摘要:学习 Pandas排序方法是开始或练习使用 Python进行基本数据分析的好方法。最常见的数据分析是使用电子表格、SQL或pandas 完成的。使用 Pandas 的一大优点是它可以处理大量数据并提供高性能的数据操作能力。
本文分享自华为云社区《Pandas Sort:你的 Python 数据排序指南》,作者:Yuchuan。
学习 Pandas排序方法是开始或练习使用 Python进行基本数据分析的好方法。最常见的数据分析是使用电子表格、SQL或pandas 完成的。使用 Pandas 的一大优点是它可以处理大量数据并提供高性能的数据操作能力。
在本教程中,您将学习如何使用.sort_values()和.sort_index(),这将使您能够有效地对 DataFrame 中的数据进行排序。
在本教程结束时,您将知道如何:
- 按一列或多列的值对Pandas DataFrame进行排序
- 使用ascending参数更改排序顺序
- 通过index使用对 DataFrame 进行排序.sort_index()
- 在对值进行排序时组织缺失的数据
- 使用set to 对DataFrame进行就地排序inplaceTrue
要学习本教程,您需要对Pandas DataFrames有基本的了解,并对从文件中读取数据有一定的了解。
Pandas 排序方法入门
快速提醒一下,DataFrame是一种数据结构,行和列都带有标记的轴。您可以按行或列值以及行或列索引对 DataFrame 进行排序。
行和列都有索引,它是数据在 DataFrame 中位置的数字表示。您可以使用 DataFrame 的索引位置从特定行或列中检索数据。默认情况下,索引号从零开始。您也可以手动分配自己的索引。
准备数据集
在本教程中,您将使用美国环境保护署 (EPA) 为 1984 年至 2021 年间制造的车辆编制的燃油经济性数据。EPA 燃油经济性数据集非常棒,因为它包含许多不同类型的信息,您可以对其进行排序上,从文本到数字数据类型。该数据集总共包含八十三列。
要继续,您需要安装pandas Python 库。本教程中的代码是使用 pandas 1.2.0 和Python 3.9.1 执行的。
注意:整个燃油经济性数据集约为 18 MB。将整个数据集读入内存可能需要一两分钟。限制行数和列数有助于提高性能,但下载数据仍需要几秒钟的时间。
出于分析目的,您将按品牌、型号、年份和其他车辆属性查看车辆的 MPG(每加仑英里数)数据。您可以指定要读入 DataFrame 的列。对于本教程,您只需要可用列的子集。
以下是将燃油经济性数据集的相关列读入 DataFrame 并显示前五行的命令:
>>> >>> import pandas as pd >>> column_subset = [ ... "id", ... "make", ... "model", ... "year", ... "cylinders", ... "fuelType", ... "trany", ... "mpgData", ... "city08", ... "highway08" ... ] >>> df = pd.read_csv( ... "https://www.fueleconomy.gov/feg/epadata/vehicles.csv", ... usecols=column_subset, ... nrows=100 ... ) >>> df.head() city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 0 19 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 3 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 4 17 4 Premium ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 [5 rows x 10 columns]
通过.read_csv()使用数据集 URL 进行调用,您可以将数据加载到 DataFrame 中。缩小列会导致更快的加载时间和更少的内存使用。为了进一步限制内存消耗并快速了解数据,您可以使用 指定要加载的行数nrows。
熟悉 .sort_values()
您用于.sort_values()沿任一轴(列或行)对 DataFrame 中的值进行排序。通常,您希望通过一列或多列的值对 DataFrame 中的行进行排序:
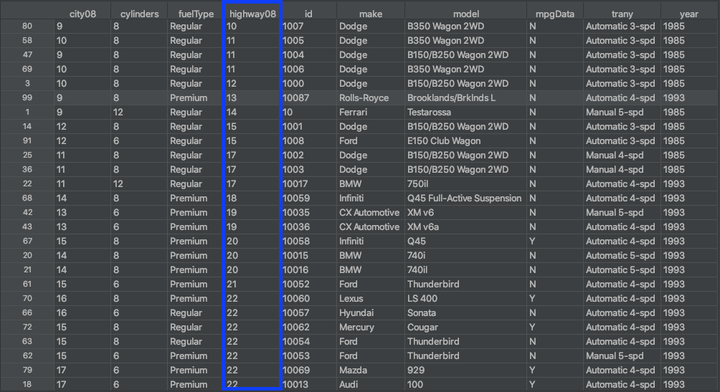
上图显示了使用.sort_values()根据highway08列中的值对 DataFrame 的行进行排序的结果。这类似于使用列对电子表格中的数据进行排序的方式。
熟悉 .sort_index()
您用于.sort_index()按行索引或列标签对 DataFrame 进行排序。与 using 的不同之处.sort_values()在于您是根据其行索引或列名称对 DataFrame 进行排序,而不是根据这些行或列中的值:

DataFrame 的行索引在上图中以蓝色标出。索引不被视为一列,您通常只有一个行索引。行索引可以被认为是从零开始的行号。
在单列上对 DataFrame 进行排序
要根据单列中的值对 DataFrame 进行排序,您将使用.sort_values(). 默认情况下,这将返回一个按升序排序的新 DataFrame。它不会修改原始 DataFrame。
按升序按列排序
要使用.sort_values(),请将单个参数传递给包含要作为排序依据的列的名称的方法。在此示例中,您按city08列对 DataFrame 进行排序,该列表示纯燃料汽车的城市 MPG:
>>> >>> df.sort_values("city08") city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 99 9 8 Premium ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 80 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 47 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 3 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 9 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 4-spd 1993 8 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 7 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 3-spd 1993 76 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 [100 rows x 10 columns]
这将使用 中的列值对您的 DataFrame 进行排序city08,首先显示 MPG 最低的车辆。默认情况下,按升序.sort_values()对数据进行排序。尽管您没有为传递给 的参数指定名称,但.sort_values()您实际上使用了by参数,您将在下一个示例中看到该参数。
更改排序顺序
的另一个参数.sort_values()是ascending。默认情况下.sort_values()已经ascending设置True。如果您希望 DataFrame 按降序排序,则可以传递False给此参数:
