1.涉及网络这块,必不可少的模块就是urllib2了。顾名思义这个模块主要负责打开URL和HTTP协议之类的,还有一个模块叫urllib,但它们不是升级版的关系
2.urllib2请求返回网页
(1)urllib2最贱的应用就是urllib2.urlopen函数了:
urllib2.urlopen(url[,data[,timeout[,cafile[,capath[,cadefault[,context]]]]]])
按照官方的文档,urllib2.urlopen可以打开HTTP,HTTPS,FTP协议的URL,主要应用于HTTP
(2)参数:
它的参数中以ca开头的都是跟身份验证相关,不太常用
data参数是以post方式提交URL时使用的
最常用的就只有URL和timeout参数:url参数是提交的网络地址(地址全称,前端需协议名,后端需端口,比如:http://192.168.1.1:80),timeout是超时时间设置
(3)函数返回对象:
****geturl()函数返回response的url信息,常用于url重定向的情况;
****info()函数返回response的基本信息
****getcode()函数返回response的状态代码,最常见的代码是200服务器成功返回页面,404请求的网页不存在,503服务器暂时不可用
(4)编写testUrllib2.py测试:
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib2
import time
import platform
import os
import gzip
import StringIO
def clear():
"""该函数用于清屏"""
print(u"内容较多,显示3秒后翻页")
time.sleep(3)
OS=platform.system()
if (OS==u'Windows'):
os.system('cls')
else:
os.system('clear')
def linkBaidu():
url='http://www.baidu.com'
try:
res=urllib2.urlopen(url,timeout=3)
response=urllib2.urlopen(url,timeout=3).read()
response=StringIO.StringIO(response)
gzipper = gzip.GzipFile(fileobj=response)
html = gzipper.read()
except urllib2.URLError:
print(u"网络地址错误")
exit()
with open('./baidu.txt','w+') as fp:
fp.write(html)
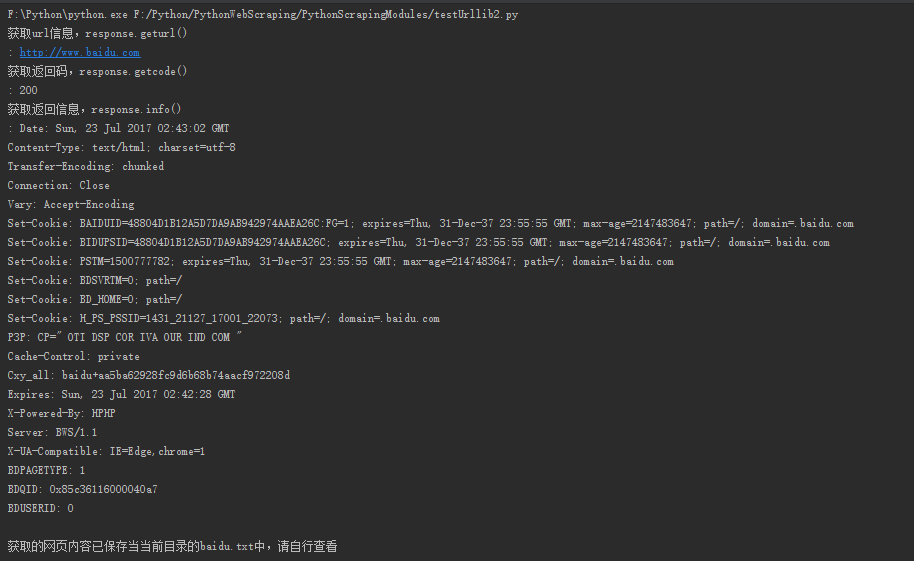
print(u"获取url信息,response.geturl() : %s" %res.geturl())
print(u"获取返回码,response.getcode() : %s" %res.getcode())
print(u"获取返回信息,response.info() : %s" %res.info())
print(u"获取的网页内容已保存当当前目录的baidu.txt中,请自行查看")
if __name__ == '__main__':
linkBaidu()
运行过程中遇到写入baidu.txt文件乱码问题
解决方法:gzip解压读写(百度确实是gzip编码),因为http请求中,如果在request header包含”Accept-Encoding”:”gzip, deflate”,
并且web服务器端支持,返回的数据是经过压缩的,这个好处是减少了网络流量,由客户端根据header,在客户端层解压,再解码。
urllib2 module,获取的http response数据是原始数据,没有经过解压,所以这是乱码的根本原因。
返回结果:
创建的baidu.txt文件:

