一、内置对象简介
JSP内置对象是WEB容器创建的一组对象,这些内置对象不需要开发人员实例化,不使用new关键字就可以使用的内置对象,在所有的JSP页面直接使用内置对象。JSP内置对象包括out、request、response、session、application、config、exception、page和pageContext。
二、九大内置对象
1、out对象
out对象是javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter类的实例,是向客户端输出内容常用的对象。考虑out对象时,基于缓冲区理解。
out对象常用的方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| void clear() | 清除缓冲区的内容,若如果在flush之后调用会抛出异常 |
| void clearBuffer() | 清除缓冲区的当前内容,若如果在flush之后调用会抛出异常 |
| void flush() | 清空流 |
| int getBufferSize() | 返回缓冲区一字节数的大小,如不设缓冲区则为0 |
| int getRemaining() | 返回缓冲区还剩多少可用 |
|
boolean isAutoFlush() |
返回缓冲区满时,是自动清空还是抛出异常 |
| void printlin() | 向客户端打印字符串 |
| void close() | 关闭输出流 |
代码示例
<body>
<h1>out内置对象</h1>
<%
out.println("<h2>静夜思</h2>");
out.print("——李白<br>");
out.print("床前明月光<br>");
out.print("flush前缓冲区容量:"+out.getRemaining()+"<br>");
out.flush();
out.print("flush后缓冲区容量:"+out.getRemaining()+"<br>");
out.println("疑是地上霜<br>");
out.println("举头望明月<br>低头思故乡<br>");
%>
缓冲区大小:<%=out.getBufferSize() %>byte<br>
缓冲区剩余大小:<%=out.getRemaining() %>byte<br>
是否自动清空缓冲区:<%=out.isAutoFlush() %><br>
</body>
运行结果截图:

注:在默认情况下:服务器端要输出到客户端的内容,不直接写到客户端,而是先写到一个输出缓冲区中,只有在下面三种情况下,才会把该缓冲区的内容输出到客户端:
(1)该JSP网页完成信息的输出
(2)输出缓冲去已满
(3)JSP中调用out.flush()或response.flushbuffer()
2、request对象 获取页面的一些标签属性和属性值
客户端的请求信息被封装在request对象中,通过它才能了解客户端的需求,然后做出响应。它是HttpServletRequest的实例,javax.http.HttpServletRequest接口继承自javax.servlet.ServletRequest接口。request对象具有请求域,即完成客户端的请求之前,该对象一直有效。
request对象的作用是与客户端交互,收集客户端的Form、Cookies、超链接,或者收集服务器端的环境变量。request对象是从客户端向服务器发送请求,包括用户提交的信息及客户端的一些信息。客户端可通过HTML表单或在网页地址后面提供参数的方法提交数据,然后通过request对象的相关方法来获取这些数据。request的各种方法主要用来处理客户端浏览器提交的请求中的各项参数和选项。
request对象常用的方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| getAttribute(String name) | 返回name指定的属性值,如不存在则返回null |
| getAttributeNames() | 返回name指定属性集合,其结果是一个枚举实例。 |
| getCookies() | 返回客户端的所有Cookie对象,结果为一个Cookie数组。 |
| getCharacterEncoding() | 返回请求中的字符编码方式。 |
| getHeader(String name) | 获得HTTP协议定义的文件头信息。 |
| getHeaders(String name) | 返回所有指定名字的request Header的所有值,其结果是一个枚举实例。 |
| getInputStream() | 返回请求的输入流,用于获得请求中的数据。 |
| getMethod() | 获得客户端向服务器端传送数据的方法,如 GET、POST、HEADER、TRACE等。 |
| getProtocol() | 获得客户端向服务器端传送数据所依据的协议名称。 |
| getParameter(String name) | 获得客户端传送给服务器端的参数值,可以获得GET和POST提交的参数。 |
| getParameterNames() | 获得客户端传送给服务器端的所有参数名字,其结果为一个枚举实例。 |
| getParameterValues(String name) | 获得指定参数的所有值。 |
| getSession([Boolean create]) | 回和请求相关的session,create为可选参数,当有参数create且为true时,如果此时客户端没有创建session,则创建一个新的session。 |
| getServerName() | 获得服务器的名字。 |
| getServletPath() | 获得客户端所请求的脚本文件的文件路径。 |
| getServerPort() | 获取服务器的端口号。 |
| removeAttribute(String name) | 删除请求中的一个属性。 |
| setAttribute(String name, java.lang.Object objt) | 设置名字为name的request参数的值,该值是由java.lang.Object类型的objt指定的。 |
代码示例:
index.jsp代码
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"
contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
isErrorPage="true" errorPage="error.jsp"
isThreadSafe="true"
session="true" buffer="8kb" autoFlush="true"
info="..."
