 'donor_idx':donor_index, 'donor_nodes':remains } elif method < method_probs[1]:# 如果method小于crossover概率的话 # subtree突变 program, removed, _ = parent.subtree_mutation(random_state) genome = {'method':'Subtree Mutation', 'parent_idx':parent_index, 'parent_nodes':removed } elif method < method_probs[2]: # hoist突变 program, removed = parent.hoist_mutation(random_state) genome = {'method':'Hoist Mutation', 'parent_idx': parent_index, 'parent_node': removed } elif method < method_probs[3]: # point突变 program, mutated = parent.point_mutation(random_state) genome = {'mehtod':'Point Mutation', 'parent_idx':parent_index, 'parent_nodes':mutated } else: # 自身拷贝 program = parent.reproduce() genome = {'mehtod': 'Reproduction', 'parent_idx':parent_index, 'parent_nodes':[] }
第三步 根据参数和第二步得到的program生成公式树
program = _SymbolTree(function_set=function_set, arities=arities, init_depth=init_depth, init_method=init_method, n_features=n_features, metric=metric, const_range=const_range, p_point_replace=p_point_replace, parsimony_coefficient=parsimony_coefficient, feature_names=feature_names, random_state=random_state, symbol_tree = program)
然后
program.parents = genome
这里的genome存储的是之前生成子树的过程中删掉的信息把他赋值给parents
第四步 根据sample_weight中的权重信息对特征列赋予权重。
if sample_weight is None: # 计算袋内数据权重 curr_sample_weight = np.ones((n_samples,)) # 如果没有权重信息那么所有样本权重都是1 else: curr_sample_weight = sample_weight.copy() oob_sample_weight = curr_sample_weight.copy() # 袋外数据
计算袋外数据的fitness
indices, not_indices = program.get_all_indices(n_samples, max_samples, random_state) # 得到选择的在袋外的数据index curr_sample_weight[not_indices] = 0 # 原数据里面属于袋外数据的其index对应的权重置为零 oob_sample_weight[indices] = 0 # 袋外数据里面不在原数据里的其index对应的权重置为零 program.raw_fitness_ = program.raw_fitness(X, y, curr_sample_weight) # 计算袋内数据的fitness
计算袋外数据的fitness
if max_samples < n_samples: # 计算袋外数据的适用性 program.oob_fitness_ = program.raw_fitness(X, y, oob_sample_weight) # 计算袋内数据的fitness
最后循环n次就得到了n颗变异后的子树programs,它里面有两个私有属性raw_fitness_,oob_fitness_分别存储了袋内袋外数据的适用性
4.SymbolicTransformer模块
4.1初始化模块
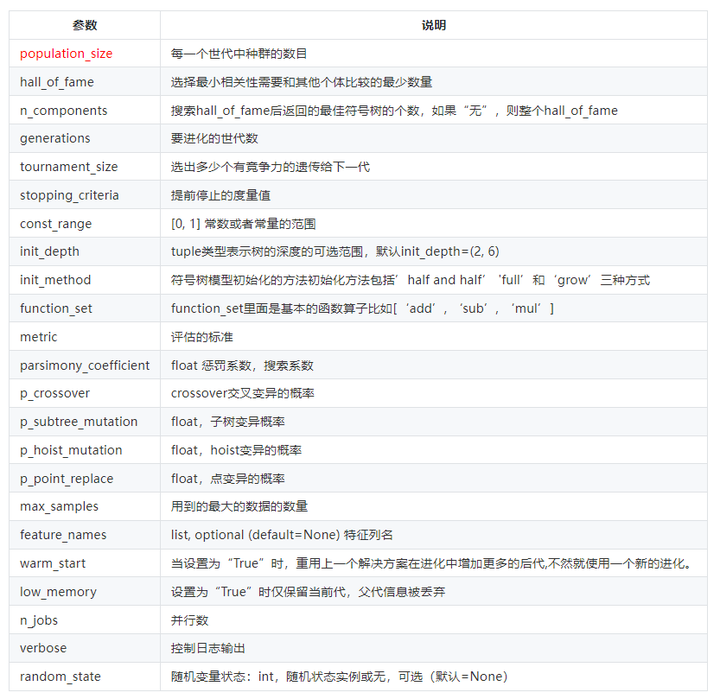
4.1.1基本属性
4.1.2方法
_verbose_reporter:控制日志输出
4.1.3 fit模块
接口
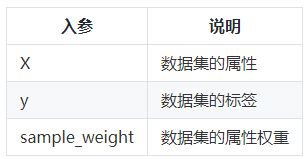
fit(self, X, y, sample_weight = None)
入参:
第1步:对数据进行校验
校验:检查X和y的长度是否一致、hall_of_fame、function_set、_arities是不是正常以及metric是不是Fitness类型 自身是否继承于TransformerMixin抽象类
然后把概率放到list里面,逐步加
self._method_probs = np.array([self.p_crossover, self.p_subtree_mutation, self.p_hoist_mutation, self.p_point_mutation])
self._method_probs = np.cumsum(self._method_probs)
然后校验_method_probs、init_method、const_range、init_depth、feature_names进行类型检查和范围检查
第2步:取出参数并对其进行赋值
params = self.get_params() print(f'params: {params}') params['_metric'] = self._metric params['function_set'] = self._function_set params['arities'] = self._arities params['method_probs'] = self._method_probs
如果不是warm_start模式就准备好_programs和 run_details_字典
if not self.warm_start or not hasattr(self, '_programs'): # warm_start为false时就重新开始,释放分配的内存 self._programs = [] # _programs里面存的是每一代的优胜者 list[list1,list2... listn] self.run_details_ = { 'generation':[], 'average_length':[], 'average_fitness':[], 'best_length':[], 'best_fitness': [], 'best_oob_fitness':[], 'generation_time':[] } prior_generations = len(self._programs) # _programs里面存的是每一代的优胜者 list[list1,list2... listn] 其长度代表迭代了多少代 n_more_generations = self.generations - prior_generations # 还有多少代需要迭代
然后是对n_more_generations进行校验
population_size代表每一个世代中种群的数目 if self.warm_start: # 丢弃之前用过的随机种子 for i in range(len(self._programs)): _ = random_state.randint(MAX_INT, size = self.population_size) if self.verbose: self._verbose_reporter()# 输出日志
第3步:并行的运行程序
循环层(从prior_generations到generations)
1)记录时间找到父类
start_time = time() if gen == 0: # 如果是第一代的话parents是None parents = None else: parents = self._programs[gen - 1] # _programs里面的最后一代
2)并行运行程序
n_jobs, n_programs, starts = _partition_estimators(self.population_size, self.n_jobs) # 把种群分成n_job份n_programs表示第几份中有多少个数据 starts记录了每组数据的起点 seeds = random_state.randint(MAX_INT, size = self.population_size) # 产生population_size个随机种子 population = Parallel(n_jobs=n_jobs, verbose=int(self.verbose > 1))( delayed(_parallel_evolve)(n_programs[i],parents, X, y,sample_weight, seeds[starts[i]:starts[i + 1]], params) for i in range(n_jobs))
对数据进行合并,得到下一代变异的种群
population[<symboltree._SymbolTree object at 0x00000118ABB89E20>, <symboltree._SymbolTree object at 0x00000118ABB89E80>, <symboltree._SymbolTree object at 0x00000118ABB89F10>, <symboltree._SymbolTree object at 0x00000118ABB89FD0>] population = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable(population))
得到种群的所有的个体的fitness和length是一个list
fitness = [program.raw_fitness_ for program in population] length = [program.length_ for program in population]
3)惩罚系数对fitness进行约束
parsimony_coefficient = None if self.parsimony_coefficient == 'auto': parsimony_coefficient = (np.cov(length, fitness)[1, 0] / np.var(length)) # 取出(length, fitness)协方差矩阵的第2行1列除以方差 for program in population: program.fitness_ = program.fitness(parsimony_coefficient) # 收缩后的适应度 self._programs.append(population) #新生成的这一代的信息放入_programs
4)删除被淘汰的个体
if not self.low_memory: for old_gen in np.arange(gen, 0, -1): # 把到gen的世代数倒序排成list类似[5 4 3 2 1] indices = [] for program in self._programs[old_gen]: # 找到上一代的种群每一个符号树 if program is not None:# 不是None的话 for idx in program.parents: # 找到他的parents_idx parents_idx里面存的是其表现最好的父类 if 'idx' in idx:# 找到其中的parent_idx indices.append(program.parents[idx]) indices = set(indices) # 去重复 for idx in range(self.population_size):# 种群内每一个个体 if idx not in indices: # 如果该个体不在最优集合里面就把他置为None self._programs[old_gen - 1][idx] = None elif gen > 0: self._programs[gen - 1] = None #不然就把上一代置为None
