只用一个模型建模获得结果没有对比性,无法判断最终的预测结果是好还是坏,因此在进行预测时候往往都不是只使用一个模型进行,而是采用至少两个模型进行对比,接下来就是使用LightGBM模型进行预测
需要先安装LightGBM模块,操作如下
然后从模块中导入回归模型,划分数据集后构建模型
from lightgbm import LGBMRegressor
y = listings_new['price']
x = listings_new.drop('price', axis =1)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state=1)
fit_params={
"early_stopping_rounds":20,
"eval_metric" : 'rmse',
"eval_set" : [(X_test,y_test)],
'eval_names': ['valid'],
'verbose': 100,
'feature_name': 'auto',
'categorical_feature': 'auto'
}
X_test.columns = ["".join (c if c.isalnum() else "_" for c in str(x)) for x in X_test.columns]
class LGBMRegressor_GainFE(LGBMRegressor):
@property
def feature_importances_(self):
if self._n_features is None:
raise LGBMNotFittedError('No feature_importances found. Need to call fit beforehand.')
return self.booster_.feature_importance(importance_type='gain')
clf = LGBMRegressor_GainFE(num_leaves= 25, max_depth=20,
random_state=0,
silent=True,
metric='rmse',
n_jobs=4,
n_estimators=1000,
colsample_bytree=0.9,
subsample=0.9,
learning_rate=0.01)
#reduce_train.columns = ["".join (c if c.isalnum() else "_" for c in str(x)) for x in reduce_train.columns]
clf.fit(X_train.values, y_train.values, **fit_params)
输出结果如下: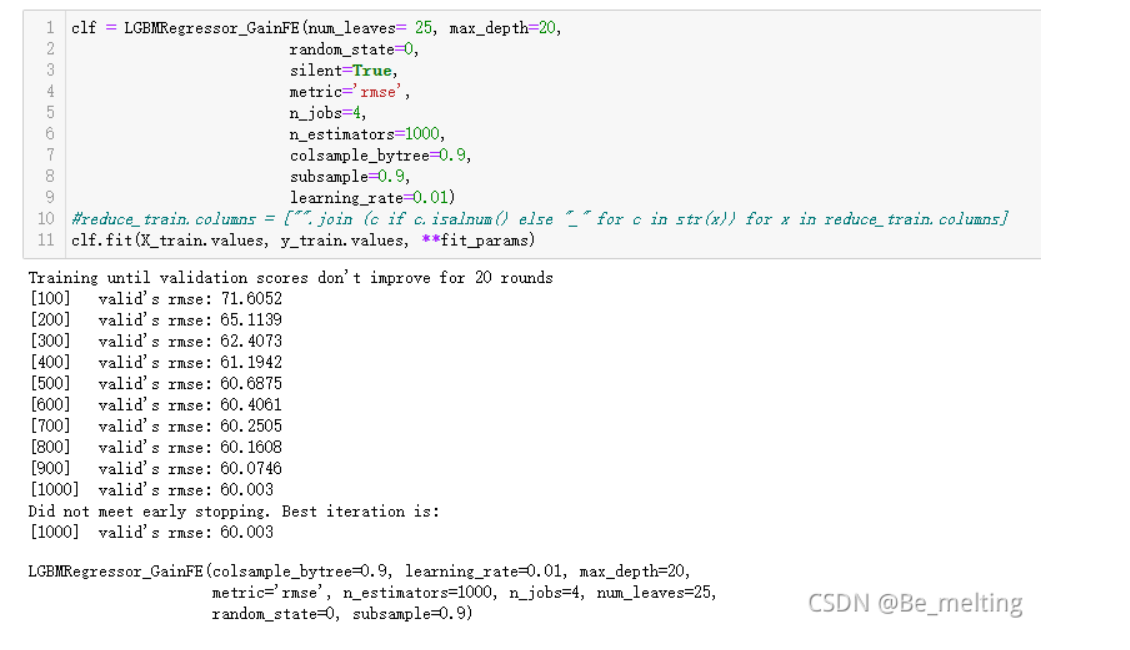
如果显示上放的输出结果说明模型训练成功,但是过程并不一定会一帆风顺,可能会运行报错如下:TypeError: Cannot interpret '<attribute 'dtype' of 'numpy.generic' objects>' as a data type,此时可以升级一下pandas和numpy的版本,比如将pandas升级到1.2.4,numpy升级到1.20.2。然后重新运行当前的notebook就可以完美解决这个问题
接着就可以使用训练好的模型进行预测并查看模型得分,顺带可以将重要的影响因素进行可视化
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test.values)
print('R^2 test: %.3f' % (r2_score(y_test, y_pred)))
feat_imp = pd.Series(clf.feature_importances_, index=x.columns)
feat_imp.nlargest(20).plot(kind='barh', figsize=(10,6))
输出结果如下:(使用LightGBM模型进行预测的得分要比随机森林模型最终的得分要高,说明此数据集较适用于LightGBM模型)