%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘index.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
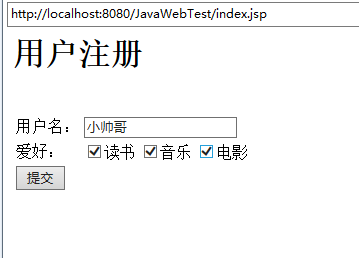
<h1>用户注册</h1>
<br>
<form action="request.jsp" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名: </td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>爱好:</td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="read"/>读书
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="music"/>音乐
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="movie"/>电影
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="提交"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<br>
<a href="request.jsp?username=小帅">测试URL传参</a>
</body>
</html>
request.jsp代码
<%@page import="org.apache.jasper.tagplugins.jstl.core.ForEach"%>
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘request.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
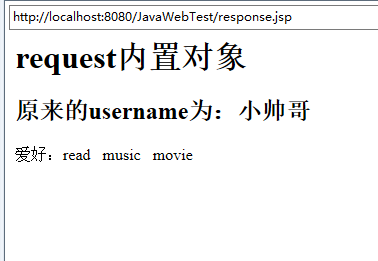
<h1>request内置对象</h1>
<%
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//解决中文乱码问题,但是解决不了url传递中的中文乱码问题
request.setAttribute("password", "123654");//对未创建的属性,先创建后赋值
out.println("<h2>原来的username为:"+request.getParameter("username")+"</h2>");
request.setAttribute("username", "女神");//对已有的属性重新赋值
%>
爱好:<% if(request.getParameterValues("favorite")!=null)
{
String []favorites=request.getParameterValues("favorite");
for(int i=0;i<favorites.length;i++)
{
out.println(favorites[i]+" ");
}
}
%>
<br>
密码:<%=request.getAttribute("password") %><br>
现在的username:<%=request.getAttribute("username") %><br>
请求体的MIME类型<%=request.getContentType() %><br>
协议类型及版本号<%=request.getProtocol() %><br>
服务器主机名:<%=request.getServerName() %><br>
服务器端口号:<%=request.getServerPort() %><br>
请求文件的长度:<%=request.getContentLength() %><br>
请求客户端的ip地址:<%=request.getRemoteAddr() %><br>
请求的真是路径:<%=request.getRealPath("request.jsp") %><br>
请求上下文的路径<%=request.getContextPath() %><br>
</body>
</html>
运行截图:

点击提交按钮后的结果截图:

点击超链接后的截图:

注:(1)request.setAttribute()方法可以对已有属性进行重新赋值,也可以对不存在的属性进行先创建后赋值。
(2)URL传值的乱码问题需要,通过配置server.xml文档解决。
在标签<Connector connectionTimeout="20000" port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1" redirectPort="8443"URIEncoding="utf-8"/>中添加红色部分,然后重启tomocate服务器。
配置完成后的运行截图:

3、response对象
response对象对客户的请求作出动态的响应,向客户端发送数据,用户可以使用该对象将服务器的数据以HTML的格式发送到用户的浏览器,它与request组成一对接收、发送数据的对象。一般在JSP文件中很少使用到response。
response对象包含客户请求的相关信息,它是HttpServletResponse类的实例,javax.http.HttpServletResponse接口,继承于javax.servlet.ServletResponse接口。
response对象常用的方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| String getCharacterEncoding() | 返回响应应用的是何种字符编码 |
| ServletOutputStream getOutputStream() | 返回响应的一个二进制输出流 |
| PrintWriter getWriter() | 返回可以向客户端输出字符的一个对象 |
| void setContenLength(int len) | 设置响应头长度 |
| void setContentType(String type) | 设置响应的MIME类型 |
| sendRedirect(java.lang.String.location) | 重新定向客户端的请求 |
| void addCookie() | 添加cookies记录 |
代码示例:
response.jsp代码
<%@page import="java.io.PrintWriter"%>
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘response.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>response内置对象</h1>
<%