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by="city08", ... ascending=False ... ) city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 9 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 4-spd 1993 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 7 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 3-spd 1993 8 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 76 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 58 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 80 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 47 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 99 9 8 Premium ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 [100 rows x 10 columns]
通过传递False到ascending,您可以颠倒排序顺序。现在,您的 DataFrame 按城市条件下测量的平均 MPG 降序排序。MPG 值最高的车辆在第一排。
选择排序算法
值得注意的是,pandas 允许您选择不同的排序算法来与.sort_values()和一起使用.sort_index()。可用的算法quicksort,mergesort和heapsort。有关这些不同排序算法的更多信息,请查看Python 中的排序算法。
对单列进行排序时默认使用的算法是quicksort。要将其更改为稳定的排序算法,请使用mergesort。您可以使用or 中的kind参数来执行此操作,如下所示:.sort_values().sort_index()
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by="city08", ... ascending=False, ... kind="mergesort" ... ) city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 7 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 3-spd 1993 8 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 9 23 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 4-spd 1993 10 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 69 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 47 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 80 9 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 99 9 8 Premium ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 [100 rows x 10 columns]
使用kind,您将排序算法设置为mergesort。之前的输出使用了默认quicksort算法。查看突出显示的索引,您可以看到行的顺序不同。这是因为quicksort不是稳定的排序算法,而是mergesort。
注意:在 Pandas 中,kind当您对多个列或标签进行排序时会被忽略。
当您对具有相同键的多条记录进行排序时,稳定的排序算法将在排序后保持这些记录的原始顺序。因此,如果您计划执行多种排序,则必须使用稳定的排序算法。
在多列上对 DataFrame 进行排序
在数据分析中,通常希望根据多列的值对数据进行排序。想象一下,您有一个包含人们名字和姓氏的数据集。先按姓然后按名字排序是有意义的,这样姓氏相同的人会根据他们的名字按字母顺序排列。
在第一个示例中,您在名为 的单个列上对 DataFrame 进行了排序city08。从分析的角度来看,城市条件下的 MPG 是决定汽车受欢迎程度的重要因素。除了城市条件下的 MPG,您可能还想查看高速公路条件下的 MPG。要按两个键排序,您可以将列名列表传递给by:
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by=["city08", "highway08"] ... )[["city08", "highway08"]] city08 highway08 80 9 10 47 9 11 99 9 13 1 9 14 58 10 11 .. ... ... 9 23 30 10 23 30 8 23 31 76 23 31 2 23 33 [100 rows x 2 columns]
通过指定列名称city08和的列表highway08,您可以使用 对两列上的 DataFrame 进行排序.sort_values()。下一个示例将解释如何指定排序顺序以及为什么注意您使用的列名列表很重要。
按升序按多列排序
要在多个列上对 DataFrame 进行排序,您必须提供一个列名称列表。例如,要按make和排序model,您应该创建以下列表,然后将其传递给.sort_values():
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by=["make", "model"] ... )[["make", "model"]] make model 0 Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 18 Audi 100 19 Audi 100 20 BMW 740i 21 BMW 740il .. ... ... 12 Volkswagen Golf III / GTI 13 Volkswagen Jetta III 15 Volkswagen Jetta III 16 Volvo 240 17 Volvo 240 [100 rows x 2 columns]
现在您的 DataFrame 按升序排序make。如果有两个或更多相同的品牌,则按 排序model。在列表中指定列名的顺序对应于 DataFrame 的排序方式。
更改列排序顺序
由于您使用多列进行排序,因此您可以指定列的排序顺序。如果要更改上一个示例中的逻辑排序顺序,则可以更改传递给by参数的列表中列名的顺序:
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by=["model", "make"] ... )[["make", "model"]] make model 18 Audi 100 19 Audi 100 16 Volvo 240 17 Volvo 240 75 Mazda 626 .. ... ... 62 Ford Thunderbird 63 Ford Thunderbird 88 Oldsmobile Toronado 42 CX Automotive XM v6 43 CX Automotive XM v6a [100 rows x 2 columns]
您的 DataFrame 现在按model升序按列排序,然后按make是否有两个或更多相同模型进行排序。您可以看到更改列的顺序也会更改值的排序顺序。
按降序按多列排序
到目前为止,您仅对多列按升序排序。在下一个示例中,您将根据make和model列按降序排序。要按降序排序,请设置ascending为False:
