配置文件格式
配置文件(*.ini)的基本格式如下:
[device] type = NULL id = 1 [comn] protocol = 0 lenth = 400 filter_min = 120 filter_max = 400 [wifi] ssid = user_ssid_null psk = user_psk_null
[device]、[comn]、[wifi] 这些叫做 sections(节),每个section下面包含多个options(参数)/items(参数对,和字典的概念类似),例如:type = NULL,这里的“type”就叫做option,而(’type’, ‘NULL’)被称为item。参数的值均是以string格式存储的。
configparser库
使用Python的configparser库来读写配置文件,configparser官方文档:
https://docs.python.org/3/library/configparser.html#configparser.ConfigParser
搜索ConfigParser Objects,这一节有函数详细的功能介绍,下面列一部分常用的:
| cf = configparser.ConfigParser() | 创建configparser实例 |
| sections() | 返回sections的列表 |
| add_section(section) | 增加一个section |
| remove_section(section) | 删除一个section |
| has_section(section) | 返回某个section是否存在 |
| options(section) | 返回某个section下的options列表 |
| has_option(section, option) | 返回某个section下的某个option是否存在 |
| remove_option(section, option) | 删除某个section下的某个option |
| items() | 获得所有的sections,包括默认section |
| items(section) | 获得某个section下的所有items/参数对 |
| read(filenames) | 读取某个配置文件filenames,加载到ConfigParser实例 |
| get(section, option) | 以string格式,返回某个section下的某个option的值 |
| getint(section, option) | 以int格式,返回某个section下的某个option的值 |
| getfloat(section, option) | 以float格式,返回某个section下的某个option的值 |
| getboolean(section, option) | 以boolean格式,返回某个section下的某个option的值 |
| set(section, option, value) | 设置某个section下的某个option的值 |
| write(fileobject) | 将当前的ConfigParser实例写入到配置文件fileobject |
生成配置文件
ConfigParser库在Python2和Python3中有点区别:
- Python3
configparser库的首字母小写
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
创建文件test_config_create_p3.py,复制下面的内容,保存退出
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano test_config_create_p3.py
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import configparser 3 4 config = configparser.ConfigParser() 5 6 config["device"] = { 7 'type' : 'NULL', 8 'id' : '1' 9 } 10 11 config["comn"] = { 12 'protocol' : '0', 13 'lenth' : '400', 14 'filter_min' : '50', 15 'filter_max' : '400' 16 } 17 18 config["wifi"] = { 19 'ssid' : 'user_ssid_null', 20 'psk' : 'user_psk_null' 21 } 22 23 with open('config.ini', 'w') as cf: 24 config.write(cf)
运行程序:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ python3 test_config_create_p3.py
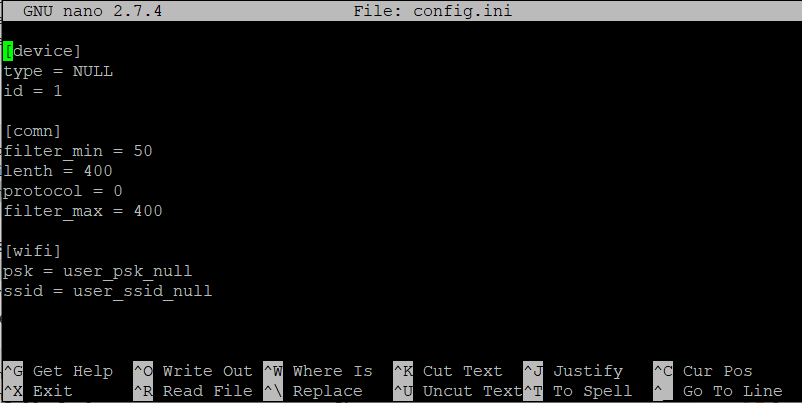
打开生成的配置文件config.ini:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano config.ini
sections和options的内容都是对的,只是section下的options的顺序与预期的不一致,不过这样也没什么问题。
- Python2
ConfigParser库的首字母大写
import ConfigParser
config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser()
python2中只能逐条添加section和option
创建文件test_config_create_p2.py,复制下面的内容,保存退出
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano test_config_create_p2.py