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");//设置响应的MIME类型
out.print("<h2>我是response对象~</h2>");
PrintWriter pw=response.getWriter();
//out.flush();刷新缓存。
pw.write("<h2>我是response对象~的printerWriter流</h2>");//printWriter类对象总是早于内置对象的输出,除非在printWriter流之前flush一下,刷新缓存。
pw.print("<h2>我是response对象~的printerWriter流1</h2>");
//response.sendRedirect("error.jsp");//请求重定向
%>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:(当没有释放out.flush()注释)

(当释放out.flush()注释)

补充:关于转发与请求重定向区别
请求重定向:客户端行为,response.sendRedirect(java.lang.String.location),从本质上等于两次请求,前一次的请求不会保存,地址栏的URL地址会改变。
请求转发:服务器行为,request.getRequestDispatcher(java.lang.String.location).forword(servletRequest req,ServletResponse resp);是一次请求,转发后请求对象会保存,地址栏的URL地址不会改变。
代码示例:
index.jsp代码
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"
contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
isErrorPage="true" errorPage="error.jsp"
isThreadSafe="true"
session="true" buffer="8kb" autoFlush="true"
info="..."
%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘index.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>用户注册</h1>
<br>
<form action="response.jsp" method="post">
<table>
<tr>
<td>用户名: </td>
<td><input type="text" name="username"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>爱好:</td>
<td>
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="read"/>读书
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="music"/>音乐
<input type="checkbox" name="favorite" value="movie"/>电影
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="提交"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<br>
<!-- <a href="request.jsp?username=小帅">测试URL传参</a> -->
</body>
</html>
response.jsp代码
<%@page import="java.io.PrintWriter"%>
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘response.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>response内置对象</h1>
<%
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");//设置响应的MIME类型
response.sendRedirect("request.jsp");//请求重定向
//request.getRequestDispatcher("request.jsp").forward(request, response);//请求转发
%>
</body>
</html>
response.jsp代码
<%@page import="org.apache.jasper.tagplugins.jstl.core.ForEach"%>
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘request.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>request内置对象</h1>
<%
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");//解决中文乱码问题,但是解决不了url传递中的中文乱码问题
out.println("<h2>原来的username为:"+request.getParameter("username")+"</h2>");
%>
爱好:<% if(request.getParameterValues("favorite")!=null)
{
String []favorites=request.getParameterValues("favorite");
for(int i=0;i<favorites.length;i++)
{
out.println(favorites[i]+" ");
}
}
%>
<br>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
请求重定向:

请求转发:
4、session对象
(1)session定义:
session表示客户端与服务器的一次会话;web中的session指的是用户在浏览某个网站时,从进入网站到浏览器关闭所经过的这段时间,也就是用户浏览这个网站所花费的时间;从上述定义可以看出,session实际上是一个特定的时间概念;在服务器的内存中保存着不同用户的session。
(2)对session对象的理解:
1)session对象是一个jsp内置对象;
2)session对象在第一个JSP页面被装载时自动创建,完成会话管理期;
3)从一个用户打开浏览器并连接到服务器开始,到客户关闭浏览器离开这个服务器结束,被称为一个会话。
4)当一个客户访问一个服务器时,可能会在服务器的几个面面之间切换,服务器应当通过某种办法知道这是一个客户,就需要session对象。
5)session对象是HttpSession类的实例,javax.http.HttpSession接口.
