队列
- 用数组实现一个顺序队列
- 用链表实现一个链式队列
- 实现一个循环队列
用数组实现一个顺序队列
几个问题:
- 队列方法:入队、出队
- 队列的存储:即队首队尾两个指针,
- 扩容:如果队列容量不够了,应该扩容,如果队尾没有位置了,队首有位置,应该把元素往前移
主要是上面三个问题,在代码中都有体现,上面的扩容方法借鉴了ArrayList的扩容方法。
package com.helius.structure.queue;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 用数组实现一个队列,即顺序队列
*/
public class ArrayQueue {
// 存储数据的数组
private Object[] elements;
//队列大小
private int size;
// 默认队列容量
private int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
// 队列头指针
private int head;
// 队列尾指针
private int tail;
private int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE-8;
/**
* 默认构造函数 初始化大小为10的队列
*/
public ArrayQueue(){
elements = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
initPointer(0,0);
}
/**
* 通过传入的容量大小创建队列
* @param capacity
*/
public ArrayQueue(int capacity){
elements = new Object[capacity];
initPointer(0,0);
}
/**
* 初始化队列头尾指针
* @param head
* @param tail
*/
private void initPointer(int head,int tail){
this.head = head;
this.tail = tail;
}
/**
* 元素入队列
* @param element
* @return
*/
public boolean enqueue(Object element){
ensureCapacityHelper();
elements[tail++] = element;//在尾指针处存入元素且尾指针后移
size++;//队列元素个数加1
return true;
}
private void ensureCapacityHelper() {
if(tail==elements.length){//尾指针已越过数组尾端
//判断队列是否已满 即判断数组中是否还有可用存储空间
//if(size<elements.length){
if(head==0){
//扩容
grow(elements.length);
}else{
//进行数据搬移操作 将数组中的数据依次向前挪动直至顶部
for(int i= head;i<tail;i++){
elements[i-head]=elements[i];
}
//数据搬移完后重新初始化头尾指针
initPointer(0,tail-head);
}
}
}
/**
* 扩容
* @param oldCapacity 原始容量
*/
private void grow(int oldCapacity) {
int newCapacity = oldCapacity+(oldCapacity>>1);
if(newCapacity-oldCapacity<0){
newCapacity = DEFAULT_CAPACITY;
}
if(newCapacity-MAX_ARRAY_SIZE>0){
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(newCapacity);
}
elements = Arrays.copyOf(elements,newCapacity);
}
private int hugeCapacity(int newCapacity) {
return (newCapacity>MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)? Integer.MAX_VALUE:newCapacity;
}
/**
* 出队列
* @return
*/
public Object dequeue(){
if(head==tail){
return null;//队列中没有数据
}
Object obj=elements[head++];//取出队列头的元素且头指针后移
size--;//队列中元素个数减1
return obj;
}
/**
* 获取队列元素个数
* @return
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
测试用例#
public class TestArrayQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayQueue queue = new ArrayQueue(4);
//入队列
queue.enqueue("helius1");
queue.enqueue("helius2");
queue.enqueue("helius3");
queue.enqueue("helius4");
//此时入队列应该走扩容的逻辑
queue.enqueue("helius5");
queue.enqueue("helius6");
//出队列
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
//此时入队列应该走数据搬移逻辑
queue.enqueue("helius7");
//出队列
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