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import ConfigParser 3 4 config = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() 5 6 config.add_section("device") 7 config.set("device", "type", 'NULL') 8 config.set("device", "id", '1') 9 10 config.add_section("comn") 11 config.set("comn", "protocol", '0' ) 12 config.set("comn", "lenth", '400') 13 config.set("comn", "filter_min", '50' ) 14 config.set("comn", "filter_max", '400' ) 15 16 config.add_section("wifi") 17 config.set("wifi", "ssid", 'user_ssid_null') 18 config.set("wifi", "psk", 'user_psk_null') 19 20 with open('config.ini', 'w') as cf: 21 config.write(cf)
先删掉可能存在的config.ini文件
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ rm -f config.ini
运行程序:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ python2 test_config_create_p2.py
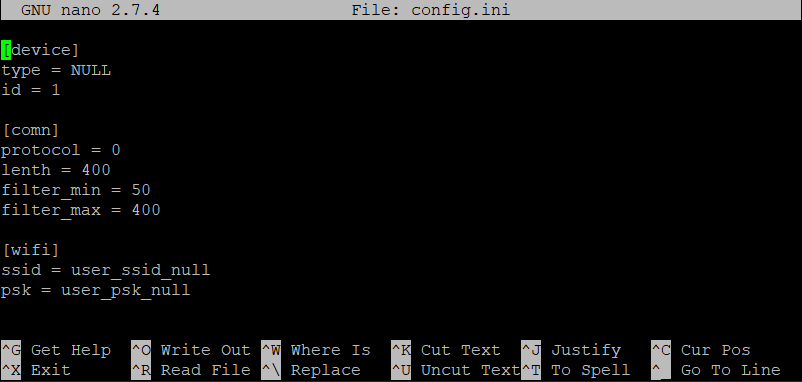
打开生成的配置文件config.ini:
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano config.ini
sections和options的内容都是对的,section下的options的顺序与预期的一致。
读取配置文件
读取配置参数时,先确认section是否存在,如果不存在就添加section,并写入默认配置参数。
这里使用的配置参数主要有两种类型:string和int,分别使用get(section, option)、getint(section, option)去读取参数。
读取完成后把所有的items都打印出来。
1 def GetConfig(filepath): 2 global PRODUCT_TYPE 3 global DEVICE_ID 4 5 global PROTOCOL_TYPE 6 global DB_PARAMS_LENGTH 7 global COMN_FILTER_MIN 8 global COMN_FILTER_MAX 9 10 global WIFI_SSID 11 global WIFI_PASSWORD 12 13 is_new_section = False 14 15 print('>> GetConfig()...') 16 print(filepath) 17 18 config = configparser.ConfigParser() 19 config.read(filepath) 20 21 if "wifi" not in config.sections(): 22 print('>> add config >> wifi...') 23 is_new_section = True 24 config.add_section("wifi") 25 config.set("wifi", "ssid", WIFI_SSID) 26 config.set("wifi", "psk", WIFI_PASSWORD) 27 else: 28 WIFI_SSID = config.get("wifi", "ssid") 29 WIFI_PASSWORD = config.get("wifi", "psk") 30 31 if "device" not in config.sections(): 32 print('>> add config >> device...') 33 is_new_section = True 34 config.add_section("device") 35 config.set("device", "type", PRODUCT_TYPE) 36 config.set("device", "id", str(DEVICE_ID)) 37 else: 38 PRODUCT_TYPE = config.get("device", "type") 39 DEVICE_ID = config.getint("device", "id") 40 41 if "comn" not in config.sections(): 42 print('>> add config >> comn...') 43 is_new_section = True 44 config.add_section("comn") 45 config.set("comn", "protocol", str(PROTOCOL_TYPE) ) 46 config.set("comn", "lenth", str(DB_PARAMS_LENGTH)) 47 config.set("comn", "filter_min", str(COMN_FILTER_MIN) ) 48 config.set("comn", "filter_max", str(COMN_FILTER_MAX) ) 49 else: 50 PROTOCOL_TYPE = config.get("comn", "protocol") 51 DB_PARAMS_LENGTH = config.getint("comn", "lenth") 52 COMN_FILTER_MIN = config.getint("comn", "filter_min") 53 COMN_FILTER_MAX = config.getint("comn", "filter_max") 54 55 print('>> list config items...') 56 for sections in config.sections(): 57 for items in config.items(sections): 58 print(items) 59 60 if True == is_new_section: 61 print('>> new section added, write to config file...') 62 with open(filepath, 'w+') as cf: 63 config.write(cf)
修改配置文件
用set(section, option, value)来设置参数值,可以把所有参数值都用str()强制转换一下。
写入之前先把所有的items都打印出来。
1 def SetConfig(filepath): 2 global WIFI_SSID 3 global WIFI_PASSWORD 4 global PRODUCT_TYPE 5 global DEVICE_ID 6 global PROTOCOL_TYPE 7 global DB_PARAMS_LENGTH 8 global COMN_FILTER_MIN 9 global COMN_FILTER_MAX 10 11 print('>> SetConfig()...') 12 print(filepath) 13 14 config = configparser.ConfigParser() 15 config.read(CONFIG_FILE) 16 17 if "device" not in config.sections(): 18 config.add_section("device") 19 if "comn" not in config.sections(): 20 config.add_section("comn") 21 if "wifi" not in config.sections(): 22 config.add_section("wifi") 23 24 config.set("wifi", "ssid", str(WIFI_SSID)) 25 config.set("wifi", "psk", str(WIFI_PASSWORD)) 26 27 config.set("device", "type", str(PRODUCT_TYPE)) 28 config.set("device", "id", str(DEVICE_ID)) 29 30 config.set("comn", "protocol", str(PROTOCOL_TYPE) ) 31 config.set("comn", "lenth", str(DB_PARAMS_LENGTH)) 32 config.set("comn", "filter_min", str(COMN_FILTER_MIN) ) 33 config.set("comn", "filter_max", str(COMN_FILTER_MAX) ) 34 35 print('>> list config items...') 36 for sections in config.sections(): 37 for items in config.items(sections): 38 print(items) 39 40 print('>> write to config file...') 41 with open(CONFIG_FILE, 'w+') as cf: 42 config.write(cf)
运行测试
使用Python3进行测试(如果用Python2,只需要把库的首字母改成大写的)
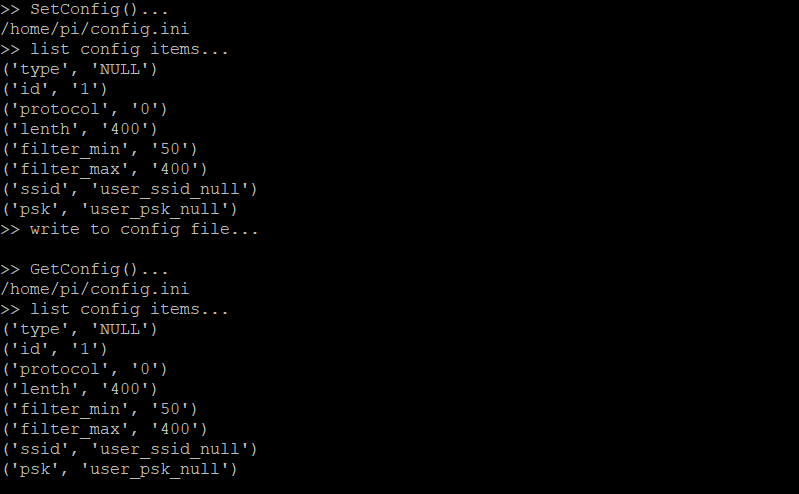
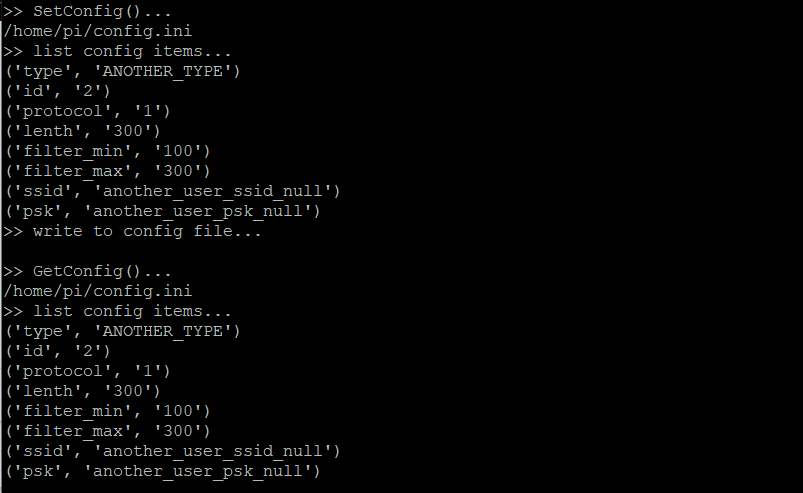
创建测试程序test_config.py。SetConfig()、GetConfig()参考上面,这里为了便于阅读省略了。
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo nano test_config.py
这个测试函数里先是把默认的配置参数写入到配置文件并读取,然后再修改配置参数,重新写入到配置文件并读取。程序会打印即将写入配置文件的参数,还有从配置文件中读取到的参数。
1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import configparser 3 4 CONFIG_FILE = '/home/pi/config.ini' 5 6 PRODUCT_TYPE = 'NULL' 7 DEVICE_ID = 1 8 PROTOCOL_TYPE = 0 9 DB_PARAMS_LENGTH = 400 10 COMN_FILTER_MIN = 50 11 COMN_FILTER_MAX = 400 12 WIFI_SSID = 'user_ssid_null' 13 WIFI_PASSWORD = 'user_psk_null' 14 15 #---- 16 def GetConfig(filepath): 17 #### 18 19 #---- 20 def SetConfig(filepath): 21 #### 22 23 #---- 24 def main(): 25 global CONFIG_FILE 26 27 global WIFI_SSID 28 global WIFI_PASSWORD 29 global PRODUCT_TYPE 30 global DEVICE_ID 31 global PROTOCOL_TYPE 32 global DB_PARAMS_LENGTH 33 global COMN_FILTER_MIN 34 global COMN_FILTER_MAX 35 36 SetConfig(CONFIG_FILE) 37 GetConfig(CONFIG_FILE) 38 39 PRODUCT_TYPE = 'ANOTHER_TYPE' 40 DEVICE_ID = 2 41 42 PROTOCOL_TYPE = 1 43 DB_PARAMS_LENGTH = 300 44 COMN_FILTER_MIN = 100 45 COMN_FILTER_MAX = 300 46 47 WIFI_SSID = 'another_user_ssid_null' 48 WIFI_PASSWORD = 'another_user_psk_null' 49 50 SetConfig(CONFIG_FILE) 51 GetConfig(CONFIG_FILE) 52 53 if __name__ == '__main__': 54 main()
用Python3运行
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ python3 test_config.py