(3)session对象常用方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| long getCreationTime() | 返回session创建的时间 |
| public String getId() | 返回session独享创建时的JSP引擎为他设置的唯一ID号 |
| long getLastAccessedTime() | 返回session里客户端最近一次请求的时间 |
| int getMaxInactiveInterval() | 返回两次请求间隔多长时间此session被取消 |
| String[] getValueNames() |
返回一个包含此session中所有可用属性的数组 |
| void invalidate() | 取消session使session不可用 |
| boolean isNew() | 返回服务器创建的一个session,客户端是否已经加入 |
| void removeValue(String name) | 删除session中指定的属性 |
| void setMaxInactiveInterval() |
设置两次请求间隔多长时间此session被取消(ms) |
代码示例:
session.jsp代码
<%@page import="java.text.SimpleDateFormat"%>
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘session.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<<h1>session内置对象</h1>
<%
Date d=new Date(session.getCreationTime());
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");//设置日期格式
session.setAttribute("username", "小帅哥");
%>
<a href="session2.jsp" target="_blank">跳转到session2.jsp</a><br>
session创建时间:<%=sdf.format(d) %><br>
session的ID编号:<%=session.getId() %><br>
</body>
</html>
session2.jsp代码
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@page import="java.text.SimpleDateFormat"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘session2.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>session2.jsp页面</h1>
<%
Date d=new Date(session.getCreationTime());
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");//设置日期格式
%>
session创建时间:<%=sdf.format(d) %><br>
session的ID编号:<%=session.getId() %><br>
session中获取用户名:<%=session.getAttribute("username") %><br>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
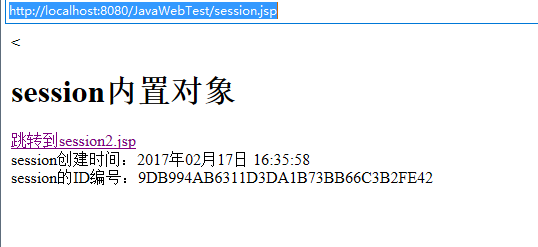
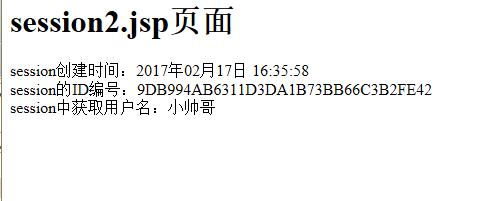
结果显示连个页面是同一个session。
(4)session的生命周期
创建
当客户端第一次访问某个jsp或者Servlet时候,服务器会为当前的会话创建一个SessionId,每次客户端向服务端发送请求时,都会将SessionId携带过去,服务器端会对此SessionId进行校验。
活动
1)某次会话中通过超链接打开的新页面属于一次会话。
2)只要当前会话页面没有关闭,重新打开新的浏览器窗口访问同一个项目资源时属于同义词会话
3)除非本次会话的所有页面都关闭后在重新访问某个JSP或者Servlet将会创建新的会话。
销毁
1)调用session.invalidate()方法
2)session过期(超时)
3)服务器重新启动。
(5)设置session超时(Tomcat默认session超时时间为30分钟)
1)session.setMaxInactiveInterval(时间);//单位是秒
2)在web.xml配置(单位是分钟)
<session-config>
<session-timeout>
10
</session-timeout>
</session-config>
5、application对象(定义,操作全局变量)
application对象实现了用户间数据的共享,可存放全局变量。它开始于服务器的启动,直到服务器的关闭,在此期间,此对象将一直存在;这样在用户的前后连接或不同用户间的连接中,可以对此对象的同一属性进行操作;在任何地方对此对象属性的操作,都将影响其他用户对此的访问。服务器的启动和关闭决定了application对象的生命。它是ServletContext类的实例。参考javax.servlet.servletContext接口。
application对象常用方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| public void setAttribute(String name,Object value) | 使用指定名称对象绑定此次会话 |
| public Object getAttribute(String name) | 返回与此会话中的指定名称绑定在一起的对象,若果没有对象绑定在该名称下,则返回null |
| Enumeration getAttributeNames() | 返回所有可用属性名的枚举 |
| String getServerInfo() | 返回JSP(SERVLET)引擎名级版本号 |
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘application.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>application内置对象</h1>
<%application.setAttribute("username", "小帅哥");
application.setAttribute("password", "123456789");
application.setAttribute("gender", "男");
%>
姓名:<%=application.getAttribute("username") %><br>
application的属性有:
<%
Enumeration attributes=application.getAttributeNames();
while(attributes.hasMoreElements()){
out.println(attributes.nextElement()+" ");
}
%><br>
JSP(SERVLET)引擎名及版本号:<%=application.getServerInfo() %>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:

6、page对象
page对象就是指向当前JSP页面本身,是当前页面转换后的Servlet类的实例,有点像类中的this指针,它是java.lang.Obejct类的实例(详细参考jdk 的api文档)。JSP页面中很少用到page对象。
page常用方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| Class getClass() | 返回此Object的类 |
| int hashCode() | 返回此Object的hash码 |
| boolean equals(Object obj) | 判断此Object是否与指定的Object对象相等 |
| void copy(Object obj) | 把此Object拷贝到指定的Object对象中 |
| Object clone() | 克隆此Object对象 |
| String toString() | 把此Object独享转换成String类的对象 |
| void notify() | 唤醒一个等待的线程 |
| void notifyAll() | 唤醒所有等待的线程 |
| void wait(int timeout) | 使一个线程处于等待直到timeout结束被唤醒 |
| void wait() | 使一个线程处于等待直到被唤醒 |
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘page.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>page内置对象</h1>
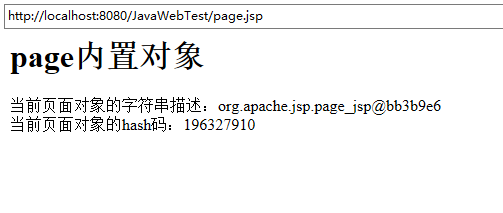
当前页面对象的字符串描述:<%=page.toString() %><br>
<% //page.wait(5);当添加这条语句时会抛出异常
out.print("当前页面对象的hash码:"+page.hashCode());
%>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
7、pageContext对象
pageContext对象提供了对JSP页面内所有的对象及名字空间的访问,也就是说可以访问本页所有对象,session,application,page等。pageContext对象相当于页面中所有功能的集大成者,pageContext对象的类名也叫pageContext,javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext类继承于javax.servlet.jsp.JspContext类。
pageContext对象的常用方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| JSPWriter getOut() | 返回当前客户端响应被使用的JSPWriter流(out) |
| HttpSession getSession() | 返回当前页面中的HttpSession对象(session) |
| Object getPage() | 返回当前页面的Object对象(page) |
| ServletRequest getRequest() | 返回当前页的ServletRequest对象(request) |
| ServletResponse getResponse() | 返回当前页的ServletResponse对象(response) |
| void setAttribute(String name,Object attribute) | 设置属性及属性值 |
| Object getAttribute(String name,int scope) | 在指定范围内取属性的值 |
| int getAttributeScope(String name) | 返回某属性的作用范围 |
| void forward(String relativeUrlPath) | 是当前页面重导到另一页面 |
| void include(String relaticve UrlPath) | 在当前位置包含另一文件 |
代码示例: (主要测试上表加红部分的方法,用于加深了解,各对象设置对象的作用范围取值scope)
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘pageContext.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>pageContext内置对象</h1>
<%
request.setAttribute("name", "男神");
session.setAttribute("name", "女神");
application.setAttribute("name", "MM");
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "GG");
%>
request对象设定的name值:<%=request.getAttribute("name") %><br>
session对象设定的name值:<%=session.getAttribute("name") %><br>
application对象设定的name值:<%=application.getAttribute("name") %><br>
pageContext对象设定的name值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name") %><br>
范围1内设定的值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name", 1) %><br>
范围2内设定的值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name",2) %><br>
范围3内设定的值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name", 3) %><br>
范围4内设定的值:<%=pageContext.getAttribute("name",4) %><br>
*************************************<br>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("city1", "北京", pageContext.PAGE_SCOPE);
pageContext.setAttribute("postcode1", "12345");
pageContext.setAttribute("city2", "上海", pageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
request.setAttribute("postcode2","23456" );
pageContext.setAttribute("city3", "广州", pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
session.setAttribute("postcode3", "34567");
pageContext.setAttribute("city4", "杭州", pageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE);
application.setAttribute("postcode4", "45678");
%>
