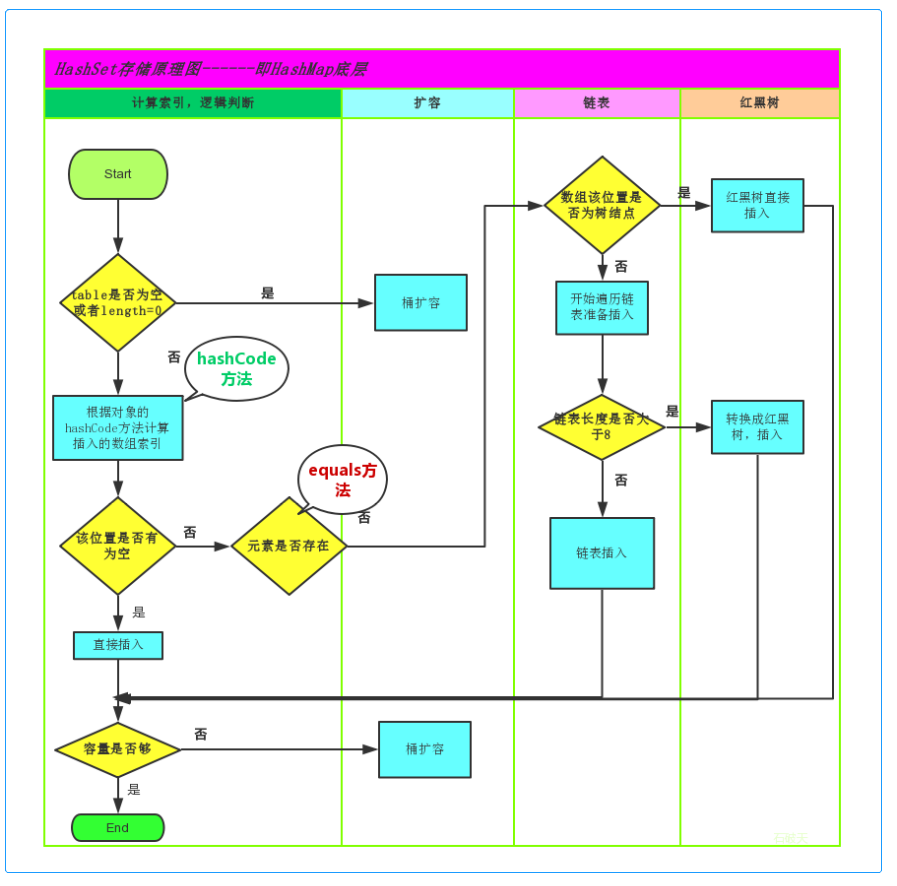
/** 1. 什么是哈希表 哈希表也叫散列表,是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。 2. 哈希算法的特点 哈希表是根据设定的哈希函数H(key)和处理冲突方法将一组关键字映射到一个有限的地址区间上,并以关键字在地址区间中的象作为记录在表中的存储位置,这种表称为哈希表或散列,所得存储位置称为哈希地址或散列地址。作为线性数据结构与表格和队列等相比,哈希表无疑是查找速度比较快的一种。 3. java中哈希表的组成结构 jdk8以前: 数组+链表 jdk8以后: 数组+链表+红黑树 */ //4. java中HashCode计算方式 /** * Returns a hash code for this string. The hash code for a * {@code String} object is computed as * <blockquote><pre> * s[0]*31^(n-1) + s[1]*31^(n-2) + ... + s[n-1] * </pre></blockquote> * using {@code int} arithmetic, where {@code s[i]} is the * <i>i</i>th character of the string, {@code n} is the length of * the string, and {@code ^} indicates exponentiation. * (The hash value of the empty string is zero.) * * @return a hash code value for this object. */ public int hashCode() { int h = hash; if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) { hash = h = isLatin1() ? StringLatin1.hashCode(value) : StringUTF16.hashCode(value); } return h; } /** HashMap是基于数组来实现哈希表的,数组就好比内存储空间,数组的index就好比内存的地址; HashMap的每个记录就是一个Entry<K, V>对象,数组中存储的就是这些对象; HashMap的哈希函数 = 计算出hashCode + 计算出数组的index; HashMap解决冲突:使用链地址法,每个Entry对象都有一个引用next来指向链表的下一个Entry; HashMap的装填因子:默认为0.75;*/ //new HashMap /*** 1. 构造方法:最终使用的是这个构造方法 ***/ // 初始容量initialCapacity为16,装填因子loadFactor为0.75 public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " + initialCapacity); if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor)) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " + loadFactor); this.loadFactor = loadFactor; threshold = initialCapacity; init();//init可以忽略,方法默认为空{},当你需要集成HashMap实现自己的类型时可以重写此方法做一些事 } /*** 2. (静态/实例)成员变量 ***/ /** 默认的容量,容量必须是2的幂 */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16 /** 最大容量2的30次方 */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** 默认装填因子0.75 */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** 默认Entry数组 */ static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {}; /** Entry数组:table */ transient Entry<K,V>[] table = (Entry<K,V>[]) EMPTY_TABLE; /** table中实际的Entry数量 */ transient int size; /** * size到达此门槛后,必须扩容table; * 值为capacity * load factor,默认为16 * 0.75 也就是12。 * 意味着默认情况构造情况下,当你存够12个时,table会第一次扩容 */ int threshold; /** 装填因子,值从一开构造HashMap时就被确定了,默认为0.75 */ final float loadFactor; /** * 哈希种子,实例化HashMap后在将要使用前设置的随机值,可以使得key的hashCode冲突更难出现 */ transient int hashSeed = 0; /** * The number of times this HashMap has been structurally modified * Structural modifications are those that change the number of mappings in * the HashMap or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g., * rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of * the HashMap fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException). */ transient int modCount; /*** 3. Map.Entry<K,V>:数组table中实际存储的类型 ***/ static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; // "Key-Value对"的Key V value; // "Key-Value对"的Key Entry<K,V> next; int hash; Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n;//链表的下一个Entry key = k; hash = h; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue()); } //存 - put(key, value)、解决冲突 /** 存放 **/ public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold);//table会被初始化为长度16,且hashSeed会被赋值; } if (key == null) //HashMap允许key为null:在table中找到null key,然后设置Value,同时其hash为0; return putForNullKey(value); // a). 计算key的hashCode,下面详细说 int hash = hash(key); // b). 根据hashCode计算index int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // c). 做覆盖,遍历index位置的Entry链表,*不是解决*冲突 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { // hashCode和equals都相等则表明:本次put是覆盖操作,下面return了被覆盖的老value V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; // d). 添加Entry,并解决冲突 // 如果需要增加table长度(size>threshold)就乘2增加,并重新计算每个元素在新table中的位置和转移 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null;//增加成功最后返回null } //详细说说上面的a). b). d). /** a). 为了防止低质量的hash函数,HashMap在这里会重新计算一遍key的hashCode **/ final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {//字符串会被特殊处理,返回32bit的整数(就是int) return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode();//将key的hashCode与h按位异或,最后赋值给h // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } /** * b). 计算此hashCode该被放入table的哪个index */ static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1);//与table的length - 1按位与,就能保证返回结果在0-length-1内 } /** * 解决冲突:链地址法 * d). addEntry(hash, key, value, i)最终是调用了此函数 */ void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex];// index的Entry拿出来 // put添加新元素是直接new Entry放在链头,如果有老的(有冲突)则将next设置为老的,如果没有正好设置next为null table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);// 在构造函数中,e代表next size++; } //取 - get(key) // 1. 根据k使用hash(k)重新计算出hashCode // 2. 根据indexFor(int h, int length)计算出该k的index // 3. 如果该index处Entry的key与此k相等,就返回value,否则继续查看该Entry的next