在python中,os.path模块在处理路径的时候非常有用
下面是我做的demo
运行效果:
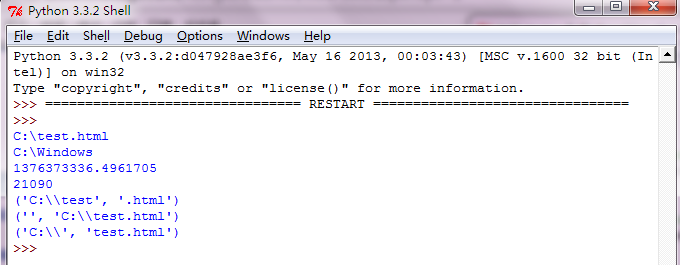
=========================================
代码部分:
=========================================
1 #python os 2 3 import os 4 5 def abspath(path): 6 '''Return a normalized absolutized version of the pathname path''' 7 return os.path.abspath(path) 8 9 def dirname(path): 10 '''Return the directory name of pathname path''' 11 return os.path.dirname(path) 12 13 def getatime(path): 14 '''Return the time of last access of path''' 15 return os.path.getatime(path) 16 17 def gettime(path): 18 '''Return the time of last modification of path''' 19 return os.path.gettime(path) 20 21 def getsize(path): 22 '''Return the size, in bytes, of path. Raise OSError if the file does not exist or is inaccessible.''' 23 return os.path.getsize(path) 24 25 def is_file(path): 26 '''Return True if path is an existing regular file. 27 This follows symbolic links, so both islink() and isfile() 28 can be true for the same path.''' 29 return os.path.isfile(path) 30 31 def is_dir(path): 32 '''Return True if path is an existing directory. This follows symbolic links, 33 so both islink() and isdir() can be true for the same path.''' 34 return os.path.isdir(path) 35 36 def is_link(path): 37 '''Return True if path refers to a directory entry that 38 is a symbolic link. Always False if symbolic links are not supported.''' 39 return os.path.islink(path) 40 41 def splitext(path): 42 ''' 43 Split the pathname path into a pair (root, ext) such that 44 root + ext == path, and ext is empty or begins with a period 45 and contains at most one period. Leading periods on the basename 46 are ignored; splitext('.cshrc') returns ('.cshrc', ''). 47 ''' 48 return os.path.splitext(path) 49 50 def splitunc(path): 51 ''' 52 Split the pathname path into a pair (unc, rest) so that unc is 53 the UNC mount point (such as r'\hostmount'), if present, 54 and rest the rest of the path (such as r'pathfile.ext'). 55 For paths containing drive letters, unc will always be the 56 empty string. 57 ''' 58 return os.path.splitunc(path) 59 60 def split(path): 61 '''Split the pathname path into a pair, (head, tail) where tail is the last 62 pathname component and head is everything leading up to that''' 63 return os.path.split(path) 64 65 def main(): 66 path_file = 'C:\test.html' 67 path_dir = 'C:\Windows\Branding' 68 print(abspath(path_file)) 69 print(dirname(path_dir)) 70 print(getatime(path_file)) 71 print(getsize(path_file)) 72 print(splitext(path_file)) 73 print(splitunc(path_file)) 74 print(split(path_file)) 75 76 77 if __name__ == '__main__': 78 main()