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by=["make", "model"], ... ascending=False ... )[["make", "model"]] make model 16 Volvo 240 17 Volvo 240 13 Volkswagen Jetta III 15 Volkswagen Jetta III 11 Volkswagen Golf III / GTI .. ... ... 21 BMW 740il 20 BMW 740i 18 Audi 100 19 Audi 100 0 Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 [100 rows x 2 columns]
该make列中的值按字母顺序model倒序排列,对于具有相同make. 对于文本数据,排序区分大小写,这意味着大写文本将首先按升序出现,最后按降序出现。
按具有不同排序顺序的多列排序
您可能想知道是否可以使用多个列进行排序并让这些列使用不同的ascending参数。使用熊猫,您可以通过单个方法调用来完成此操作。如果要按升序对某些列进行排序,并按降序对某些列进行排序,则可以将布尔值列表传递给ascending.
在这个例子中,您排列数据帧由make,model和city08列,与前两列按照升序排序和city08按降序排列。为此,您将列名列表传递给by和布尔值列表传递给ascending:
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by=["make", "model", "city08"], ... ascending=[True, True, False] ... )[["make", "model", "city08"]] make model city08 0 Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 19 18 Audi 100 17 19 Audi 100 17 20 BMW 740i 14 21 BMW 740il 14 .. ... ... ... 11 Volkswagen Golf III / GTI 18 15 Volkswagen Jetta III 20 13 Volkswagen Jetta III 18 17 Volvo 240 19 16 Volvo 240 18 [100 rows x 3 columns]
现在你的数据帧进行排序make,并model在按升序排列,但与city08按降序排列列。这很有用,因为它按分类顺序对汽车进行分组,并首先显示最高 MPG 的汽车。
根据索引对 DataFrame 进行排序
在对索引进行排序之前,最好先了解索引代表什么。DataFrame 有一个.index属性,默认情况下它是其行位置的数字表示。您可以将索引视为行号。它有助于快速行查找和识别。
按升序按索引排序
您可以根据行索引对 DataFrame 进行排序.sort_index()。像在前面的示例中一样按列值排序会重新排序 DataFrame 中的行,因此索引变得杂乱无章。当您过滤 DataFrame 或删除或添加行时,也会发生这种情况。
为了说明 的使用.sort_index(),首先使用以下方法创建一个新的排序 DataFrame .sort_values():
>>> >>> sorted_df = df.sort_values(by=["make", "model"]) >>> sorted_df city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 0 19 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 18 17 6 Premium ... Y Automatic 4-spd 1993 19 17 6 Premium ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 20 14 8 Premium ... N Automatic 5-spd 1993 21 14 8 Premium ... N Automatic 5-spd 1993 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 12 21 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 13 18 4 Regular ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 15 20 4 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 16 18 4 Regular ... Y Automatic 4-spd 1993 17 19 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1993 [100 rows x 10 columns]
您已经创建了一个使用多个值排序的 DataFrame。请注意行索引是如何没有特定顺序的。要将新 DataFrame 恢复到原始顺序,您可以使用.sort_index():
>>> >>> sorted_df.sort_index() city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 0 19 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 3 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 4 17 4 Premium ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95 17 6 Regular ... Y Automatic 3-spd 1993 96 17 6 Regular ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 97 15 6 Regular ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 98 15 6 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 99 9 8 Premium ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 [100 rows x 10 columns]
现在索引按升序排列。就像in.sort_values()的默认参数是,您可以通过传递 更改为降序。对索引进行排序对数据本身没有影响,因为值不变。ascending.sort_index()TrueFalse
当您使用.set_index(). 如果要使用make和model列设置自定义索引,则可以将列表传递给.set_index():
>>> >>> assigned_index_df = df.set_index( ... ["make", "model"] ... ) >>> assigned_index_df city08 cylinders ... trany year make model ... Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 19 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1985 Ferrari Testarossa 9 12 ... Manual 5-spd 1985 Dodge Charger 23 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1985 B150/B250 Wagon 2WD 10 8 ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 Subaru Legacy AWD Turbo 17 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 ... ... ... ... ... Pontiac Grand Prix 17 6 ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 Grand Prix 17 6 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 Grand Prix 15 6 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 Grand Prix 15 6 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Rolls-Royce Brooklands/Brklnds L 9 8 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 [100 rows x 8 columns]
