1.快速排序
这种排序是.net中使用的,均衡性比较好,效率相对来说最高,
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { int[] arr = {7,6,5,4,3,2,1}; List<int> list = arr.ToList<int>(); QuickSortClass qu = new QuickSortClass(); Response.Write("<br><br><br>"); //qu.show(list, " "); Response.Write("<br><br><br><br>"); qu.QuickSort(list, 0, list.Count - 1); //Response.Write(qu.count); } } public class QuickSortClass { public int count = 0; ///<summary> /// 分割函数 ///</summary> ///<param name="list">待排序的数组</param> ///<param name="left">数组的左下标</param> ///<param name="right"></param> ///<returns></returns> public int Division(List<int> list, int left, int right) { show(list, " List:"); //首先挑选一个基准元素 int baseNum = list[left]; HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(" Left:" + left + " Right:" + right + "<br>"); while (left < right) { count++; //从数组的右端开始向前找,一直找到比base小的数字为止(包括base同等数) while (left < right && list[right] >= baseNum) right = right - 1; //最终找到了比baseNum小的元素,要做的事情就是此元素放到base的位置 list[left] = list[right]; show(list," Righ:"); //从数组的左端开始向后找,一直找到比base大的数字为止(包括base同等数) while (left < right && list[left] <= baseNum) left = left + 1; //最终找到了比baseNum大的元素,要做的事情就是将此元素放到最后的位置 list[right] = list[left]; show(list, " Left:"); } //最后就是把baseNum放到该left的位置 list[left] = baseNum; show(list, " Last:"); HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("<br><br><br>"); //最终,我们发现left位置的左侧数值部分比left小,left位置右侧数值比left大 //至此,我们完成了第一篇排序 return left; } public void QuickSort(List<int> list, int left, int right) { //左下标一定小于右下标,否则就超越了 if (left < right) { //对数组进行分割,取出下次分割的基准标号 int i = Division(list, left, right); HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("I:" + i+"<br>"); //对“基准标号“左侧的一组数值进行递归的切割,以至于将这些数值完整的排序 HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("对“基准标号“左侧的一组数值进行递归的切割,以至于将这些数值完整的排序<br>"); QuickSort(list, left, i - 1); //对“基准标号“右侧的一组数值进行递归的切割,以至于将这些数值完整的排序 HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("对“基准标号“右侧的一组数值进行递归的切割,以至于将这些数值完整的排序<br>"); QuickSort(list, i + 1, right); } //HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("count:"+count + "<br>"); } public void show(List<int> list,string a) { if (list == null) return; StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder(); strBuilder.Append("<span style='40px'>"+a+"</span>"); foreach (var li in list) { strBuilder.Append(" " + li.ToString()); } HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(strBuilder.ToString() + "<br><br>"); } }
堆排序
http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2011/11/16/2251196.html
除了最后一个父节点以外,每个父节点都必须有两个子节点
大根堆: 就是说父节点要比左右孩子都要大。
小根堆: 就是说父节点要比左右孩子都要小。
每次重构以后发现位置不一定一样,但是根节点一定是一样的。
这种排序在找数组中最大,最小的值时效率最高,几个也行,找的值越多,效率越低。
protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { int[] arr = {9,7,8,6,3,4,1,5,2}; List<int> list = arr.ToList<int>(); HeapSort(list); show(list, ""); } ///<summary> /// 构建堆 ///</summary> ///<param name="list">待排序的集合</param> ///<param name="parent">父节点</param> ///<param name="length">输出根堆时剔除最大值使用</param> public static void HeapAdjust(List<int> list, int parent, int length) { show(list, "I:" + parent.ToString() + ",Length:" + length.ToString()+" "); //temp保存当前父节点 int temp = list[parent]; //得到左孩子(这可是二叉树的定义,大家看图也可知道) int child = 2 * parent + 1; while (child < length) //判断该节点是否还有子节点 { //如果parent有右孩子,则要判断左孩子是否小于右孩子 if (child + 1 < length && list[child] < list[child + 1]) child++; //父亲节点大于子节点,就不用做交换 if (temp >= list[child]) break; //将较大子节点的值赋给父亲节点 list[parent] = list[child]; //然后将子节点做为父亲节点,已防止是否破坏根堆时重新构造 parent = child; //找到该父亲节点较小的左孩子节点 child = 2 * parent + 1; } //最后将temp值赋给较大的子节点,以形成两值交换 list[parent] = temp; } ///<summary> /// 堆排序 ///</summary> ///<param name="list"></param> public static void HeapSort(List<int> list) { //list.Count/2-1:就是堆中父节点的个数 for (int i = list.Count / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) { HeapAdjust(list, i, list.Count); } //上面就是按照数组建立一个二叉树,符合二叉树的标准,是大根堆,最上面的就是最大的,父节点比子节点大 HttpContext.Current.Response.Write("-----------------<br>"); //最后输出堆元素,在每次构建堆后,list[0]都是最大的,每次找出最大的放在数组最后,再把二叉树的长度减1,形成的由小到大排列 for (int i = list.Count - 1; i > 0; i--) { //堆顶与当前堆的第i个元素进行值对调 int temp = list[0]; list[0] = list[i]; list[i] = temp; //因为两值交换,可能破坏根堆,所以必须重新构造 HeapAdjust(list, 0, i); //在把现有的二叉树内的最大值找出,i是二叉树的长度 show(list, "List: "); } } public static void show(List<int> list, string a="") { if (list == null) return; StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder(); strBuilder.Append("<span style='40px'>" + a + "</span>"); foreach (var li in list) { strBuilder.Append(" " + li.ToString()); } HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(strBuilder.ToString() + "<br><br>"); }
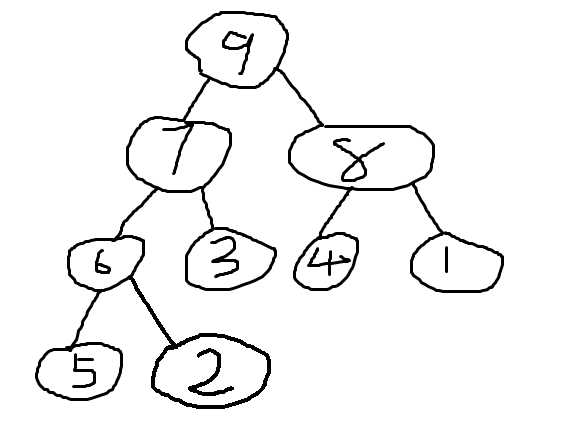
二叉排序树(主要应用于查找)
http://www.cnblogs.com/huangxincheng/archive/2011/11/27/2265427.html
若根节点有左子树,则左子树的所有节点都比根节点小。
若根节点有右子树,则右子树的所有节点都比根节点大。
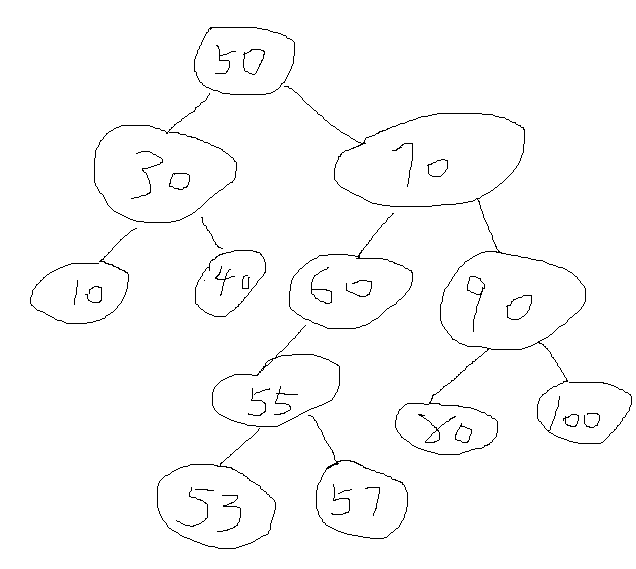
看出节点的左右子节点都可以存在,每次添加元素时位置是唯一的
public partial class Default2 : System.Web.UI.Page { protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) { List<int> list = new List<int>() { 50, 30, 70, 10, 40, 90, 80 }; BSTree bsTree = CreateBST(list); //中序遍历 LDR_BST(bsTree); Response.Write("<br>"); bool isExist = SearchBST(bsTree, 40); Response.Write(isExist.ToString()); } ///<summary> /// 定义一个二叉排序树结构 ///</summary> public class BSTree { public int data; public BSTree left; public BSTree right; } ///<summary> /// 二叉排序树的插入操作 ///</summary> ///<param name="bsTree">排序树</param> ///<param name="key">插入数</param> ///<param name="isExcute">是否执行了if语句</param> static void InsertBST(BSTree bsTree, int key, ref bool isExcute) { if (bsTree == null) return; //如果父节点大于key,则遍历左子树 