看了上一篇随笔之后可以对本篇有更好的了解!
使用的poi的jar包依然是上一篇的poi-3.17.jar....
import pojo.UserPojo(上一篇里有,这里就不粘贴了!)
不废话了,直接上菜。。。
1 package util; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.FileNotFoundException; 5 import java.io.FileOutputStream; 6 import java.io.IOException; 7 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 8 import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; 9 import java.util.ArrayList; 10 import java.util.Date; 11 import java.util.List; 12 13 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFCellStyle; 14 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFSheet; 15 import org.apache.poi.hssf.usermodel.HSSFWorkbook; 16 import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Cell; 17 import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.HorizontalAlignment; 18 import org.apache.poi.ss.usermodel.Row; 19 20 import pojo.UserPojo; 21 22 /** 23 * 24 * @ClassName: UpdatedExcelUtil 25 * @Description: 全自动Excel工具类(升级版) 26 * @date 2018年6月6日 27 * 28 */ 29 public class UpdatedExcelUtil { 30 31 /** 32 * @注: 将此方法提取出去可以变成一个工具类 33 * 34 * @Description: 得到生成的Excel,并且导出到指定的文件夹中 35 * @Title: getExcel 36 * @date 2018-06-06 37 * @param sqlColumn 38 * 数据列,对应着你需要的字段(比如:sql里面的字段 "username") 39 * @param sqlColumnName 40 * 数据列名,对应着你需要的字段名(比如:sql里面的字段 username的 "用户名称") 41 * @param 这里我们直接传入list(根据需要传入什么数据---》可以是sql哟,或者其他的什么) 42 * @param file 43 * 文件路径 44 * @return void 返回类型 45 * 46 */ 47 public static void getExcel(String[] sqlColumn, String[] sqlColumnName, List<UserPojo> list, File file) { 48 // 创建一个Excel 49 @SuppressWarnings("resource") 50 HSSFWorkbook wb = new HSSFWorkbook(); 51 // 创建工作表 52 HSSFSheet sheet = wb.createSheet(); 53 // 创建行 54 Row row = sheet.createRow(0); 55 56 // 创建样式 57 HSSFCellStyle style = wb.createCellStyle(); 58 // style.setDataFormat(format.getFormat("@")); 59 60 // 居中格式 61 style.setAlignment(HorizontalAlignment.CENTER); 62 63 // 创建单元格(生成动态的表头),且让各表头居中显示 64 // Cell cell=row.createCell(0); 65 Cell cell = null; 66 for (int i = 0; i < sqlColumn.length; i++) { 67 // 创建传入进来的表头的个数 68 cell = row.createCell((short) i); 69 // 表头的值就是传入进来的值 70 cell.setCellValue(sqlColumnName[i]); 71 sheet.setColumnWidth(i, 20 * 200);// 设置列宽 72 cell.setCellStyle(style); 73 } 74 75 // list 不能为空 76 if (list != null) { 77 for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { 78 // 一组数据,新增一行 79 row = sheet.createRow((int) i + 1); 80 // 得到所有的行 一个result就代表 一行 81 UserPojo result = list.get(i); 82 // 创建 Field类,使用反射,得到实体类的属性值 83 Field[] fl = result.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); 84 // 在有所有的记录基础之上,遍历传入进来的表头,再创建N行 86 for (int j = 0; j < sqlColumn.length; j++) { 87 // 创建单元格,根据表头数量对应每行多少单元格数据 88 cell = row.createCell(j); 89 // 得到当i=n时,j=n时的UserPojo的第n个属性值 90 Field f = fl[j]; 91 // 允许反射时访问私有变量 92 f.setAccessible(true); 93 Object value; 94 try { 95 // 得到当前状态下的实体类属性的值 96 value = f.get(result); 97 // 放入对应的单元格内 98 cell.setCellValue(value.toString()); 99 } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { 100 e.printStackTrace(); 101 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 102 e.printStackTrace(); 103 } 104 105 } 106 } 107 } 108 109 try { 110 FileOutputStream fileOutputStreane = new FileOutputStream(file); 111 wb.write(fileOutputStreane); 112 fileOutputStreane.flush(); 113 fileOutputStreane.close(); 114 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { 115 e.printStackTrace(); 116 } catch (IOException e) { 117 e.printStackTrace(); 118 } 119 120 } 121 122 /** 123 * 124 * @Description: 以实现功能为主,没有分层,一般来说这些应该处于controller里面 125 * @Title: exproExcel 126 * @date 2018-06-06 参数 127 * @return void 返回类型 128 * 129 */ 130 public static void exproExcel() { 131 File file = new File("D:/" + getFileName() + ".xls"); 132 String[] sqlColumn = { "uid", "uname", "upass", "udate" }; 133 String[] sqlColumnName = { "人员编号", "人员姓名", "登录密码", "注册时间" }; 134 // 将此方法提取出去,可以生成一个util工具类 135 getExcel(sqlColumn, sqlColumnName, listUser(), file); 136 } 137 138 /** 139 * @Description: 运行测试 140 * @author WengQuan 141 * @Title: main 142 * @date 2018-06-06 143 * @param args 144 * 参数 145 * @return void 返回类型 146 * 147 */ 148 public static void main(String[] args) { 149 exproExcel(); 150 } 151 152 /** 153 * 生成一个以系统时间为文件名的字符串(精确到了毫秒) 154 */ 155 public static String getFileName() { 156 SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMddHHmmssSSS");// 设置日期格式 157 String nowDataSystem = df.format(new Date()); 158 return nowDataSystem; 159 } 160 161 /** 162 * 163 * @Description: 一组测试数据 164 * @Title: listUser 165 * @date 2018-06-06 166 * @return 参数 167 * @return List<UserPojo> 返回类型 168 * 169 */ 170 public static List<UserPojo> listUser() { 171 List<UserPojo> list = new ArrayList<UserPojo>(); 172 UserPojo up1 = new UserPojo(91, "小明", "xiaoming1", "2018、03、21"); 173 UserPojo up2 = new UserPojo(100, "安妮", "anni", "2018-03-22"); 174 UserPojo up3 = new UserPojo(93, "dinosaurs", "dinosaurs", "2018年03月02日"); 175 list.add(up1); 176 list.add(up2); 177 list.add(up3); 178 return list; 179 } 180 }
效果截图:
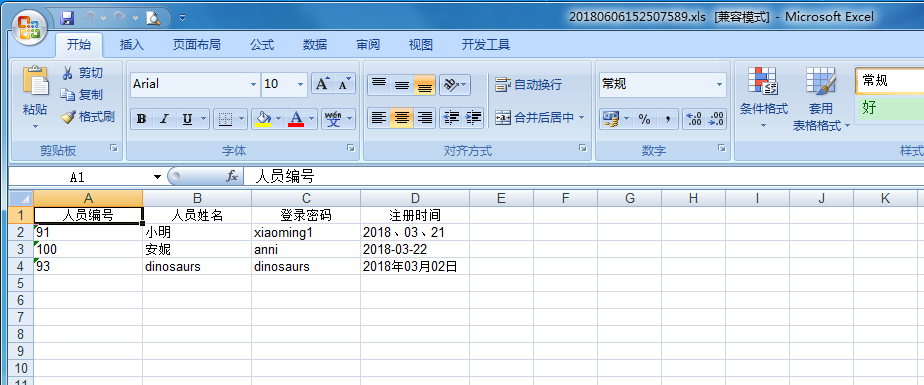
希望谁看到了哪里有问题可以联系我,提醒我,本人以学习为主。大神请勿喷!
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,可以转载,但请保留本文地址,谢谢大家!