//入队列
queue.enqueue("helius8");
//出队列
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
//入队列
queue.enqueue("helius9");
queue.enqueue("helius10");
queue.enqueue("helius11");
queue.enqueue("helius12");
//出队列
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
System.out.println(queue.dequeue());
}
}
结果:#
helius1
helius2
helius3
helius4
helius5
helius6
helius7
helius8
null
helius9
helius10
循环队列#
用java实现循环队列的方法:
-
增加一个属性size用来记录目前的元素个数。目的是当head=rear的时候,通过size=0还是size=数组长度,来区分队列为空,或者队列已满。
-
数组中只存储数组大小-1个元素,保证rear转一圈之后不会和head相等,也就是队列满的时候,rear+1=head,中间刚好空一个元素。
当rear=head的时候,一定是队列空了。
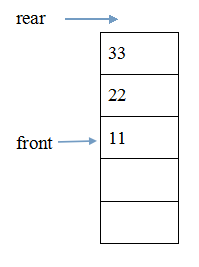
队列(Queue)两端允许操作的类型不一样:
可以进行删除的一端称为队头,这种操作也叫出队dequeue;
可以进行插入的一端称为队尾,这种操作也叫入队enqueue。
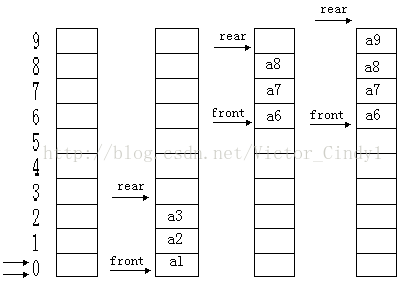
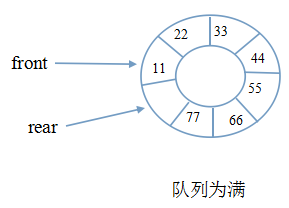
队列的示意图
实现队列时,要注意的是假溢出现象,如上图的最后一幅图。
如图所示的假溢出现象,顺序队列可以如此,循环队列我们可以让这个尾指针指向front前面的元素,这也正符合我们想要的循环队列的定义。
解决办法:使用链式存储,这显然可以。在顺序存储时,我们常见的解决办法是把它首尾相接,构成循环队列,这可以充分利用队列的存储空间。
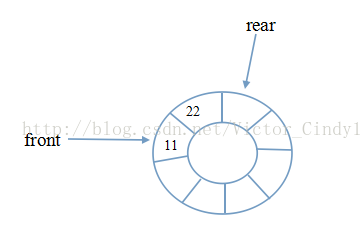
循环队列示意图:
在上图中,front指向队列中第一个元素,rear指向队列队尾的下一个位置。
但依然存在一个问题:当front和rear指向同一个位置时,这代表的是队空还是队满呢?大家可以想象下这种情景。
解决这种问题的常见做法是这样的:
使用一标记,用以区分这种易混淆的情形。
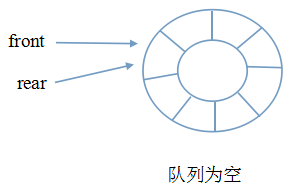
牺牲一个元素空间。当front和rear相等时,为空;当rear的下一个位置是front时,为满。
如下图:
下面我们给出循环队列,并采用第二种方式,即牺牲一个元素空间来区分队空和队满的代码.
几个重点:
1、front指向队头,rear指向队尾的下一个位置。
2、队为空的判断:frontrear;队为满的判断:(rear+1)%MAXSIZEfront。
上面说的rear即为代码中的的tail
/**
* 使用数组实现循环队列
* @author Helius
*/
public class CirculiQueue {
//存储队列数据的数组
private Object[] elements;
//默认数组容量
private int DEFAULT_CAPACITY=10;
//队列中元素个数
private int size;
// 队列头指针
private int head;
//队列尾指针
private int tail;
/**
* 默认构造函数
*/
public CirculiQueue(){
elements = new Object[DEFAULT_CAPACITY];
}
/**
* 通过传入的容量参数构造队列
* @param capacity
*/
public CirculiQueue(int capacity){
elements = new Object[capacity];
}
/**
* 元素入队列
* @param element
* @return
*/
public boolean enqueue(Object element){
//判断队列是否已满
if(head == (tail+1)%elements.length){
//队列已满
return false;
}
//将元素存入tail位置上
elements[tail]=element;
//尾指针后移
/*tail++;
if(tail==elements.length){
tail = 0;
}*/
tail = (tail+1)%elements.length;
size++;
return true;
}
/**
* 元素出队列
* @return
*/
public Object dequeue(){
//判断队列是否为空
if(head==tail){
return null;
}
//获取head位置上的元素
Object element = elements[head];
//头指针后移
/*head++;
if(head==elements.length){
head = 0;
}*/
head = (head+1)%elements.length;
size--;
return element;
}
/**
* 获取队列大小
* @return
*/
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int maxSize = 100;
// 定义
template <class T>
class SqListClass
{
private:
T *data; // 存放顺序表中的元素
int length; // 存放顺序表的长度
public:
SqListClass(); // 构造函数
~SqListClass(); // 析构函数
void CreateList(T a[], int n); // 由a数组中的元素建造顺序表
