一.auth模块
from django.contrib import auth
django.contrib.auth中提供了许多方法,这里主要介绍其中的三个。
1 .authenticate()
验证用户输入的用户名和密码是否相同
提供了用户认证,即验证用户名以及密码是否正确,一般需要username password两个关键字参数
如果认证信息有效,会返回一个 User 对象。authenticate()会在User 对象上设置一个属性标识那种认证后端认证了该用户,且该信息在后面的登录过程中是需要的。当我们试图登陆一个从数据库中直接取出来不经过authenticate()的User对象会报错的。
user = authenticate(username='someone',password='somepassword')
2 .login(HttpRequest, user):登录
该函数接受一个HttpRequest对象,以及一个认证了的User对象
此函数使用django的session框架给某个已认证的用户附加上session id等信息。
# 登录例子的视图函数:
from django.contrib.auth import authenticate, login
def login(request):
# 通过auth组件实现
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, "login.html")
elif request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("pwd")
valid_num = request.POST.get("valid_num")
# 验证填写验证码的正确性
keep_str = request.session.get("keep_str")
if keep_str.upper() == valid_num.upper():
user = auth.authenticate(username=username, password=password)
# 验证用户名和密码
if user:
# 如果认证成功,就让登录,这个login里面包括了session操作和cookie
auth.login(request, user)
return redirect("/index/")
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "有错误"})
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "验证码输入错误"})
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "有错误"})
3.logout(request) 注销用户
该函数接受一个HttpRequest对象,无返回值。当调用该函数时,当前请求的session信息会全部清除。该用户即使没有登录,使用该函数也不会报错。
from django.contrib.auth import logout
# 退出登录
def logout(request):
logout(request)
# request.session.flush() #session方法退出,步骤一
rep = redirect("/login/") # 退出返回登录页面
# rep.delete_cookie("is_login") # session方法退出,步骤二
return rep
二.User对象
User 对象属性:username, password(必填项)password用哈希算法保存到数据库
is_staff : 用户是否拥有网站的管理权限.
is_active : 是否允许用户登录, 设置为``False``,可以不用删除用户来禁止 用户登录
1.创建用户:create_user
使用 create_user 辅助函数创建用户分三种创建方式:
(1)create:
创建一个普通用户,密码是明文的.(一般不推荐使用,因为无法结合auth组件的使用)
(2) create_user:
创建一个普通用户,密码是密文的.
(3)create_superuser:
创建一个超级用户,密码是密文的,要多传一个email参数.
例:下面用上面上中方式创建了三个用户和设置密码

然后对数据库中的auth_user 进行查询:
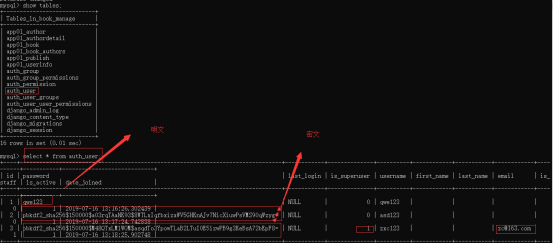
通过如上数据可以得出:
方式一:密码为明文,方式二:密码为密文,方式三:密码为密文,而且需要填写邮箱,而且在是否为super用户字段处的值为:1。
2.check_password(passwd) 密码检查
用户需要修改密码的时候 首先要让他输入原来的密码 ,如果给定的字符串通过了密码检查,返回 True
3.set_password() 修改密码
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
user = User.objects.get(username='')
user.set_password(password='')
user.save
4.user对象的 is_authenticated()
要求:
(1)用户登录后才能访问某些页面
(2)如果用户没有登录就访问该页面的话直接跳转登录页面
(3)用户在跳转的登录界面中完成登录后,自动访问跳转到之前访问的地址
注意:下面两个方法是用于到登录页之前的网页的判断。
方法一:自己写的装饰器
# 自己写的装饰器
def login_required(func):
def inner(request, *args, **kwargs):
if not request.user.is_authenticated: # 没有登录成功
path = request.path
return redirect('/login/?next=%s' % path)
ret = func(request, *args, **kwargs)
return ret
return inner
方法二:django已经为我们设计好了一个用于此种情况的装饰器:login_requierd()
from django.contrib.auth.decorators import login_required
@login_required
def my_view(request):
...
若用户没有登录,则会跳转到django默认的 登录URL '/accounts/login/ ' (这个值可以在settings文件中通过LOGIN_URL进行修改)。并传递 当前访问url的绝对路径 (登陆成功后,会重定向到该路径)。
三.简单的例子
1.登录验证
# 登录函数
def login(request):
# 通过auth组件实现
if request.method == "GET":
return render(request, "login.html")
elif request.method == "POST":
username = request.POST.get("username")
password = request.POST.get("pwd")
valid_num = request.POST.get("valid_num")
# 验证填写验证码的正确性
keep_str = request.session.get("keep_str")
if keep_str.upper() == valid_num.upper():
user = auth.authenticate(username=username, password=password) # 验证用户名和密码
if user:
# if not request.user.is_authenticated():
# 如果认证成功,就让登录,这个login里面包括了session操作和cookie
auth.login(request, user)
# 路径为上一个路径或者返回一个主页,这里的book_list可以为主页的路径一般名为:index
path = request.GET.get("next") or "/book_list/"
return redirect(path)
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "有错误"})
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "验证码输入错误"})
else:
return render(request, "login.html", {"error": "有错误"})
2.注册验证
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
# 注册及验证
def register(request):
if request.method == "GET":
form = UserInfoForm() # 初始化form对象
return render(request, "register.html", {"form": form})
if request.is_ajax():
ret = {"status": 1, "msg": None}
print(request.POST)
form = UserInfoForm(request.POST)
if form.is_valid():
print(form.cleaned_data)
data = form.cleaned_data # 效验通过的数据,是字典的类型数据
# 需要删除字典中验证密码,不需要保存到数据库中
data.pop("cf_password")
User.objects.create_user(**data) # User是以个对象
print(data)
else:
print(form.errors)
ret['status'] = 0
ret['msg'] = form.errors
return JsonResponse(ret)
3.修改密码验证
# 修改密码
@login_required #内置验证是否是登录状态的装饰器
def change_pwd(request):
if request.method == "POST":
oldpassword = request.POST.get("oldpassword", "")
newpassword = request.POST.get("newpassword", "")
# 得到当前登录的用户,判断旧密码是不是和当前的密码一样
username = request.user # 打印的是当前登录的用户名
user = User.objects.get(username=username) # 查看用户
print(user)
ret = user.check_password(oldpassword) # 检查密码是否正确
print(ret)
if ret:
user.set_password(newpassword) # 如果正确就给设置一个新密码
user.save() # 保存
return redirect("/login/")
else:
info = "输入密码有误"
return render(request, "change_pwd.html", {"info": info})
return render(request, "change_pwd.html")
4.退出
from django.contrib.auth import logout
# 退出登录
def logout_user(request):
logout(request)
rep = redirect("/login/")
return rep