当当前目录下已经创建过baidu.txt文件时,程序运行会出错,需要删除该文件再运行
爬取一般网站可以用以下代码:
# !/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import urllib2
import time
import platform
import os
def clear():
"""该函数用于清屏"""
print(u"内容较多,显示3秒后翻页")
time.sleep(3)
OS=platform.system()
if (OS==u'Windows'):
os.system('cls')
else:
os.system('clear')
def linkBaidu():
url='http://www.hqu.edu.cn'
try:
response=urllib2.urlopen(url,timeout=3)
except urllib2.URLError:
print(u"网络地址错误")
exit()
with open('./baidu.txt','w+') as fp:
fp.write(response.read())
print(u"获取url信息,response.geturl() : %s" %response.geturl())
print(u"获取返回码,response.getcode() : %s" %response.getcode())
print(u"获取返回信息,response.info() : %s" %response.info())
print(u"获取的网页内容已保存当当前目录的baidu.txt中,请自行查看")
if __name__ == '__main__':
linkBaidu()
3.urllib2使用代理访问网页:在使用网络爬虫时,有的网络拒绝了一些IP的直接访问,这时就不得不利用代理了,至于免费的代理网络上很多,选择一个确定可用的proxy
编写testUrllib2WithProxy.py测试代理访问网页:
#!/usr/bin/env python
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
__author__ = 'hstking hstking@hotmail.com'
import urllib2
import sys
import re
def testArgument():
'''测试输入参数,只需要一个参数 '''
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print(u'只需要一个参数就够了')
tipUse()
exit()
else:
TP = TestProxy(sys.argv[1])
def tipUse():
'''显示提示信息 '''
print(u'该程序只能输入一个参数,这个参数必须是一个可用的proxy')
print(u'usage: python testUrllib2WithProxy.py http://1.2.3.4:5')
print(u'usage: python testUrllib2WithProxy.py https://1.2.3.4:5')
class TestProxy(object):
'''这个类的作用是测试proxy是否有效 '''
def __init__(self,proxy):
self.proxy = proxy
self.checkProxyFormat(self.proxy)
self.url = 'http://www.baidu.com'
self.timeout = 5
self.flagWord = '百度' #在网页返回的数据中查找这个关键词
self.useProxy(self.proxy)
def checkProxyFormat(self,proxy):
try:
proxyMatch = re.compile('http[s]?://[d]{1,3}.[d]{1,3}.[d]{1,3}.[d]{1,3}:[d]{1,5}$')
re.search(proxyMatch,proxy).group()
except AttributeError:
tipUse()
exit()
flag = 1
proxy = proxy.replace('//','')
try:
protocol = proxy.split(':')[0]
ip = proxy.split(':')[1]
port = proxy.split(':')[2]
except IndexError:
print(u'下标出界')
tipUse()
exit()
flag = flag and len(proxy.split(':')) == 3 and len(ip.split('.')) == 4
flag = ip.split('.')[0] in map(str,xrange(1,256)) and flag
flag = ip.split('.')[1] in map(str,xrange(256)) and flag
flag = ip.split('.')[2] in map(str,xrange(256)) and flag
flag = ip.split('.')[3] in map(str,xrange(1,255)) and flag
flag = protocol in [u'http',u'https'] and flag
flag = port in map(str,range(1,65535)) and flag
'''这里是在检查proxy的格式 '''
if flag:
print(u'输入的http代理服务器符合标准')
else:
tipUse()
exit()
def useProxy(self,proxy):
'''利用代理访问百度,并查找关键词 '''
protocol = proxy.split('//')[0].replace(':','')
ip = proxy.split('//')[1]
opener = urllib2.build_opener(urllib2.ProxyHandler({protocol:ip}))
urllib2.install_opener(opener)
try:
response = urllib2.urlopen(self.url,timeout = self.timeout)
except:
print(u'连接错误,退出程序')
exit()
str = response.read()
if re.search(self.flagWord,str):
print(u'已取得特征词,该代理可用')
else:
print(u'该代理不可用')
if __name__ == '__main__':
testArgument()
执行结果如下:

代码详细解释:
(1)sys.argv:
sys.argv[]说白了就是一个从程序外部获取参数的桥梁,这个“外部”很关键,所以那些试图从代码来说明它作用的解释一直没看明白。因为我们从外部取得的参数可以是多个,所以获得的是一个列表(list),也就是说sys.argv其实可以看作是一个列表,所以才能用[]提取其中的元素。其第一个元素是程序本身,随后才依次是外部给予的参数。
(2)re.compile:compile(pattern[,flags] ) 根据包含正则表达式的字符串创建模式对象。

通过help可以看到compile方法的介绍,返回一个pattern对象,但是却没有对第二个参数flags进行介绍。第二个参数flags是匹配模式,可以使用按位或’|’表示同时生效,也可以在正则表达式字符串中指定。Pattern对象是不能直接实例化的,只能通过compile方法得到。

(3)re.search(proxyMatch,proxy).group():正则表达式中,group()用来提出分组截获的字符串,()用来分组
import re
a = "123abc456"
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)",a).group(0) #123abc456,返回整体
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)",a).group(1) #123
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)",a).group(2) #abc
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)",a).group(3) #456
1. 正则表达式中的三组括号把匹配结果分成三组
- group() 同group(0)就是匹配正则表达式整体结果
- group(1) 列出第一个括号匹配部分,group(2) 列出第二个括号匹配部分,group(3) 列出第三个括号匹配部分。
2. 没有匹配成功的,re.search()返回None
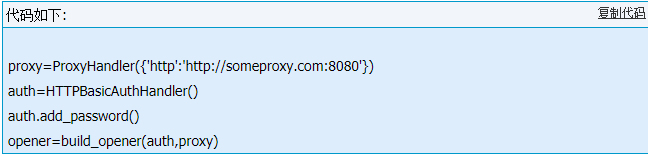
(4)urllib2.build_opener:urllib2.urlopen()函数不支持验证、cookie或者其它HTTP高级功能。要支持这些功能,必须使用build_opener()函数创建自定义Opener对象

参数handler是Handler实例,常用的有HTTPBasicAuthHandler、HTTPCookieProcessor、ProxyHandler等。
build_opener ()返回的对象具有open()方法,与urlopen()函数的功能相同。
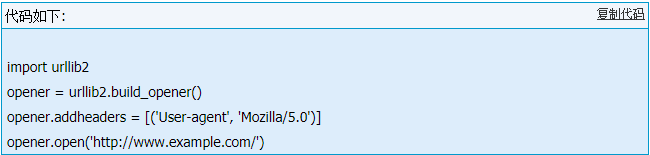
如果要修改http报头,可以用:
install_opener(opener):安装不同的opener对象作为urlopen()使用的全局opener。
代理(ProxyHandler):ProxyHandler(proxies)参数proxies是一个字典,将协议名称(http,ftp)等映射到相应代理服务器的URL,本程序中:urllib2.ProxyHandler({protocol:ip})
密码验证(HTTPBasicAuthHandler):HTTPBasicAuthHandler()处理程序可用add_password()来设置密码。
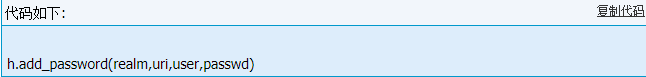
realm是与验证相关联的名称或描述信息,取决于远程服务器。uri是基URL。user和passwd分别指定用户名和密码。