void DispList(); // 输出顺序表L中的所有元素
int ListLength(); // 求顺序表的长度
bool GetElem(int i, T &e); // 求顺序表中某序列号的元素值
int LocateElem(T e); // 按元素查找其第一个序号位置
bool ListInsert(int i, T e); // 在位置i插入数据元素e
bool ListDelete(int i); // 在位置i删除数据元素
void ReverseList(SqListClass<T> &L); // 翻转顺序表
};
// 线性表的初始化
template<class T>
SqListClass<T>::SqListClass() // 构造函数
{
data = new T[maxSize];
length = 0;
}
// 线性表的销毁
template<class T>
SqListClass<T>::~SqListClass() // 析构函数
{
delete [] data;
}
// 实现
// 线性表的创建,时间复杂度为O(n)
template<class T>
void SqListClass<T>::CreateList(T a[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<n; i++){
data[i] = a[i];
}
length = i;
}
// 输出线性表的所有元素,时间复杂度为O(n)
template<class T>
void SqListClass<T>::DispList(){
cout << "Out:" << endl;
for(int i=0; i<length; i++){
cout << data[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 求线性表的长度,时间复杂度为O(1)
template<class T>
int SqListClass<T>::ListLength(){
return length;
}
// 求顺序表中某序列号的元素值,,时间复杂度为O(1)
template<class T>
bool SqListClass<T>::GetElem(int i, T &e){
if(i<0 || i>length) return false;
e = data[i-1];
return true;
}
// 按元素查找其第一个序号位置,时间复杂度为O(n)
template<class T>
int SqListClass<T>::LocateElem(T e){
int i = 0;
while(i<length && data[i]!=e) i++;
if(i>=length) return 0;
else return i+1;
}
// 在位置i插入数据元素e,时间复杂度为O(n)
template<class T>
bool SqListClass<T>::ListInsert(int i, T e){
if(i<0 || i>length) return false;
for(int j=length; j>=i; j--){
data[j]=data[j-1];
}
data[i-1] = e;
length++;
return true;
}
// 在位置i删除数据元素,时间复杂度为O(n)
template<class T>
bool SqListClass<T>::ListDelete(int i){
if(i<0 || i>length) return false;
for(int j=i-1; j< length; j++){
data[j] = data[j+1];
}
length--;
return true;
}
// 翻转顺序表
template<class T>
void SqListClass<T>::ReverseList(SqListClass<T> &L){
T temp;
for(int j=0; j<L.length/2; j++){
temp = L.data[j];
L.data[j] = L.data[length-j-1];
L.data[length-j-1] = temp;
}
}
// 主函数
int main(){
SqListClass<int> sqList;
int arr[3] = {3,4,5};
// 创建线性表
sqList.CreateList(arr, 3);
// 输出线性表
sqList.DispList();
// 输出线性表的长度
cout << "sqList length is " << sqList.ListLength() << endl;
// 求第二个位置的元素
int a;
sqList.GetElem(2, a);
cout <<"The 2 local is elem " << a << endl;
// 查找元素5的位置
cout << "The elem 5 local is " << sqList.LocateElem(5) << endl;
// 在位置4插入元素6
sqList.ListInsert(2, 6);
sqList.DispList();
// 在位置1删除数据元素
sqList.ListDelete(1);
sqList.DispList();
// 翻转顺序表
sqList.ReverseList(sqList);
sqList.DispList();
return 0;
}
用链表实现一个链式队列使用链表实现队列,需要一个对头指向对列头部管理数据出对,一个队尾管理数据入队;还需要队列的数据区域
那么就需要用两个结构管理队列,一个是数据节点,一个队列
队列节点结构,专门管理数据的
typedef struct queueNode{
int data; //数据域,存放的是有效数据
struct queueNode * next; //指向队列的下一个节点
}queueNode;
队列管理结构:
typedef struct linkqueue{