page设置的city1属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("city1") %><br>
page设置的postcode1属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("postcode1") %><br>
request设置的city2属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("city2") %><br>
request设置的postcode2属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("postcode2") %><br>
session设置的city3属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("city3") %><br>
session设置的postcode3属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("postcode3") %><br>
application设置的city4属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("city4") %><br>
application设置的postcode4属性的scope值:<%=pageContext.getAttributesScope("postcode4") %><br>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
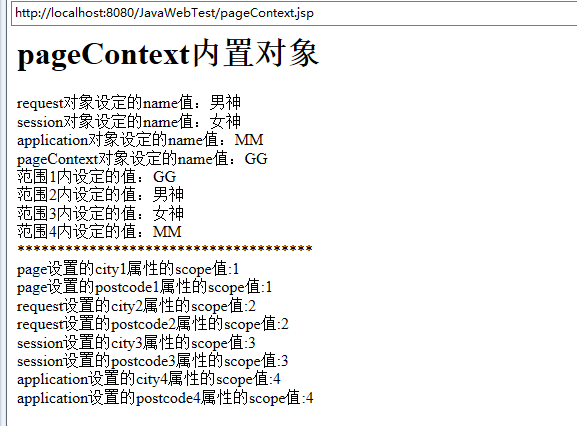
分析结论:(1)各对象设置属性的范围取值scope:
| 内置对象名 | scope值 |
| page | 1 |
| request | 2 |
| session | 3 |
| application | 4 |
(2)重点分析代码段背景加颜色的代码段以及代码运行的打印结果:可知pageContext对象的setAtrribute(String name,Object attribute)方法,没有指定以什么对象的身份创建属性,并给属性赋值。其实默认是page对象创建,getAttribute(String name)方法,再取出属性的时候也并没有指定以什么身份去指定属性的取属性值,默认是以page对象去获取。所以其scope值为1.
8、config对象
javax.servlet.ServletCofig示例,该实例代表JSP的配置信息。config对象是在一个Servlet初始化时,JSP引擎向它传递信息用的,此信息包括Servlet初始化时要用到的参数(通过属性名和属性值构成)及服务器的有关信息(通过传递一个ServletContext对象)。
config对象常用的方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| ServletContext getServletContext() | 返回含有服务器相关信息的ServletContext对象 |
| String getInitParameter(String name) | 返回初始化参数的值 |
| Enumeration getInitParameterNames() | 返回Servlet初始化所需所有参数的枚举 |
代码示例:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘config.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>config内置对象</h1>
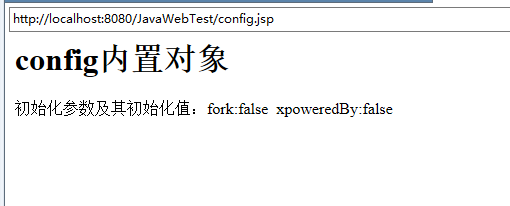
初始化参数及其初始化值:<%
Enumeration eu=config.getInitParameterNames();
while(eu.hasMoreElements())
{
//获取属性名
String obj=(String)eu.nextElement();
//打印属性名及属性值
out.print(obj+":"+config.getInitParameter(obj)+" ");
}
%>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
9、exception对象
exception对象是一个异常对象,当一个页面在运行过程中发生异常,就产生这个对象。若果一个JSP页面要应用此对象,就必须要把isErrorPage设为true(jsp<%@page%>指令中设置),否则无法编译。它实际上是Java.lang.Throwable(详细可查jdk api 文档)的对象。
exception对象常用的方法表
| 方法 | 说明 |
| String getMessage() | 返回描述异常的信息 |
| String toString() | 返回关于异常的简短描述信息 |
| void printStackTrace() | 显示异常及其栈轨迹 |
| Throwable FillInStackTrace() | 重写异常的执行栈轨迹 |
代码示例:
exception_text.jsp代码
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8" errorPage="exception.jsp"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘exception_text.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>测试异常的页面</h1>
<%
out.print(1/0);
%>
</body>
</html>
exception.jsp代码:
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8" isErrorPage="true"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()+"://"+request.getServerName()+":"+request.getServerPort()+path+"/";
%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<base href="<%=basePath%>">
<title>My JSP ‘exception.jsp‘ starting page</title>
<meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache">
<meta http-equiv="expires" content="0">
<meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3">
<meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page">
<!--
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
-->
</head>
<body>
<h1>exception对象</h1>
异常的消息:<%=exception.getMessage() %><br>
异常的字符串描述:<%=exception.toString() %>
</body>
</html>
运行结果截图:
