图像处理之霍夫变换(直线检測算法)
霍夫变换是图像变换中的经典手段之中的一个,主要用来从图像中分离出具有某种同样特征的几何
形状(如,直线,圆等)。霍夫变换寻找直线与圆的方法相比与其他方法能够更好的降低噪
声干扰。经典的霍夫变换经常使用来检測直线,圆,椭圆等。
霍夫变换算法思想:
以直线检測为例,每一个像素坐标点经过变换都变成都直线特质有贡献的统一度量,一个简单
的样例例如以下:一条直线在图像中是一系列离散点的集合,通过一个直线的离散极坐标公式,
能够表达出直线的离散点几何等式例如以下:
X *cos(theta) + y * sin(theta) = r 当中角度theta指r与X轴之间的夹角,r为到直线几何垂
直距离。不论什么在直线上点,x, y都能够表达,当中 r, theta是常量。该公式图形表演示样例如以下:
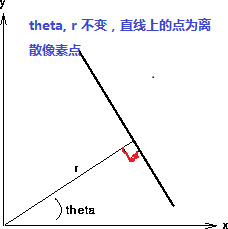
然而在实现的图像处理领域,图像的像素坐标P(x, y)是已知的,而r, theta则是我们要寻找
的变量。假设我们能绘制每一个(r, theta)值依据像素点坐标P(x, y)值的话,那么就从图像笛卡
尔坐标系统转换到极坐标霍夫空间系统,这样的从点到曲线的变换称为直线的霍夫变换。变换
通过量化霍夫參数空间为有限个值间隔等分或者累加格子。当霍夫变换算法開始,每一个像素
坐标点P(x, y)被转换到(r, theta)的曲线点上面,累加到相应的格子数据点,当一个波峰出现
时候,说明有直线存在。相同的原理,我们能够用来检測圆,仅仅是对于圆的參数方程变为如
下等式:
(x –a ) ^2 + (y-b) ^ 2 = r^2当中(a, b)为圆的中心点坐标,r圆的半径。这样霍夫的參数空间就
变成一个三维參数空间。给定圆半径转为二维霍夫參数空间,变换相对简单,也比較经常使用。
编程思路解析:
1. 读取一幅带处理二值图像,最好背景为黑色。
2. 取得源像素数据
3. 依据直线的霍夫变换公式完毕霍夫变换,预览霍夫空间结果
4. 寻找最大霍夫值,设置阈值,反变换到图像RGB值空间(程序难点之中的一个)
5. 越界处理,显示霍夫变换处理以后的图像
关键代码解析:
直线的变换角度为[0 ~ PI]之间,设置等份为500为PI/500,同一时候依据參数直线參数方程的取值
范围为[-r, r]有例如以下霍夫參数定义:
// prepare for hough transform int centerX = width / 2; int centerY = height / 2; double hough_interval = PI_VALUE/(double)hough_space; int max = Math.max(width, height); int max_length = (int)(Math.sqrt(2.0D) * max); hough_1d = new int[2 * hough_space * max_length];
实现从像素RGB空间到霍夫空间变换的代码为:
// start hough transform now....
int[][] image_2d = convert1Dto2D(inPixels);
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
int p = image_2d[row][col] & 0xff;
if(p == 0) continue; // which means background color
// since we does not know the theta angle and r value,
// we have to calculate all hough space for each pixel point
// then we got the max possible theta and r pair.
// r = x * cos(theta) + y * sin(theta)
for(int cell=0; cell < hough_space; cell++ ) {
max = (int)((col - centerX) * Math.cos(cell * hough_interval) + (row - centerY) * Math.sin(cell * hough_interval));
max += max_length; // start from zero, not (-max_length)
if (max < 0 || (max >= 2 * max_length)) {// make sure r did not out of scope[0, 2*max_lenght]
continue;
}
hough_2d[cell][max] +=1;
}
}
}
寻找最大霍夫值计算霍夫阈值的代码例如以下:
// find the max hough value
int max_hough = 0;
for(int i=0; i<hough_space; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<2*max_length; j++) {
hough_1d[(i + j * hough_space)] = hough_2d[i][j];
if(hough_2d[i][j] > max_hough) {
max_hough = hough_2d[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println("MAX HOUGH VALUE = " + max_hough);
// transfer back to image pixels space from hough parameter space
int hough_threshold = (int)(threshold * max_hough);
从霍夫空间反变换回像素数据空间代码例如以下:
// transfer back to image pixels space from hough parameter space
int hough_threshold = (int)(threshold * max_hough);
for(int row = 0; row < hough_space; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < 2*max_length; col++) {
if(hough_2d[row][col] < hough_threshold) // discard it
continue;
int hough_value = hough_2d[row][col];
boolean isLine = true;
for(int i=-1; i<2; i++) {
for(int j=-1; j<2; j++) {
if(i != 0 || j != 0) {
int yf = row + i;
int xf = col + j;
if(xf < 0) continue;
if(xf < 2*max_length) {
if (yf < 0) {
yf += hough_space;
}
if (yf >= hough_space) {
yf -= hough_space;
}
if(hough_2d[yf][xf] <= hough_value) {
continue;
}
isLine = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(!isLine) continue;
// transform back to pixel data now...
double dy = Math.sin(row * hough_interval);
double dx = Math.cos(row * hough_interval);
if ((row <= hough_space / 4) || (row >= 3 * hough_space / 4)) {
for (int subrow = 0; subrow < height; ++subrow) {
int subcol = (int)((col - max_length - ((subrow - centerY) * dy)) / dx) + centerX;
if ((subcol < width) && (subcol >= 0)) {
image_2d[subrow][subcol] = -16776961;
}
}
} else {
for (int subcol = 0; subcol < width; ++subcol) {
int subrow = (int)((col - max_length - ((subcol - centerX) * dx)) / dy) + centerY;
if ((subrow < height) && (subrow >= 0)) {
image_2d[subrow][subcol] = -16776961;
}
}
}
}
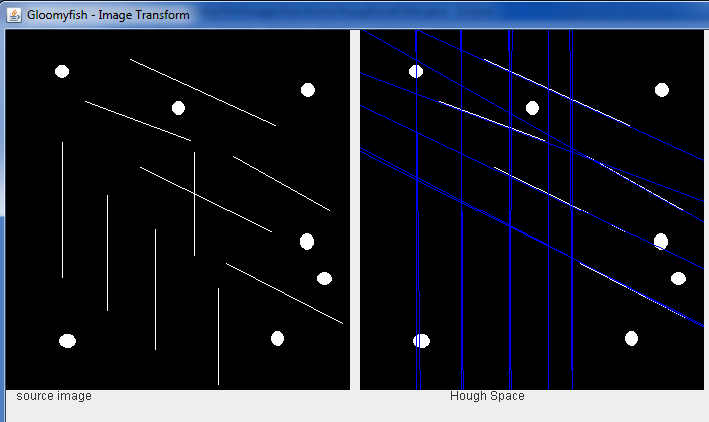
}霍夫变换源图例如以下: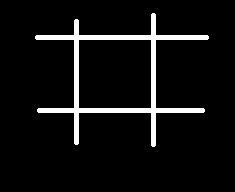
霍夫变换以后,在霍夫空间显演示样例如以下:(白色表示已经找到直线信号)
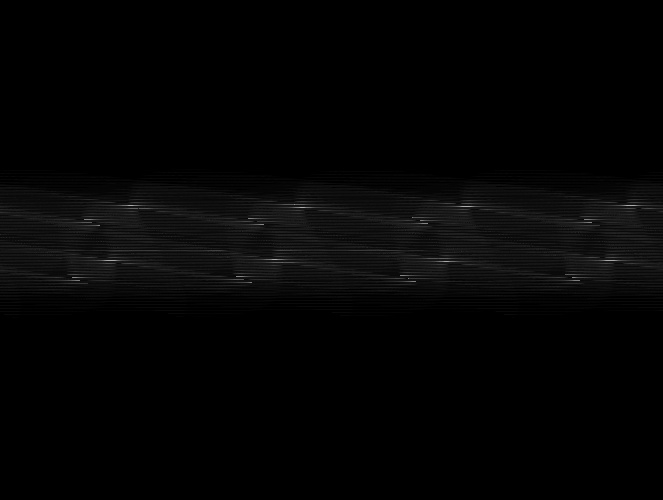
终于反变换回到像素空间效果例如以下:
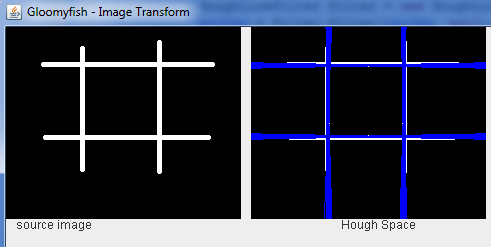
一个更好的执行监測直线的结果(输入为二值图像):
完整的霍夫变换源码例如以下:
package com.gloomyfish.image.transform;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import com.process.blur.study.AbstractBufferedImageOp;
public class HoughLineFilter extends AbstractBufferedImageOp {
public final static double PI_VALUE = Math.PI;
private int hough_space = 500;
private int[] hough_1d;
private int[][] hough_2d;
private int width;
private int height;
private float threshold;
private float scale;
private float offset;
public HoughLineFilter() {
// default hough transform parameters
// scale = 1.0f;
// offset = 0.0f;
threshold = 0.5f;
scale = 1.0f;
offset = 0.0f;
}
public void setHoughSpace(int space) {
this.hough_space = space;
}
public float getThreshold() {
return threshold;
}
public void setThreshold(float threshold) {
this.threshold = threshold;
}
public float getScale() {
return scale;
}
public void setScale(float scale) {
this.scale = scale;
}
public float getOffset() {
return offset;
}
public void setOffset(float offset) {
this.offset = offset;
}
@Override
public BufferedImage filter(BufferedImage src, BufferedImage dest) {
width = src.getWidth();
height = src.getHeight();
if ( dest == null )
dest = createCompatibleDestImage( src, null );
int[] inPixels = new int[width*height];
int[] outPixels = new int[width*height];
getRGB( src, 0, 0, width, height, inPixels );
houghTransform(inPixels, outPixels);
setRGB( dest, 0, 0, width, height, outPixels );
return dest;
}
private void houghTransform(int[] inPixels, int[] outPixels) {
// prepare for hough transform
int centerX = width / 2;
int centerY = height / 2;
double hough_interval = PI_VALUE/(double)hough_space;
int max = Math.max(width, height);
int max_length = (int)(Math.sqrt(2.0D) * max);
hough_1d = new int[2 * hough_space * max_length];
// define temp hough 2D array and initialize the hough 2D
hough_2d = new int[hough_space][2*max_length];
for(int i=0; i<hough_space; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<2*max_length; j++) {
hough_2d[i][j] = 0;
}
}
// start hough transform now....
int[][] image_2d = convert1Dto2D(inPixels);
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
int p = image_2d[row][col] & 0xff;
if(p == 0) continue; // which means background color
// since we does not know the theta angle and r value,
// we have to calculate all hough space for each pixel point
// then we got the max possible theta and r pair.
// r = x * cos(theta) + y * sin(theta)
for(int cell=0; cell < hough_space; cell++ ) {
max = (int)((col - centerX) * Math.cos(cell * hough_interval) + (row - centerY) * Math.sin(cell * hough_interval));
max += max_length; // start from zero, not (-max_length)
if (max < 0 || (max >= 2 * max_length)) {// make sure r did not out of scope[0, 2*max_lenght]
continue;
}
hough_2d[cell][max] +=1;
}
}
}
// find the max hough value
int max_hough = 0;
for(int i=0; i<hough_space; i++) {
for(int j=0; j<2*max_length; j++) {
hough_1d[(i + j * hough_space)] = hough_2d[i][j];
if(hough_2d[i][j] > max_hough) {
max_hough = hough_2d[i][j];
}
}
}
System.out.println("MAX HOUGH VALUE = " + max_hough);
// transfer back to image pixels space from hough parameter space
int hough_threshold = (int)(threshold * max_hough);
for(int row = 0; row < hough_space; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < 2*max_length; col++) {
if(hough_2d[row][col] < hough_threshold) // discard it
continue;
int hough_value = hough_2d[row][col];
boolean isLine = true;
for(int i=-1; i<2; i++) {
for(int j=-1; j<2; j++) {
if(i != 0 || j != 0) {
int yf = row + i;
int xf = col + j;
if(xf < 0) continue;
if(xf < 2*max_length) {
if (yf < 0) {
yf += hough_space;
}
if (yf >= hough_space) {
yf -= hough_space;
}
if(hough_2d[yf][xf] <= hough_value) {
continue;
}
isLine = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if(!isLine) continue;
// transform back to pixel data now...
double dy = Math.sin(row * hough_interval);
double dx = Math.cos(row * hough_interval);
if ((row <= hough_space / 4) || (row >= 3 * hough_space / 4)) {
for (int subrow = 0; subrow < height; ++subrow) {
int subcol = (int)((col - max_length - ((subrow - centerY) * dy)) / dx) + centerX;
if ((subcol < width) && (subcol >= 0)) {
image_2d[subrow][subcol] = -16776961;
}
}
} else {
for (int subcol = 0; subcol < width; ++subcol) {
int subrow = (int)((col - max_length - ((subcol - centerX) * dx)) / dy) + centerY;
if ((subrow < height) && (subrow >= 0)) {
image_2d[subrow][subcol] = -16776961;
}
}
}
}
}
// convert to hough 1D and return result
for (int i = 0; i < this.hough_1d.length; i++)
{
int value = clamp((int)(scale * this.hough_1d[i] + offset)); // scale always equals 1
this.hough_1d[i] = (0xFF000000 | value + (value << 16) + (value << 8));
}
// convert to image 1D and return
for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
outPixels[(col + row * width)] = image_2d[row][col];
}
}
}
public BufferedImage getHoughImage() {
BufferedImage houghImage = new BufferedImage(hough_2d[0].length, hough_space, BufferedImage.TYPE_4BYTE_ABGR);
setRGB(houghImage, 0, 0, hough_2d[0].length, hough_space, hough_1d);
return houghImage;
}
public static int clamp(int value) {
if (value < 0)
value = 0;
else if (value > 255) {
value = 255;
}
return value;
}
private int[][] convert1Dto2D(int[] pixels) {
int[][] image_2d = new int[height][width];
int index = 0;
for(int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
for(int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
index = row * width + col;
image_2d[row][col] = pixels[index];
}
}
return image_2d;
}
}
转载文章请务必注明出自本博客!!