struct queueNode *front; // 指向队列头部
struct queueNode *rear; // 指向队列尾部
}linkqueue;
1. front 只指向队列的头节点,通过头节点的next指针去访问数据节点,实现出对操作,
2. 链式队列没有满的情况,当队列为空时,头和尾都指向头节点(头节点只是用来管理这个链式对列,并不存放有效数据)
3. 队尾用来插入队列,对头用来出入操作
创建一个空的队列:

插 入队列一个数据
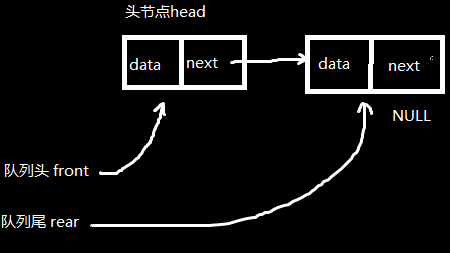
这样通过队尾rear 一直指向链表的尾部管理的数据插入队列操作
举例说明: 队列 linkqueue *qe;
(1) 插入一个新节点 queueNode *pnew
(2)qe->rear->next 是当前节点的next指针,用来连接新节点的 qe->rear->next = pnew
(3)新节点的next指针指向空NULL , pnew->next = NULL;
(4)最后是把尾指针,移动指向尾部节点 qe->rear = qe->rear->next;
linkqueue.c文件:
#include "linkqueue.h"
linkqueue *create_linkqueue(void)
{
//创建队列
linkqueue *qe=NULL;
qe = (linkqueue*)malloc(sizeof(linkqueue));
if(qe == NULL)
{
printf("create queue malloc error
");
return NULL;
}
//创建队列节点
qe->front = (queueNode*)malloc(sizeof(queueNode));
if(qe->front == NULL)
{
free(qe);
printf("create node malloc error
");
return NULL;
}
qe->front->next = NULL;//队列头的next指向实际的数据节点
qe->front->data = 0;
qe->rear = qe->front; //队列空时,对头和对尾指向同一个位置
return qe;
}
//插入数据,入队列,对尾入对
int in_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe, u16 value)
{
if(qe == NULL)
{
printf("in lingkqueue is null
");
return -1;
}
queueNode *pnew = NULL;//入对的新节点
pnew = (queueNode*)malloc(sizeof(queueNode));
if(pnew == NULL)
{
printf("in pnew malloc is fail
");
return -1;
}
pnew->data = value;//入对的数据
pnew->next = NULL;
qe->rear->next = pnew;//把入对的节点链接到队列上
qe->rear = qe->rear->next;//把指向对尾的指针,继续移动到队尾,即指向新插入的节点位置
return 1;
}
//判断队列是否空,空返回1,非空返回0, 其他返回-1
int is_empty_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe)//判空
{
if(qe == NULL)
{
printf("is empty lingkqueue is null
");
return -1;
}
return ((qe->front == qe->rear) ? 1 : 0);
}
int out_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe, u16 *dat)//出队列
{
if(qe == NULL)
{
printf("out lingkqueue is null
");
return -1;
}
if(is_empty_linkqueue(qe) == 1)//队列为空
{
printf("out lingkqueue is empty
");
return 0;
}
queueNode *pdel = NULL;//出对的节点
if(qe->front->next == NULL) //出对列,到对尾时
{
qe->rear = qe->front;
return 0;
}
pdel = qe->front->next;//对头front永远头节点,出对时是头节点的下一个节点
qe->front->next = pdel->next;//把要删除的节点的下一个节点地址链接到对列头上
*dat = pdel->data; //对头的数据
free(pdel);
pdel = NULL;
return 1;
}
//显示队列内容,从对头开始显示
void show_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe)//显示队列内容
{
if(qe == NULL)
{
printf("show lingkqueue is null
");
return;
}
if(is_empty_linkqueue(qe) == 1)//队列为空
{
printf("show lingkqueue is empty
");
return;
}
queueNode *pcur = qe->front->next;//找到数据节点开始
while(pcur != NULL)
{
printf("%d
",pcur->data);
pcur = pcur->next;
}
}
linkqueue.h文件:
#ifndef __LINKQUEUE_H
#define __LINKQUEUE_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int u16;
//数据节点