使用此方法,您可以用两个轴标签替换默认的基于整数的行索引。这被认为是一个MultiIndex或一个层次索引。您的 DataFrame 现在由多个键索引,您可以使用.sort_index()以下键进行排序:
>>> >>> assigned_index_df.sort_index() city08 cylinders ... trany year make model ... Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 19 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1985 Audi 100 17 6 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 100 17 6 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 BMW 740i 14 8 ... Automatic 5-spd 1993 740il 14 8 ... Automatic 5-spd 1993 ... ... ... ... ... Volkswagen Golf III / GTI 21 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Jetta III 18 4 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 Jetta III 20 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Volvo 240 18 4 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 240 19 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 [100 rows x 8 columns]
首先使用make和列为 DataFrame 分配一个新索引model,然后使用 对索引进行排序.sort_index()。您可以.set_index()在 pandas 文档中阅读有关使用的更多信息。
按索引降序排序
对于下一个示例,您将按索引按降序对 DataFrame 进行排序。请记住,通过对 DataFrame 进行排序.sort_values(),您可以通过设置ascending为来反转排序顺序False。此参数也适用于.sort_index(),因此您可以按相反顺序对 DataFrame 进行排序,如下所示:
>>> >>> assigned_index_df.sort_index(ascending=False) city08 cylinders ... trany year make model ... Volvo 240 18 4 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 240 19 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Volkswagen Jetta III 18 4 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 Jetta III 20 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Golf III / GTI 18 4 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 ... ... ... ... ... BMW 740il 14 8 ... Automatic 5-spd 1993 740i 14 8 ... Automatic 5-spd 1993 Audi 100 17 6 ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 100 17 6 ... Manual 5-spd 1993 Alfa Romeo Spider Veloce 2000 19 4 ... Manual 5-spd 1985 [100 rows x 8 columns]
现在您的 DataFrame 按其索引按降序排序。使用.sort_index()and之间的一个区别.sort_values()是它.sort_index()没有by参数,因为它默认在行索引上对 DataFrame 进行排序。
探索高级索引排序概念
在数据分析中有很多情况您希望对分层索引进行排序。你已经看到了如何使用make和model在MultiIndex。对于此数据集,您还可以将该id列用作索引。
将id列设置为索引可能有助于链接相关数据集。例如,EPA 的排放数据集也用于id表示车辆记录 ID。这将排放数据与燃油经济性数据联系起来。在 DataFrame 中对两个数据集的索引进行排序可以使用其他方法(例如.merge(). 要了解有关在 Pandas 中组合数据的更多信息,请查看在 Pandas 中使用 merge()、.join() 和 concat() 组合数据。
对 DataFrame 的列进行排序
您还可以使用 DataFrame 的列标签对行值进行排序。使用设置为.sort_index()的可选参数将按列标签对 DataFrame 进行排序。排序算法应用于轴标签而不是实际数据。这有助于对 DataFrame 进行目视检查。axis1
使用数据框 axis
当您在.sort_index()不传递任何显式参数axis=0的情况下使用时,它将用作默认参数。DataFrame的轴指的是索引 ( axis=0) 或列 ( axis=1)。您可以使用这两个轴来索引和选择DataFrame 中的数据以及对数据进行排序。
使用列标签进行排序
您还可以使用 DataFrame 的列标签作为.sort_index(). 设置根据列标签对 DataFrame 的列axis进行1排序:
>>> >>> df.sort_index(axis=1) city08 cylinders fuelType ... mpgData trany year 0 19 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 1 9 12 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1985 2 23 4 Regular ... Y Manual 5-spd 1985 3 10 8 Regular ... N Automatic 3-spd 1985 4 17 4 Premium ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95 17 6 Regular ... Y Automatic 3-spd 1993 96 17 6 Regular ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 97 15 6 Regular ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 98 15 6 Regular ... N Manual 5-spd 1993 99 9 8 Premium ... N Automatic 4-spd 1993 [100 rows x 10 columns]
