一、CLOB
1.1CLOB简介
CLOB全称是(Character Large Object)字符大对象,用于存储大量的文本数据。
字符大对象的操作不同于一般数据,是通过流来完成的。
1.2MySQL中相关类型
-tinytext:最大255个字节(2^8-1)。
-text:最大65535个字节(2^16-1)。
-mediumtext:最大16777215 个字节(2^24-1)。
-longtext:最大4294967295个字节(2^32-1)。
1.3CLOB对象的写入与读取
void java.sql.PreparedStatement.setClob(int parameterIndex, Reader reader);
设置CLOB在数据库中对应列标位置及输入流,即将reader流所代表的文件(或信息)写入到数据库第parameterIndex列。
Reader java.sql.Clob.getCharacterStream();//获取CLOB对象的字符流
文本内容:

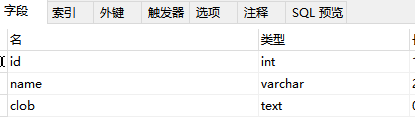
建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `test_clob` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL, `clob` text, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; public class TestJDBC{ public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{ final String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"; String userName = "root"; String passWord = "123456"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,userName,passWord); conn.setAutoCommit(false); ps = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO `mybatis`.`test_clob`" + "(`id`,`name`, `clob`) " + "VALUES (?, ?, ?);"); ps.setObject(1, 1); ps.setObject(2, "1");
//clob通过流的形式进行写入
//也可以通过这种方法将指定字符放入数据库
//ps.setClob(3, new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new ByteArrayInputStream("testClob".getBytes())))); ps.setClob(3, new FileReader(new File("F:\TestJava\testClob.txt"))); ps.execute(); ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from test_clob where id = ?"); ps.setObject(1, 1); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); conn.commit(); while(rs.next()){//获取clob的字符流 Reader re = rs.getClob("clob").getCharacterStream(); int intToChar = -1;//将返回内容依次读取 while((intToChar = re.read()) != -1){ System.out.print((char)intToChar); } } System.out.println("select 成功"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
testClob.txt
testClob.txt
testClob.txt
testClob.txt
testClob.txtselect 成功
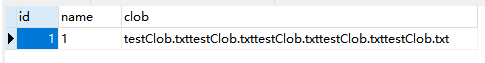
CLOB通过流方法将数据添加到数据库,从数据库中获取CLOB也是通过流的方式读取内容。
二、BLOB
1.1BLOB简介
BLOB全称是( Large Object)字符大对象,用于存储大量的数据(如图片、视频等)。
字符大对象的操作不同于一般数据,是通过流来完成的。
1.2MySQL中相关类型
-tinyblob:最大255个字节(2^8-1)。
-blob:最大65535个字节(2^16-1)。
-mediumtblob:最大16777215 个字节(2^24-1)。
-longblob:最大4294967295个字节(2^32-1)。
2.3BLOB对象的写入与读取
方法和上述CLOB使用方法基本相同。
void java.sql.PreparedStatement.setBlob(int parameterIndex, InputStream inputStream) ;
//设置放入数据库BLOB对象的输入流,及列标。
InputStream java.sql.Blob.getBinaryStream()
//获取数据库BLOB对象的输入流
(表字段及类型)
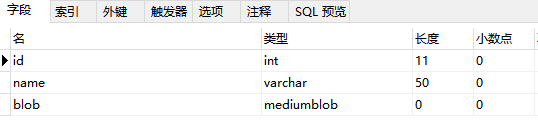
建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `test_blob` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL, `name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL, `blob` mediumblob, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.io.OutputStream; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; public class TestJDBC{ public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{ final String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"; String userName = "root"; String passWord = "123456"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; OutputStream os = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,userName,passWord); conn.setAutoCommit(false); ps = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO `mybatis`.`test_blob`" + "(`id`,`name`, `blob`) " + "VALUES (?, ?, ?);"); ps.setObject(1, 1); ps.setObject(2, "1");
//将该文件以BLOB对象形式放入数据库中 ps.setBlob(3, new FileInputStream("F:/依风/Pictures/下载图片/bg.jpg"));; ps.execute();
ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from test_blob where id = ?"); ps.setObject(1, 1);
//获取查询结果 ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); conn.commit(); byte[] buff = new byte[1024]; int step = -1;
//指定输出流写出位置 F:TestJava est.jpg os = new FileOutputStream("F:\TestJava\test.jpg"); while(rs.next()){
//获取数据库中BLOB对象的输入流 InputStream is = rs.getBlob("blob").getBinaryStream();
//读入BLOB对象内容,并将其写入指定位置 while((step = is.read(buff)) != -1){ os.write(buff, 0, step); } is.close(); os.close(); } System.out.println("成功"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果: select 成功
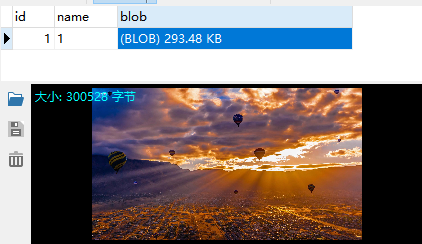
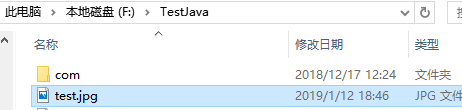
上述代码先将图片放入数据库中,然后从数据库中获取到对应的BLOB对象,
最后获取BLOB的输入流,并将其写入到指定文件夹,可以看到数据库(以图片方式查看)和指定文件夹中都有图片。