typedef struct queueNode{
u16 data;
struct queueNode *next;
}queueNode;
//队列结构
typedef struct linkqueue{
queueNode *front; //对列头节点
queueNode *rear; //队列尾节点
}linkqueue, *linkqueue_p;
linkqueue *create_linkqueue(void);
int in_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe, u16 value);//插入数据,入对列
int is_empty_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe);//判空
int out_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe, u16 *dat);//出队列
void show_linkqueue(linkqueue *qe);//显示队列内容
#endif
测试文件main.c:
#include "linkqueue.h" int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { linkqueue *s = NULL; s=create_linkqueue(); in_linkqueue(s,1); show_linkqueue(s); putchar(10); in_linkqueue(s,2); in_linkqueue(s,3); in_linkqueue(s,4); in_linkqueue(s,5); show_linkqueue(s); putchar(10); int a=0; out_linkqueue(s,&a); printf("-------test------! "); out_linkqueue(s,&a); show_linkqueue(s); return 0; }
//circular Queue 循环队列实现
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef int ElemType ;
typedef struct
{
ElemType *base; //存储内存分配基地址
int front; //队列头索引
int rear; //队列尾索引
}circularQueue;
//初始化队列
InitQueue(circularQueue *q)
{
q->base = (ElemType *)malloc((MAXSIZE) * sizeof(ElemType));
if (!q->base) exit(0);
q->front = q->rear = 0;
}
//入队列操作
InsertQueue(circularQueue *q, ElemType e)
{
if ((q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == q->front) return; //队列已满时,不执行入队操作
q->base[q->rear] = e; //将元素放入队列尾部
q->rear = (q->rear + 1) % MAXSIZE; //尾部元素指向下一个空间位置,取模运算保证了索引不越界(余数一定小于除数)
}
//出队列操作
DeleteQueue(circularQueue *q, ElemType *e)
{
if (q->front == q->rear) return; //空队列,直接返回
*e = q->base[q->front]; //头部元素出队
q->front = (q->front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
import java.io.*;
public class QueueArray {
Object[] a; //对象数组,队列最多存储a.length-1个对象
int front; //队首下标
int rear; //队尾下标
public QueueArray(){
this(10); //调用其它构造方法
}
public QueueArray(int size){
a = new Object[size];
front = 0;
rear =0;
}
/**
* 将一个对象追加到队列尾部
* @param obj 对象
* @return 队列满时返回false,否则返回true
*/
public boolean enqueue(Object obj){
if((rear+1)%a.length==front){
return false;
}
a[rear]=obj;
rear = (rear+1)%a.length;
return true;
}
/**
* 队列头部的第一个对象出队
* @return 出队的对象,队列空时返回null
*/
public Object dequeue(){
if(rear==front){
return null;
}
Object obj = a[front];
front = (front+1)%a.length;
return obj;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QueueArray q = new QueueArray(4);
System.out.println(q.enqueue("张三"));
System.out.println(q.enqueue("李斯"));
System.out.println(q.enqueue("赵五"));
System.out.println(q.enqueue("王一"));//无法入队列,队列满
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
System.out.println(q.dequeue());
}
}
}