DataFrame 的列按字母升序从左到右排序。如果要按降序对列进行排序,则可以使用ascending=False:
>>> >>> df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=False) year trany mpgData ... fuelType cylinders city08 0 1985 Manual 5-spd Y ... Regular 4 19 1 1985 Manual 5-spd N ... Regular 12 9 2 1985 Manual 5-spd Y ... Regular 4 23 3 1985 Automatic 3-spd N ... Regular 8 10 4 1993 Manual 5-spd N ... Premium 4 17 .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95 1993 Automatic 3-spd Y ... Regular 6 17 96 1993 Automatic 4-spd N ... Regular 6 17 97 1993 Automatic 4-spd N ... Regular 6 15 98 1993 Manual 5-spd N ... Regular 6 15 99 1993 Automatic 4-spd N ... Premium 8 9 [100 rows x 10 columns]
使用axis=1in .sort_index(),您可以按升序和降序对 DataFrame 的列进行排序。这在其他数据集中可能更有用,例如列标签对应于一年中的几个月的数据集。在这种情况下,按月按升序或降序排列数据是有意义的。
在 Pandas 中排序时处理丢失的数据
通常,现实世界的数据有很多缺陷。虽然 Pandas 有多种方法可用于在排序前清理数据,但有时在排序时查看丢失的数据还是不错的。你可以用na_position参数来做到这一点。
本教程使用的燃油经济性数据子集没有缺失值。为了说明 的使用na_position,首先您需要创建一些缺失的数据。以下代码基于现有mpgData列创建了一个新列,映射True了mpgData等于Y和NaN不等于的位置:
>>> >>> df["mpgData_"] = df["mpgData"].map({"Y": True}) >>> df city08 cylinders fuelType ... trany year mpgData_ 0 19 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True 1 9 12 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 NaN 2 23 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True 3 10 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN 4 17 4 Premium ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 True 96 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 97 15 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 98 15 6 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN 99 9 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN [100 rows x 11 columns]
现在你有一个名为新列mpgData_包含这两个True和NaN值。您将使用此列查看na_position使用这两种排序方法时的效果。要了解有关使用 的更多信息.map(),您可以阅读Pandas 项目:使用 Python 和 Pandas 制作成绩簿。
了解na_position参数.sort_values()
.sort_values()接受一个名为 的参数na_position,它有助于在您排序的列中组织缺失的数据。如果您对缺失数据的列进行排序,那么具有缺失值的行将出现在 DataFrame 的末尾。无论您是按升序还是降序排序,都会发生这种情况。
当您对缺失数据的列进行排序时,您的 DataFrame 如下所示:
>>> >>> df.sort_values(by="mpgData_") city08 cylinders fuelType ... trany year mpgData_ 0 19 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True 55 18 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 56 18 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 57 16 6 Premium ... Manual 5-spd 1993 True 59 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 94 18 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 96 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 97 15 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 98 15 6 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN 99 9 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN [100 rows x 11 columns]
要改变这种行为,并有丢失的数据第一次出现在你的数据帧,可以设置na_position到first。该na_position参数只接受值last,这是默认值,和first。以下是如何使用na_postion的.sort_values():
>>> >>> df.sort_values( ... by="mpgData_", ... na_position="first" ... ) city08 cylinders fuelType ... trany year mpgData_ 1 9 12 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 NaN 3 10 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN 4 17 4 Premium ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN 5 21 4 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 NaN 11 18 4 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 32 15 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 33 15 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 37 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 True 85 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 95 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 True [100 rows x 11 columns]
现在,您用于排序的列中的任何缺失数据都将显示在 DataFrame 的顶部。当您第一次开始分析数据并且不确定是否存在缺失值时,这非常有用。
了解na_position参数.sort_index()
.sort_index()也接受na_position。您的 DataFrame 通常不会将NaN值作为其索引的一部分,因此此参数在.sort_index(). 但是,很高兴知道,如果您的 DataFrame 确实NaN在行索引或列名中存在,那么您可以使用.sort_index()和快速识别这一点na_position。
默认情况下,此参数设置为last,将NaN值放置在排序结果的末尾。要改变这种行为,并在你的数据帧先有丢失的数据,设置na_position到first。
使用排序方法修改你的 DataFrame
在所有的例子你迄今所看到的,都.sort_values()和.sort_index()已经返回数据帧对象时,你叫那些方法。这是因为在熊猫排序不工作到位默认。通常,这是使用 Pandas 分析数据的最常见和首选方法,因为它会创建一个新的 DataFrame 而不是修改原始数据。这允许您保留从文件中读取数据时的数据状态。
但是,您可以通过指定inplace值为的可选参数来直接修改原始 DataFrame True。大多数 Pandas 方法都包含inplace参数。下面,您将看到一些inplace=True用于对 DataFrame 进行适当排序的示例。
.sort_values()就地使用
随着inplace设置为True,您修改原始数据帧,所以排序方法返回None。city08像第一个示例一样按列的值对 DataFrame 进行排序,但inplace设置为True:
>>> >>> df.sort_values("city08", inplace=True)
请注意调用如何.sort_values()不返回 DataFrame。这是原件的df样子:
>>> >>> df city08 cylinders fuelType ... trany year mpgData_ 99 9 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 1 9 12 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 NaN 80 9 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN 47 9 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN 3 10 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 9 23 4 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 True 8 23 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1993 True 7 23 4 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 True 76 23 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1993 True 2 23 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True [100 rows x 11 columns]
在df对象中,值现在基于city08列按升序排序。您的原始 DataFrame 已被修改,更改将持续存在。避免inplace=True用于分析通常是个好主意,因为对 DataFrame 的更改无法撤消。
.sort_index()就地使用
下一个示例说明这inplace也适用于.sort_index().
由于索引是在您将文件读入 DataFrame 时按升序创建的,因此您可以df再次修改对象以使其恢复到初始顺序。使用.sort_index()与inplace设置为True修改数据框:
>>> >>> df.sort_index(inplace=True) >>> df city08 cylinders fuelType ... trany year mpgData_ 0 19 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True 1 9 12 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 NaN 2 23 4 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1985 True 3 10 8 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1985 NaN 4 17 4 Premium ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN .. ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 95 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 3-spd 1993 True 96 17 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 97 15 6 Regular ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN 98 15 6 Regular ... Manual 5-spd 1993 NaN 99 9 8 Premium ... Automatic 4-spd 1993 NaN [100 rows x 11 columns]
现在您的 DataFrame 已使用.sort_index(). 由于您的 DataFrame 仍然具有其默认索引,因此按升序对其进行排序会将数据放回其原始顺序。
如果您熟悉 Python 的内置函数sort()and sorted(),那么inplacepandas 排序方法中可用的参数可能会感觉非常相似。有关更多信息,您可以查看如何在 Python 中使用 sorted() 和 sort()。
结论
您现在知道如何使用 pandas 库的两个核心方法:.sort_values()和.sort_index(). 有了这些知识,您就可以使用 DataFrame 执行基本的数据分析。虽然这两种方法之间有很多相似之处,但通过查看它们之间的差异,可以清楚地知道使用哪一种方法来执行不同的分析任务。
在本教程中,您学习了如何:
- 按一列或多列的值对Pandas DataFrame进行排序
- 使用ascending参数更改排序顺序
- 通过index使用对 DataFrame 进行排序.sort_index()
- 在对值进行排序时组织缺失的数据
- 使用set to 对DataFrame进行就地排序inplaceTrue
这些方法是精通数据分析的重要组成部分。它们将帮助您建立一个强大的基础,您可以在此基础上执行更高级的 Pandas 操作。如果您想查看 Pandas 排序方法更高级用法的一些示例,那么 Pandas文档是一个很好的资源。