if (bsTree.data > key) InsertBST(bsTree.left, key, ref isExcute); else InsertBST(bsTree.right, key, ref isExcute); if (!isExcute) { //构建当前节点 BSTree current = new BSTree() { data = key, left = null, right = null }; //插入到父节点的当前元素 if (bsTree.data > key) bsTree.left = current; else bsTree.right = current; isExcute = true; } } ///<summary> /// 创建二叉排序树 ///</summary> ///<param name="list"></param> static BSTree CreateBST(List<int> list) { //构建BST中的根节点 BSTree bsTree = new BSTree() { data = list[0], left = null, right = null }; for (int i = 1; i < list.Count; i++) { bool isExcute = false; InsertBST(bsTree, list[i], ref isExcute); } return bsTree; } ///<summary> /// 在排序二叉树中搜索指定节点 ///</summary> ///<param name="bsTree"></param> ///<param name="key"></param> ///<returns></returns> static bool SearchBST(BSTree bsTree, int key) { //如果bsTree为空,说明已经遍历到头了 if (bsTree == null) return false; if (bsTree.data == key) return true; if (bsTree.data > key) return SearchBST(bsTree.left, key); else return SearchBST(bsTree.right, key); } ///<summary> /// 中序遍历二叉排序树 ///</summary> ///<param name="bsTree"></param> ///<returns></returns> static void LDR_BST(BSTree bsTree) { if (bsTree != null) { //遍历左子树 LDR_BST(bsTree.left); //输入节点数据 HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(bsTree.data + "||"); //遍历右子树 LDR_BST(bsTree.right); } } ///<summary> /// 删除二叉排序树中指定key节点 ///</summary> ///<param name="bsTree"></param> ///<param name="key"></param> static void DeleteBST(ref BSTree bsTree, int key) { if (bsTree == null) //循环到底了,没有指定key的节点 return; if (bsTree.data == key) { //第一种情况:叶子节点 if (bsTree.left == null && bsTree.right == null) { bsTree = null; return; } //第二种情况:左子树不为空 if (bsTree.left != null && bsTree.right == null) { bsTree = bsTree.left; return; } //第三种情况,右子树不为空 if (bsTree.left == null && bsTree.right != null) { bsTree = bsTree.right; return; } //第四种情况,左右子树都不为空 if (bsTree.left != null && bsTree.right != null) { var node = bsTree.right; //找到右子树中的最左节点 while (node.left != null) { //遍历它的左子树 node = node.left; } //交换左右孩子 node.left = bsTree.left; //判断是真正的叶子节点还是空左孩子的父节点 if (node.right == null) { //删除掉右子树最左节点 DeleteBST(ref bsTree, node.data); node.right = bsTree.right; } //重新赋值一下 bsTree = node; } } if (bsTree.data > key) { DeleteBST(ref bsTree.left, key); } else { DeleteBST(ref bsTree.right, key); } } public static void show(List<int> list, string a = "") { if (list == null) return; StringBuilder strBuilder = new StringBuilder(); strBuilder.Append("<span style='40px'>" + a + "</span>"); foreach (var li in list) { strBuilder.Append(" " + li.ToString()); } HttpContext.Current.Response.Write(strBuilder.ToString() + "<br><br>"); } }

可以看出这种方式也可以排序,每次排序时先找一个根节点
每次插入元素时循环判断大小,找到唯一的位置插入。
查询:最左边的节点的左叶节点-->最左边的节点-->最左边的节点的右叶节点-->父节点-->
判断是否有节点(有的话 左叶节点-->节点-->右节点)。。。。