第4步进行运行的信息
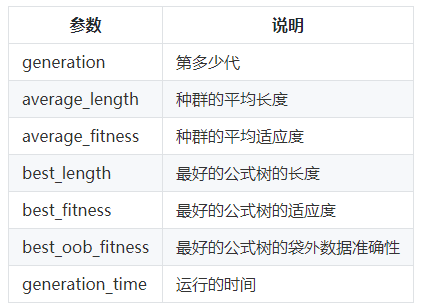
对应代码
# 记录运行信息 if self._metric.greater_is_better: # 如果是越大越好的话 best_program = population[np.argmax(fitness)] else: best_program = population[np.argmin(fitness)] self.run_details_['generation'].append(gen) self.run_details_['average_length'].append(np.mean(length)) self.run_details_['average_fitness'].append(np.mean(fitness)) self.run_details_['best_length'].append(best_program.length_) self.run_details_['best_fitness'].append(best_program.raw_fitness_) oob_fitness = np.nan if self.max_samples < 1.0: oob_fitness = best_program.oob_fitness_ self.run_details_['best_oob_fitness'].append(oob_fitness) # 袋外数据准确性 generation_time = time() - start_time self.run_details_['generation_time'].append(generation_time) # 运行时间
处理early stopping
if self._metric.greater_is_better: best_finess = fitness[np.argmax(fitness)] if best_finess >= self.stopping_criteria: # 达到停止标准的时候 break else: best_finess = fitness[np.argmix(fitness)] if best_finess <= self.stopping_criteria: # 达到停止标准的时候 break
到这里循环结束,得到所有的世代。
第5步如果是变换的话
a)首先得到hall_of_fame个索引
fitness = np.array(fitness) # 找到这一代种群的fitness if self._metric.greater_is_better: # 越大越好的好就倒序选择 hall_of_fame = fitness.argsort()[::-1][:self.hall_of_fame] #得到hall_of_fame个fitness的索引 else: hall_of_fame = fitness.argsort()[:self.hall_of_fame] # 越小越好就正序选择
对最后一代的种群里所有的个体(其中属于hall_of_fame的)进行计算得到预测的值
evaluation = np.array([gp.execute(X) for gp in [self._programs[-1][i] for i in hall_of_fame]])
如果指标是spearman系数的话,计算得到evaluation每一组数据的排序值
if self.metric == 'spearman': evaluation = np.apply_along_axis(rankdata, 1, evaluation) from scipy.stats import rankdata evaluation = np.array([[1,2,3,4], [6,5,7,8], [9,10,11,12]]) print(np.apply_along_axis(rankdata, 1, evaluation)) #输出 [[1. 2. 3. 4.] [2. 1. 3. 4.] [1. 2. 3. 4.]]
然后计算相关系数矩阵
with np.errstate(divide = 'ignore', invalid = 'ignore'): # 去掉除0 无效值等警告 correlations = np.abs(np.corrcoef(evaluation)) # 得到相关系数矩阵 如果是spearman系数这里就是spearman相关系数 [[1. 2. 3. 4.] [2. 1. 3. 4.] [1. 2. 3. 4.]] [[1. 0.8 1. ] [0.8 1. 0.8] [1. 0.8 1. ]] np.fill_diagonal(correlations, 0.) # 对角线元素填充0 components = list(range(self.hall_of_fame)) # hall_of_frame个0到hall_of_frame的数字 indices = list(range(self.hall_of_fame)) # X_shape(354, 13) # evaluation:(50, 354) # 迭代删除最小相关的的元素 while len(components) > self.n_components: # 如果最小相关个体大于要留的个数 # correlations_shape(50, 50) most_correlated = np.unravel_index(np.argmax(correlations), correlations.shape) # 得到最大值的索引 相关性越大越不好 # 通过适应度对相关矩阵进行排序,确定最不合适的索引 worst = max(most_correlated) # worst就是索引大的那一列 components.pop(worst) indices.remove(worst) # 从序列号中删除 correlations = correlations[:, indices][indices, :] indices = list(range(len(components))) self._best_programs = [self._programs[-1][i] for i in hall_of_fame[components]]